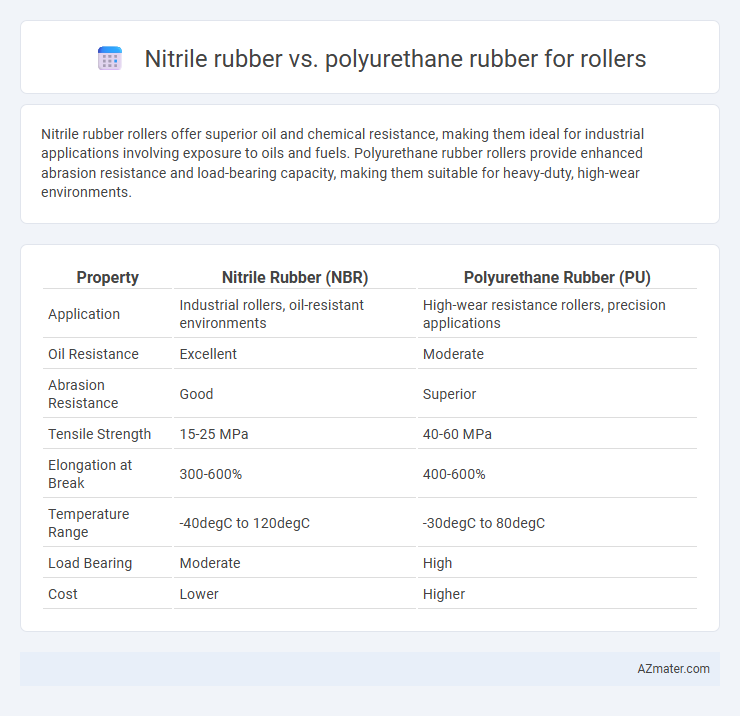
Nitrile rubber rollers offer superior oil and chemical resistance, making them ideal for industrial applications involving exposure to oils and fuels. Polyurethane rubber rollers provide enhanced abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for heavy-duty, high-wear environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nitrile Rubber (NBR) | Polyurethane Rubber (PU) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Industrial rollers, oil-resistant environments | High-wear resistance rollers, precision applications |
| Oil Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Tensile Strength | 15-25 MPa | 40-60 MPa |
| Elongation at Break | 300-600% | 400-600% |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 120degC | -30degC to 80degC |
| Load Bearing | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Roller Materials: Nitrile Rubber vs Polyurethane Rubber
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial roller applications exposed to harsh environments. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and high load-bearing capacity, extending roller life in heavy-duty processing. Selecting between nitrile and polyurethane depends on specific operational demands such as chemical exposure and mechanical stress tolerance.
Chemical Composition and Structural Differences
Nitrile rubber (NBR) is a synthetic copolymer made from acrylonitrile and butadiene, known for its strong resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals due to the polar nitrile groups in its structure. Polyurethane rubber (PU) consists of segmented block copolymers formed from polyols and diisocyanates, offering superior abrasion resistance and elasticity through hard and soft segment microphase separation. The key structural difference lies in NBR's elastomeric carbon-carbon backbone versus PU's segmented arrangement, resulting in distinct mechanical properties and chemical resistance profiles ideal for roller applications.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oil, fuel, and abrasion with tensile strength ranging from 15 to 25 MPa and elongation at break between 300-500%, making it ideal for rollers in harsh chemical environments. Polyurethane rubber exhibits superior tear resistance and hardness, with tensile strength up to 50 MPa and elongation around 400%, providing enhanced durability under heavy load and impact conditions. While nitrile excels in chemical stability and flexibility, polyurethane outperforms in mechanical toughness and longevity, crucial for roller applications requiring high wear resistance and mechanical stress endurance.
Durability and Lifespan in Industrial Applications
Nitrile rubber excels in oil and chemical resistance, making it highly durable for rollers exposed to petroleum-based substances, with a typical lifespan of 3-5 years in harsh industrial environments. Polyurethane rubber offers superior abrasion resistance and tensile strength, extending roller lifespan up to 7 years in applications involving heavy mechanical wear and tear. Choosing polyurethane rubber can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs in industries requiring prolonged durability under abrasive conditions.
Resistance to Chemicals, Oils, and Solvents
Nitrile rubber offers superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, oils, and solvents, making it an ideal choice for rollers exposed to petroleum-based fluids and hydrocarbons. Polyurethane rubber excels in resisting abrasion and has good resistance to aliphatic oils and some solvents but is less effective than nitrile when exposed to aromatic and chlorinated solvents. Selecting nitrile rubber ensures enhanced durability in chemically aggressive environments, while polyurethane may be preferred for mechanical wear and moderate chemical exposure.
Performance Under High and Low Temperature Conditions
Nitrile rubber exhibits excellent resistance to high temperatures up to 120degC and maintains flexibility down to -40degC, making it suitable for roller applications involving extreme thermal conditions. Polyurethane rubber offers superior wear resistance and mechanical strength but typically withstands high temperatures only up to 80degC, with limited performance below -20degC. For rollers operating under severe thermal cycling, nitrile rubber delivers more reliable elasticity and durability compared to polyurethane rubber.
Abrasion and Wear Resistance Analysis
Nitrile rubber exhibits superior abrasion resistance compared to polyurethane rubber, making it highly effective for applications involving oil and chemical exposure. Polyurethane rubber, while offering excellent wear resistance and mechanical strength, tends to perform better under heavy load and impact conditions but may degrade faster in harsh chemical environments. Selecting the optimal roller material depends on balancing the abrasion resistance of nitrile with the wear resilience of polyurethane according to specific operational demands.
Cost Considerations for Manufacturing Rollers
Nitrile rubber offers a cost-effective solution for roller manufacturing due to its lower raw material expenses and good resistance to oils and abrasives, making it suitable for industrial applications with moderate operating conditions. Polyurethane rubber, while generally more expensive, provides superior durability, abrasion resistance, and load-bearing capacity, which can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs in high-demand settings. Manufacturers should balance upfront material costs against lifecycle performance to optimize total cost of ownership in roller production.
Typical Applications and Industry Preferences
Nitrile rubber rollers excel in oil resistance and are predominantly used in automotive, aerospace, and printing industries for fuel handling and hydraulic systems. Polyurethane rubber rollers offer superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for conveyor belts, packaging, and heavy machinery sectors. Industry preferences favor nitrile for environments exposed to oils and chemicals, while polyurethane is preferred for applications demanding durability and mechanical strength.
Choosing the Right Rubber: Key Factors for Roller Selection
Nitrile rubber offers excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and chemicals, making it ideal for rollers used in industrial applications involving hydrocarbons. Polyurethane rubber provides superior abrasion resistance and load-bearing capacity, suitable for heavy-duty rollers in manufacturing processes requiring durability and resilience. Selecting the right roller rubber depends on factors such as chemical exposure, mechanical stress, and operational environment to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Nitrile rubber vs Polyurethane rubber for Roller
 azmater.com
azmater.com