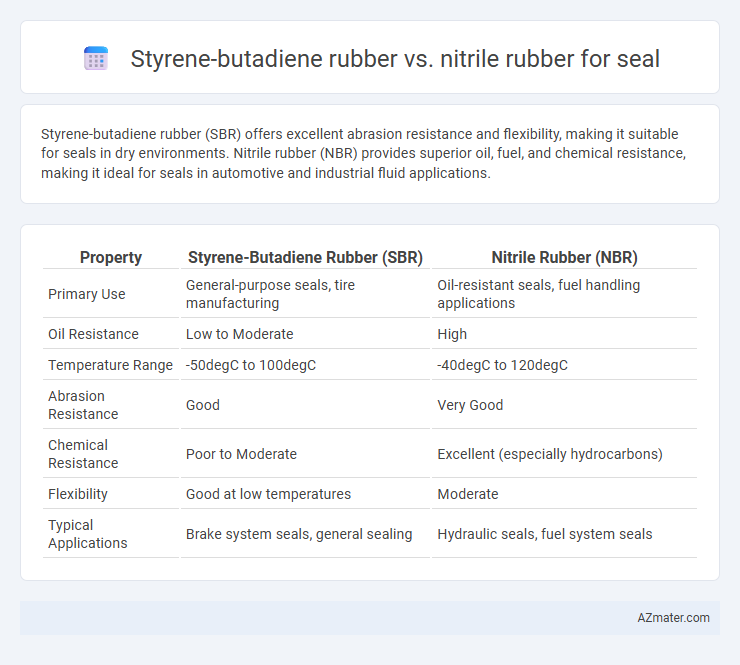
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for seals in dry environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for seals in automotive and industrial fluid applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General-purpose seals, tire manufacturing | Oil-resistant seals, fuel handling applications |
| Oil Resistance | Low to Moderate | High |
| Temperature Range | -50degC to 100degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Very Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Poor to Moderate | Excellent (especially hydrocarbons) |
| Flexibility | Good at low temperatures | Moderate |
| Typical Applications | Brake system seals, general sealing | Hydraulic seals, fuel system seals |
Introduction to Seal Materials: SBR vs Nitrile Rubber
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good aging stability, making it suitable for general-purpose seal applications where mechanical stress is moderate. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, and various chemicals, which is critical for seals in automotive and industrial environments exposed to hydrocarbons. The choice between SBR and Nitrile rubber for seals depends on the required chemical resistance, temperature range, and mechanical durability specific to the application.
Chemical Structure and Composition Overview
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) is a copolymer consisting of styrene and butadiene monomers, offering a balanced combination of elasticity and abrasion resistance due to its saturated hydrocarbon backbone with aromatic rings. Nitrile rubber (NBR), composed of acrylonitrile and butadiene, features polar nitrile groups that provide superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for seals in harsh environments. The distinct chemical structures--non-polar SBR with aromatic styrene units versus polar NBR with nitrile functionalities--directly influence their performance characteristics in seal applications.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and good tensile strength, making it suitable for seals exposed to mechanical wear and moderate temperatures up to 100degC. Nitrile rubber (NBR) excels in oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, with a typical operating temperature range from -40degC to 120degC, making it ideal for seals used in automotive and industrial applications involving petroleum-based fluids. Both materials provide good elasticity and compression set resistance, but NBR generally outperforms SBR in chemical stability and resistance to swelling in hydrocarbons.
Oil and Chemical Resistance Differences
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers limited oil resistance, making it less suitable for seals exposed to petroleum-based fluids compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), which excels in oil and fuel resistance due to its acrylonitrile content. Nitrile rubber provides superior chemical resistance against hydrocarbons, mineral oils, and some acids, while SBR is more susceptible to swelling and degradation when in contact with these substances. For applications requiring prolonged exposure to oils and chemicals, nitrile rubber seals ensure enhanced durability and reduced material breakdown.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate temperature tolerance, typically functioning effectively between -50degC and 100degC, making it suitable for general sealing applications with moderate heat exposure. In contrast, nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior temperature resistance, operating efficiently from -40degC up to 120degC or higher, with excellent resistance to oils and fuels, enhancing seal longevity in demanding environments. The higher thermal stability and chemical resistance of nitrile rubber contribute to its preferred use in automotive and industrial seals where elevated temperatures and exposure to hydrocarbons are common.
Abrasion and Wear Characteristics
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate abrasion resistance suitable for general sealing applications, while nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior wear resistance, especially against oils and fuels. NBR's enhanced durability and resistance to swelling ensure longer seal life in harsh environments with repeated mechanical stress. For seals exposed to aggressive chemicals and continuous friction, nitrile rubber outperforms SBR in maintaining dimensional stability and minimizing wear-related failures.
Application Suitability in Sealing Uses
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) excels in automotive and general industrial seals due to its good abrasion resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for dry and low-temperature environments. Nitrile rubber (NBR) offers superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for seals in hydraulic systems, fuel handling, and applications involving exposure to petroleum-based fluids. The choice between SBR and NBR depends on the sealing environment, with NBR preferred for oil-intensive settings and SBR favored for wear-resistant, cost-sensitive uses.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers a cost-effective solution with widespread availability, making it ideal for seals in general applications where budget constraints are critical. Nitrile rubber (NBR), while typically more expensive, provides superior resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, justifying the cost in demanding environments. The choice between SBR and NBR seals depends largely on balancing initial expenditure against specific performance requirements and material availability in the supply chain.
Longevity and Maintenance Factors
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers moderate resistance to abrasion and weathering but tends to degrade faster under high heat and oil exposure compared to nitrile rubber (NBR), which excels in oil resistance and retains flexibility over a wider temperature range. Nitrile rubber seals provide superior longevity in harsh chemical environments and require less frequent maintenance due to their enhanced resistance to swelling and cracking. Maintenance costs are generally lower for nitrile rubber seals, making them ideal for applications demanding durability and minimal downtime.
Choosing the Right Rubber Seal for Your Needs
Styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) offers excellent abrasion resistance and is cost-effective for general-purpose seals, making it ideal for applications involving dry and mild conditions. Nitrile rubber (NBR) provides superior oil, fuel, and chemical resistance, ensuring optimal performance in automotive, aerospace, and industrial seals exposed to petroleum-based fluids. Selecting the right rubber seal depends on evaluating exposure to chemicals, temperature range, and mechanical stresses specific to your application requirements.
Infographic: Styrene-butadiene rubber vs Nitrile rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com