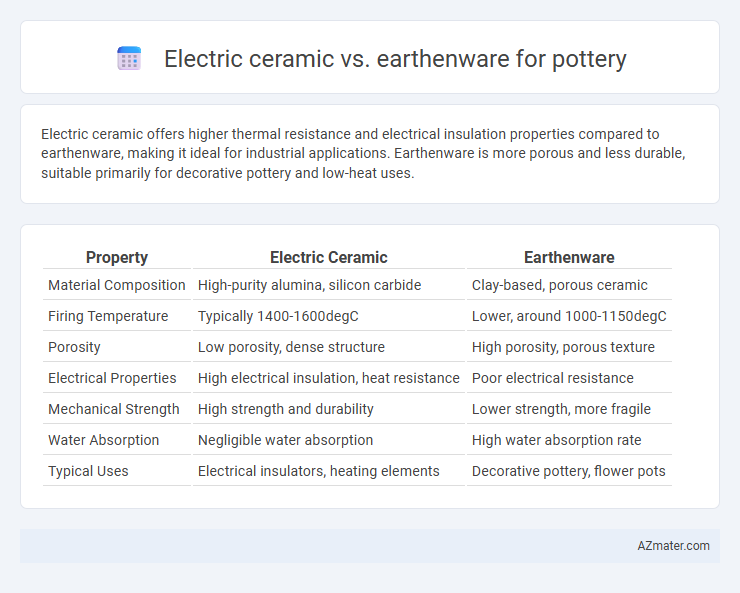
Electric ceramic offers higher thermal resistance and electrical insulation properties compared to earthenware, making it ideal for industrial applications. Earthenware is more porous and less durable, suitable primarily for decorative pottery and low-heat uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Electric Ceramic | Earthenware |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity alumina, silicon carbide | Clay-based, porous ceramic |
| Firing Temperature | Typically 1400-1600degC | Lower, around 1000-1150degC |
| Porosity | Low porosity, dense structure | High porosity, porous texture |
| Electrical Properties | High electrical insulation, heat resistance | Poor electrical resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and durability | Lower strength, more fragile |
| Water Absorption | Negligible water absorption | High water absorption rate |
| Typical Uses | Electrical insulators, heating elements | Decorative pottery, flower pots |
Introduction to Electric Ceramic and Earthenware
Electric ceramic relies on electric kilns that provide consistent, high-temperature firing ideal for stoneware and porcelain, enhancing durability and glaze quality. Earthenware, typically fired at lower temperatures in traditional or electric kilns, remains porous and less vitrified, often used for decorative and functional pottery with rustic charm. Choosing between electric ceramic firing and earthenware depends on desired strength, finish, and firing technique in pottery creation.
Key Material Differences
Electric ceramic, typically made from refined clay and fired at higher temperatures between 1,200degC and 1,400degC, achieves greater vitrification and durability compared to earthenware, which is fired at lower temperatures around 1,000degC to 1,150degC. Earthenware remains porous and more susceptible to chipping due to its lower firing temperature and coarser clay composition, whereas electric ceramic's dense, glass-like surface enhances water resistance and strength. The differing thermal properties and mineral content of these materials also influence their shrinkage rates and color variation after firing, making electric ceramics more suitable for functional and decorative pieces requiring longevity.
Firing Techniques and Temperature Ranges
Electric ceramic kilns provide precise temperature control, ideal for firing stoneware and porcelain at high ranges between 1200degC and 1400degC, ensuring durability and vitrification. Earthenware typically fires at lower temperatures, around 1000degC to 1150degC, using traditional gas or wood firing techniques, which result in more porous and less vitrified pottery. The consistent heat distribution in electric kilns improves glaze maturation and reduces defects compared to the variable atmospheres in earthenware firing methods.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Electric ceramic pottery exhibits superior durability due to its higher firing temperatures, resulting in a denser, more vitrified structure that resists chipping and cracking better than earthenware. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures, remains more porous and less resilient, leading to a shorter lifespan and increased vulnerability to moisture and impact damage. Consequently, electric ceramic pieces typically demonstrate enhanced longevity and are preferred for functional pottery requiring greater strength and durability.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finish
Electric ceramic offers a smooth, glossy surface finish with vibrant, consistent coloration, enhancing intricate details and modern designs in pottery. Earthenware provides a warm, rustic aesthetic featuring porous textures and natural matte finishes that emphasize handcrafted appeal. Both materials cater to different artistic preferences, with electric ceramic favoring precision and brightness, while earthenware embraces organic, tactile qualities.
Workability and Artist Preferences
Electric ceramic clay offers superior workability with its smooth plasticity and longer open time, making it ideal for intricate, detailed pottery designs preferred by artists who value precision and fine textures. Earthenware clay, being softer and more porous, allows for easier hand-building and is favored by artists seeking a more rustic, organic feel with quicker firing cycles. Artists often choose electric ceramic for functional ware requiring durability, while earthenware appeals to those emphasizing artistic expression and textural variety in their pottery.
Practical Uses in Pottery
Electric ceramics, fired at higher temperatures typically between 1200degC and 1400degC, offer superior durability and water resistance ideal for functional pottery like dishes and cookware. Earthenware, fired at lower temperatures around 1000degC to 1150degC, remains porous and is better suited for decorative and garden pottery that doesn't require high strength or water tightness. Potters choose electric ceramics for utilitarian items demanding longevity, while earthenware is favored for affordable, aesthetically versatile pieces.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electric ceramic firing uses controlled kiln temperatures, reducing fuel consumption and emissions compared to traditional earthenware firing methods that often involve wood or gas, thus lowering environmental impact. Earthenware pottery, being porous and fired at lower temperatures, typically consumes less energy per unit, though its reliance on non-renewable fuels can increase carbon footprint. Sustainable pottery favors electric ceramic kilns powered by renewable energy, promoting energy efficiency and reducing harmful pollutants, aligning with eco-friendly practices in ceramic production.
Cost Analysis: Electric Ceramic vs Earthenware
Electric ceramic pottery typically incurs higher initial costs due to the need for specialized electric kilns and advanced materials, while earthenware is more budget-friendly with lower material and firing expenses. Maintenance and energy consumption for electric ceramic kilns increase long-term operational costs compared to the simpler, low-temperature firing process of earthenware. Cost analysis favors earthenware for beginners and budget-conscious artisans, whereas electric ceramic suits professionals seeking precision and durability despite the steeper investment.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Electric ceramics offer high durability, superior heat resistance, and a uniform texture, making them ideal for precise and functional pottery projects like cookware or electrical insulators. Earthenware, with its porous nature and lower firing temperature, is better suited for decorative items or sculptural pieces where a rustic, earthy aesthetic is preferred. When choosing the right material, consider the intended use, durability requirements, and desired finish to ensure optimal performance and appearance in your pottery project.
Infographic: Electric ceramic vs Earthenware for Pottery
 azmater.com
azmater.com