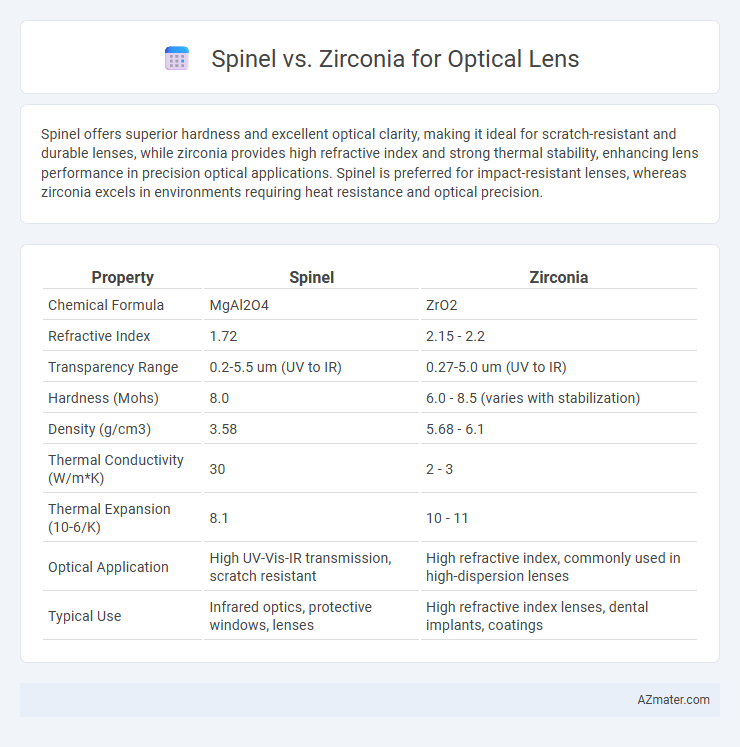
Spinel offers superior hardness and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for scratch-resistant and durable lenses, while zirconia provides high refractive index and strong thermal stability, enhancing lens performance in precision optical applications. Spinel is preferred for impact-resistant lenses, whereas zirconia excels in environments requiring heat resistance and optical precision.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Spinel | Zirconia |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | MgAl2O4 | ZrO2 |
| Refractive Index | 1.72 | 2.15 - 2.2 |
| Transparency Range | 0.2-5.5 um (UV to IR) | 0.27-5.0 um (UV to IR) |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 8.0 | 6.0 - 8.5 (varies with stabilization) |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.58 | 5.68 - 6.1 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 30 | 2 - 3 |
| Thermal Expansion (10-6/K) | 8.1 | 10 - 11 |
| Optical Application | High UV-Vis-IR transmission, scratch resistant | High refractive index, commonly used in high-dispersion lenses |
| Typical Use | Infrared optics, protective windows, lenses | High refractive index lenses, dental implants, coatings |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Spinel and zirconia are advanced materials used in optical lenses due to their unique physical and optical properties. Spinel offers exceptional hardness and high thermal stability with a refractive index around 1.7, making it suitable for durable, high-performance lenses. Zirconia features a higher refractive index near 2.2 and excellent toughness, enhancing lens clarity and resistance to wear in demanding optical applications.
Overview of Spinel in Optical Applications
Spinel is highly valued in optical applications due to its exceptional hardness and excellent optical clarity, making it ideal for durable lenses and transparent armor. Its wide transmission range from ultraviolet to infrared wavelengths enhances performance across diverse optical systems. Spinel's chemical stability and resistance to abrasion contribute to its superiority over traditional materials like zirconia in high-precision optical components.
Properties of Zirconia in Optics
Zirconia exhibits exceptional optical properties, including high refractive index (approximately 2.15) and low dispersion, making it ideal for precision lenses requiring superior light transmission and minimal chromatic aberration. Its robust mechanical strength and thermal stability contribute to enhanced durability and consistent optical performance under varying environmental conditions. The high density and chemical inertness of zirconia further support resistance to wear and environmental degradation in demanding optical applications.
Optical Clarity: Spinel vs Zirconia
Spinel offers exceptional optical clarity with high light transmission and low refractive index, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. Zirconia, while durable, has a higher refractive index and more light scattering, which can slightly reduce clarity in optical applications. Spinel's superior transparency and minimal birefringence provide clearer, sharper images compared to zirconia lenses.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Spinel exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to zirconia, with a higher hardness rating of around 8.5 on the Mohs scale versus zirconia's 6.5-7, making it more resistant to scratches and deformation. The fracture toughness of spinel is also notably greater, enhancing its durability under stress and impact conditions critical for optical lens applications. Zirconia offers excellent toughness but is more prone to surface wear, whereas spinel's combination of hardness and toughness ensures longer-lasting optical clarity and performance.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Spinel exhibits superior thermal stability compared to zirconia, maintaining optical clarity and structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 2000degC, which makes it ideal for high-temperature optical lens applications. Zirconia, while offering high refractive index and mechanical strength, has a lower melting point around 2700degC but tends to undergo phase transitions that can degrade lens performance under thermal stress. The exceptional thermal resilience and robust optical properties of spinel ensure consistent performance in demanding environments, setting it apart from zirconia in thermal stability and long-term lens reliability.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Spinel lenses offer higher durability and superior optical clarity but come at a significantly higher cost compared to zirconia, which is more affordable and widely available. Zirconia is extensively used in mass-market optical applications due to its lower price and easier manufacturing process, whereas spinel's limited supply and complex synthesis drive up its expense. The cost-effectiveness and wide availability of zirconia make it the preferred choice for consumer-grade lenses, while spinel is reserved for specialized, high-performance optical instruments.
Durability and Scratch Resistance
Spinel exhibits superior durability and scratch resistance compared to zirconia, making it an excellent choice for optical lenses subjected to frequent handling and harsh environments. Its hardness rating of 8 on the Mohs scale ensures long-lasting clarity and minimal surface damage, whereas zirconia, with a lower hardness of around 7.5, is more prone to abrasion over time. Optical lenses crafted from spinel maintain their optical performance and surface integrity significantly better under daily wear and exposure to contaminants.
Applications in Modern Optics
Spinel offers superior hardness and excellent light transmission, making it ideal for high-durability optical lenses in aerospace and military applications. Zirconia, known for its high refractive index and fracture toughness, is preferred in precision optics such as camera lenses and medical devices for enhanced image clarity. Both materials play crucial roles in modern optics, with spinel excelling in extreme environments and zirconia optimizing performance in compact, high-resolution systems.
Choosing the Optimal Material: Spinel or Zirconia
Choosing between spinel and zirconia for optical lenses depends on factors like durability, optical clarity, and cost-effectiveness. Spinel offers superior scratch resistance and excellent optical transparency across ultraviolet to mid-infrared wavelengths, making it ideal for high-performance, demanding environments. Zirconia provides high refractive indices and toughness but often falls short in optical clarity and scratch resistance compared to spinel, influencing its use in applications prioritizing impact resistance over optical precision.
Infographic: Spinel vs Zirconia for Optical lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com