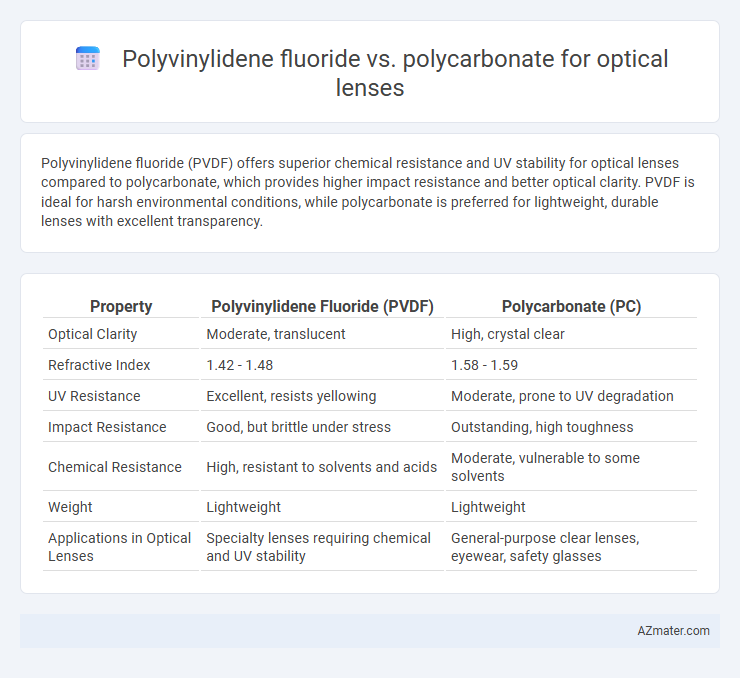
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and UV stability for optical lenses compared to polycarbonate, which provides higher impact resistance and better optical clarity. PVDF is ideal for harsh environmental conditions, while polycarbonate is preferred for lightweight, durable lenses with excellent transparency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Optical Clarity | Moderate, translucent | High, crystal clear |
| Refractive Index | 1.42 - 1.48 | 1.58 - 1.59 |
| UV Resistance | Excellent, resists yellowing | Moderate, prone to UV degradation |
| Impact Resistance | Good, but brittle under stress | Outstanding, high toughness |
| Chemical Resistance | High, resistant to solvents and acids | Moderate, vulnerable to some solvents |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight |
| Applications in Optical Lenses | Specialty lenses requiring chemical and UV stability | General-purpose clear lenses, eyewear, safety glasses |
Introduction to Optical Lens Materials
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) and polycarbonate (PC) are common materials used in optical lens manufacturing, each offering distinct advantages. PVDF provides excellent chemical resistance and UV stability, making it suitable for outdoor applications with prolonged sun exposure. Polycarbonate, known for its high impact resistance and clarity, excels in protective eyewear and safety lenses where durability and optical quality are critical.
Overview of Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF)
Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) offers excellent chemical resistance, high thermal stability, and superior UV resistance, making it a durable choice for optical lens applications requiring long-term exposure to harsh environments. Its low refractive index and inherent opacity limit its use in certain transparent lens designs, but its robustness and resistance to yellowing provide advantages in specialized optical components. PVDF's mechanical strength and excellent dimensional stability contribute to maintaining optical clarity and precise lens performance over time.
Properties of Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) offers exceptional optical clarity with high light transmittance of approximately 89%, making it ideal for precision optical lenses. It exhibits excellent impact resistance, up to 250 times greater than glass, ensuring durability and safety in eyewear applications. The material also features a high heat distortion temperature around 147degC, providing stability under varying environmental conditions.
Optical Clarity: PVDF vs Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate offers superior optical clarity with a high light transmittance of approximately 89%, making it ideal for precise optical lens applications where transparency and minimal distortion are critical. Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) generally has lower optical clarity, with more light scattering and lower transmittance, limiting its suitability for high-performance lenses. The inherent molecular structure of polycarbonate ensures better UV resistance and impact strength without compromising on transparency, whereas PVDF is more suited for chemical resistance than optical precision.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and impact strength compared to polycarbonate (PC), making it highly durable under harsh environmental conditions. Polycarbonate excels in toughness with high impact resistance and flexibility but is more prone to surface scratching and UV degradation without coatings. For optical lenses requiring prolonged mechanical strength and durability, PVDF provides enhanced resistance to abrasion and chemical attack, while polycarbonate is favored for lighter weight and impact absorption in less demanding environments.
Chemical Resistance in Lens Applications
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) exhibits superior chemical resistance to solvents, acids, and alkalis compared to polycarbonate (PC), making PVDF ideal for optical lenses exposed to harsh chemical environments. Polycarbonate is more prone to stress cracking and degradation when exposed to chemicals, which can compromise lens clarity and durability. Therefore, PVDF lenses provide enhanced longevity and performance in applications requiring robust chemical stability.
UV Stability and Weathering Performance
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) outperforms polycarbonate (PC) in UV stability, maintaining optical clarity and mechanical integrity under prolonged sunlight exposure due to its intrinsic resistance to photodegradation. PVDF exhibits superior weathering performance, resisting yellowing and surface erosion even in harsh environmental conditions. While polycarbonate is prone to UV-induced discoloration and surface cracking without adequate coatings, PVDF's chemical structure ensures long-term durability for outdoor optical lens applications.
Weight and Design Flexibility
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers significantly lower weight compared to polycarbonate (PC), making it an excellent choice for lightweight optical lenses used in wearable technology and mobile devices. PVDF exhibits superior design flexibility due to its chemical resistance and thermal stability, allowing for intricate lens shapes and customizable optic properties. Polycarbonate remains popular for its impact resistance but is generally heavier and less adaptable to complex lens designs than PVDF.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers a lower material cost and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for cost-sensitive optical lens manufacturing with enhanced durability. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior impact resistance and optical clarity but entails higher raw material expenses and more complex molding processes that increase production costs. Manufacturing PVDF lenses benefits from easier processing and lower equipment wear, whereas polycarbonate lenses require precision injection molding and may incur higher tooling and maintenance expenses.
Optimal Material Choice for Optical Lenses
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) offers superior chemical resistance and high UV stability, making it an optimal choice for optical lenses exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Polycarbonate provides excellent impact resistance and high optical clarity, ideal for applications requiring durability and lightweight properties. For optical lenses, selecting between PVDF and polycarbonate hinges on prioritizing either environmental resistance or impact strength and transparency.
Infographic: Polyvinylidene fluoride vs Polycarbonate for Optical Lens
 azmater.com
azmater.com