Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance and affordability for laboratoryware, while polysulfone provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength for high-temperature applications. Choosing between polypropylene and polysulfone depends on the specific laboratory environment and required durability.
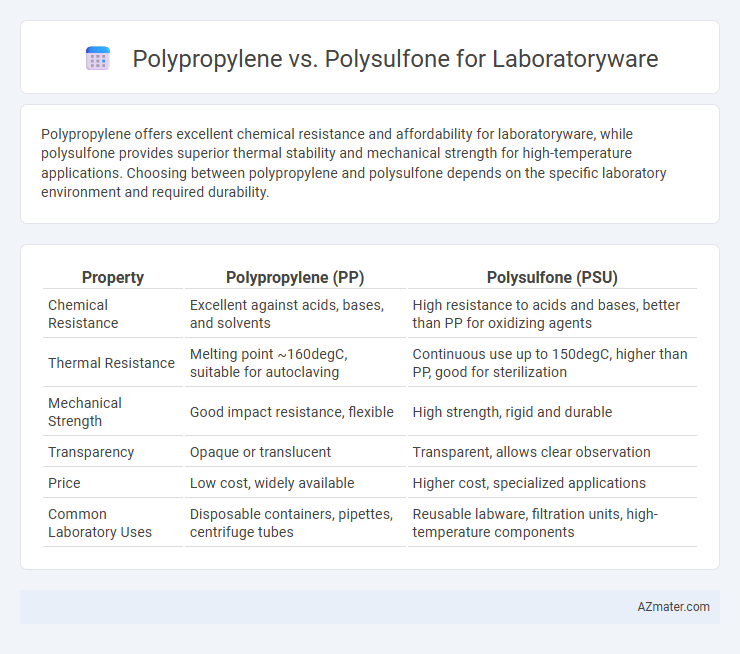
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polysulfone (PSU) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent against acids, bases, and solvents | High resistance to acids and bases, better than PP for oxidizing agents |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~160degC, suitable for autoclaving | Continuous use up to 150degC, higher than PP, good for sterilization |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance, flexible | High strength, rigid and durable |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Transparent, allows clear observation |
| Price | Low cost, widely available | Higher cost, specialized applications |
| Common Laboratory Uses | Disposable containers, pipettes, centrifuge tubes | Reusable labware, filtration units, high-temperature components |
Introduction to Laboratoryware Materials
Polypropylene and polysulfone are two widely used materials in laboratoryware due to their distinct chemical and thermal properties. Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for disposable containers and general-purpose labware. Polysulfone provides superior thermal stability, toughness, and resistance to hydrolysis, which suits high-heat applications and autoclave sterilization in laboratory environments.
Overview of Polypropylene: Properties and Applications
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its excellent chemical resistance, high melting point around 160degC, and strong impact resistance, making it ideal for laboratoryware that requires frequent sterilization and exposure to harsh chemicals. Its lightweight and cost-effective nature contribute to widespread use in manufacturing beakers, test tubes, and various storage containers in both research and clinical laboratories. The material's ability to withstand autoclaving processes without deformation ensures durability and reusability, which is essential for maintaining laboratory efficiency and safety.
Polysulfone: Material Characteristics and Common Uses
Polysulfone exhibits exceptional thermal stability, chemical resistance, and impact strength, making it ideal for laboratoryware requiring sterilization and exposure to harsh chemicals. Its transparency and dimensional stability enable precise liquid measurement and repeated autoclaving without degradation. Common uses of polysulfone in laboratoryware include filtration devices, centrifuge tubes, and culture flasks, where durability and resistance to aggressive solvents are critical.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Polysulfone exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to polypropylene, making it highly resistant to stress and impact in laboratoryware applications. Its high tensile strength and excellent dimensional stability ensure durability under repeated sterilization and thermal cycling. Polypropylene offers flexibility and chemical resistance but lacks the rigidity and toughness of polysulfone, limiting its use in demanding mechanical environments.
Chemical Resistance: Polypropylene vs Polysulfone
Polypropylene exhibits excellent chemical resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and organic solvents, making it suitable for general laboratory applications where acids and alkalis are common. Polysulfone offers superior resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals such as chlorinated solvents and strong oxidizing agents, maintaining structural integrity in demanding laboratory environments. Selecting polypropylene or polysulfone depends on the specific chemicals involved and temperature conditions, with polysulfone preferred for harsher chemical exposures and polypropylene favored for cost-effective, routine use.
Temperature Tolerance and Sterilization Options
Polypropylene exhibits excellent chemical resistance and can withstand autoclave sterilization temperatures up to 121degC, making it suitable for routine laboratory applications requiring steam sterilization. Polysulfone offers superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity at continuous use temperatures up to 160degC and withstanding repeated autoclaving cycles without degradation. Both materials support common sterilization methods, but polysulfone's higher thermal stability provides greater durability for high-temperature sterilization protocols in demanding laboratory environments.
Transparency and Visual Clarity in Laboratory Tasks
Polysulfone offers superior transparency and visual clarity compared to polypropylene, making it ideal for laboratoryware requiring clear observation of samples. Its excellent resistance to heat and chemicals ensures clear viewing without distortion or cloudiness during sterilization and use. Polypropylene, while more chemically resistant and cost-effective, often exhibits a more opaque and frosted appearance, limiting visual accuracy in precise laboratory tasks.
Cost Analysis: Budget Considerations
Polypropylene offers a cost-effective solution for laboratoryware, with prices significantly lower than polysulfone, making it ideal for budget-conscious laboratories. Polysulfone provides superior chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance, but these benefits come with a higher material and manufacturing cost. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including durability and replacement frequency, is essential for determining the most economical choice between polypropylene and polysulfone.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polypropylene (PP) offers significant environmental advantages in laboratoryware due to its high recyclability and lower energy consumption during production compared to polysulfone (PSU). Polysulfone, while durable and heat-resistant, poses challenges in recycling processes and typically requires more energy-intensive manufacturing methods, leading to a larger carbon footprint. Selecting polypropylene labware supports sustainable laboratory practices by enabling efficient recycling and reducing overall environmental impact.
Choosing the Right Material for Laboratoryware
Polypropylene offers excellent chemical resistance, affordability, and versatility, making it ideal for general-purpose laboratoryware such as storage containers and tubes. Polysulfone provides superior thermal stability and mechanical strength, suitable for applications requiring autoclaving and repeated sterilization. Selecting the right material depends on the specific laboratory needs, balancing factors like chemical compatibility, temperature tolerance, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polysulfone for Laboratoryware
 azmater.com
azmater.com