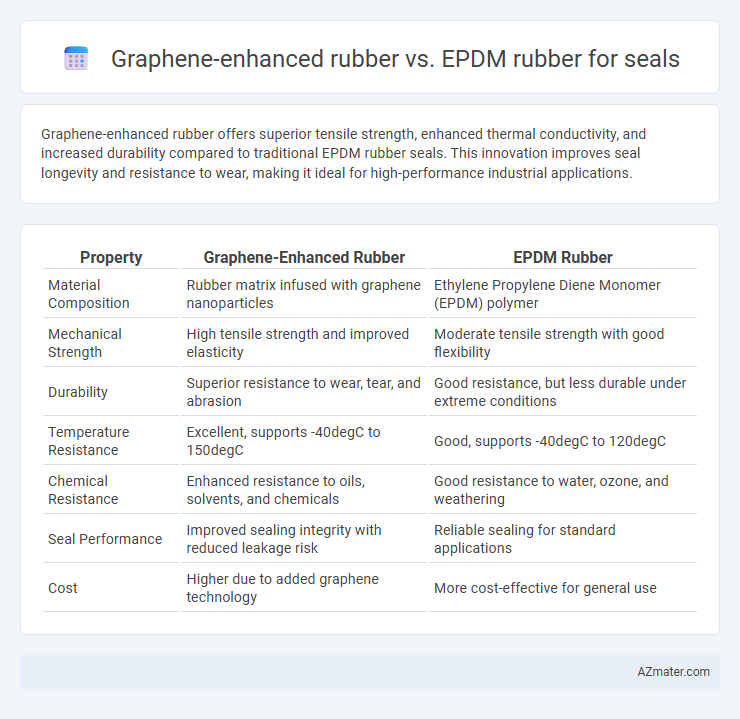
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior tensile strength, enhanced thermal conductivity, and increased durability compared to traditional EPDM rubber seals. This innovation improves seal longevity and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-performance industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Graphene-Enhanced Rubber | EPDM Rubber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Rubber matrix infused with graphene nanoparticles | Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) polymer |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and improved elasticity | Moderate tensile strength with good flexibility |
| Durability | Superior resistance to wear, tear, and abrasion | Good resistance, but less durable under extreme conditions |
| Temperature Resistance | Excellent, supports -40degC to 150degC | Good, supports -40degC to 120degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Enhanced resistance to oils, solvents, and chemicals | Good resistance to water, ozone, and weathering |
| Seal Performance | Improved sealing integrity with reduced leakage risk | Reliable sealing for standard applications |
| Cost | Higher due to added graphene technology | More cost-effective for general use |
Introduction to Rubber Materials for Seals
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior mechanical properties and enhanced wear resistance compared to traditional EPDM rubber, making it an innovative choice for seals requiring high durability and performance. EPDM rubber, known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering, remains a popular option in sealing applications where chemical stability and flexibility are critical. The integration of graphene into rubber formulations significantly improves tensile strength and thermal conductivity, providing advanced sealing solutions in demanding industrial environments.
What is Graphene-Enhanced Rubber?
Graphene-enhanced rubber integrates graphene nanoparticles into a rubber matrix, significantly improving the material's mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and wear resistance compared to conventional EPDM rubber. This innovation results in seals with enhanced durability, better chemical resistance, and prolonged service life under extreme conditions. The superior performance of graphene-enhanced rubber seals makes them ideal for automotive, industrial, and aerospace applications where reliability and longevity are critical.
Overview of EPDM Rubber
EPDM rubber, or Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer, is a highly versatile synthetic elastomer known for its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. Commonly used in seals, EPDM provides superior durability and flexibility under varying environmental conditions, making it ideal for automotive and industrial applications. Its inherent chemical stability and cost-effectiveness offer a reliable alternative to graphene-enhanced rubber, especially in sealing solutions requiring long-term performance without complex reinforcement.
Comparative Mechanical Properties
Graphene-enhanced rubber demonstrates significantly higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance compared to EPDM rubber, contributing to extended seal durability under mechanical stress. The incorporation of graphene improves elasticity and tear resistance, making these composites more effective in dynamic sealing applications where flexibility and resilience are critical. EPDM rubber, while offering good weather and ozone resistance, typically exhibits lower mechanical robustness than graphene-enhanced variants, limiting its effectiveness in high-performance sealing environments.
Chemical and Environmental Resistance
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to EPDM rubber, effectively withstanding oils, solvents, and harsh chemicals, making it ideal for aggressive industrial environments. It also offers enhanced environmental resistance, including improved UV stability and reduced degradation under ozone exposure, resulting in longer seal life in outdoor or harsh climate applications. EPDM rubber, while resistant to weathering, excels primarily in acid, alkaline, and steam environments but has limitations against hydrocarbons and solvents where graphene-enhanced variants perform better.
Longevity and Durability in Sealing Applications
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior longevity and durability compared to EPDM rubber in sealing applications due to graphene's exceptional mechanical strength and resistance to wear and tear. The incorporation of graphene significantly improves the material's tensile strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance, resulting in extended service life under harsh environmental conditions. EPDM rubber, while effective in resistance to ozone and weathering, often falls short in maintaining performance under high mechanical stress and prolonged exposure, where graphene-enhanced rubber outperforms by reducing degradation and sealing failure.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Graphene-enhanced rubber exhibits superior thermal stability and flexibility at extreme temperatures compared to EPDM rubber, maintaining elasticity from -60degC to 250degC. EPDM rubber typically performs well within a temperature range of -50degC to 150degC but can degrade faster under prolonged exposure to high heat. The integration of graphene significantly improves the seal's resistance to thermal degradation and mechanical wear, making it ideal for applications in harsh environmental conditions.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Graphene-enhanced rubber seals offer higher durability and conductivity but come with increased material costs and require advanced manufacturing techniques, impacting overall production expenses. EPDM rubber seals are cost-effective, widely available, and compatible with standard molding and extrusion processes, making them economical for large-scale production. Manufacturing graphene-enhanced rubber involves specialized equipment and quality control, whereas EPDM benefits from established supply chains and streamlined fabrication, reducing lead times and operational costs.
Industry Applications: Graphene-Enhanced vs EPDM
Graphene-enhanced rubber demonstrates superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and electrical properties compared to EPDM rubber, making it highly suitable for advanced industrial seals in automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors. EPDM rubber, known for its excellent weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, remains a preferred choice for outdoor and HVAC sealing applications where durability and environmental resilience are critical. In industries requiring enhanced performance, graphene-enhanced seals offer improved wear resistance and longevity, enabling reduced maintenance and enhanced operational efficiency.
Future Trends in Rubber Seal Technologies
Graphene-enhanced rubber offers superior mechanical strength, thermal conductivity, and chemical resistance compared to traditional EPDM rubber, driving innovation in seal durability and performance. Future trends in rubber seal technologies emphasize integrating nanomaterials like graphene to extend service life and improve environmental resilience under extreme conditions. Advances in graphene composites enable lightweight, energy-efficient seals that support sustainability goals and evolving industrial standards.
Infographic: Graphene-enhanced rubber vs EPDM rubber for Seal
 azmater.com
azmater.com