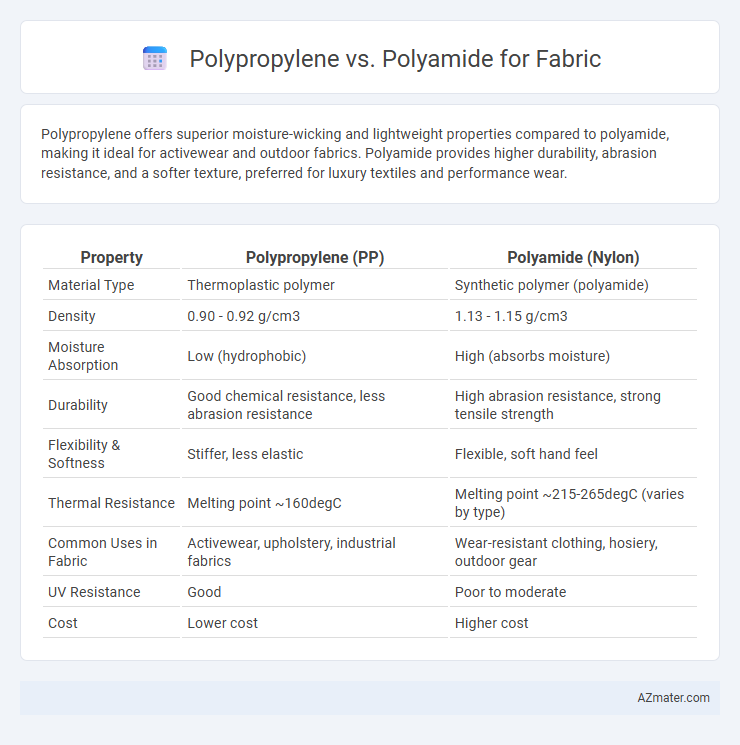
Polypropylene offers superior moisture-wicking and lightweight properties compared to polyamide, making it ideal for activewear and outdoor fabrics. Polyamide provides higher durability, abrasion resistance, and a softer texture, preferred for luxury textiles and performance wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyamide (Nylon) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Synthetic polymer (polyamide) |
| Density | 0.90 - 0.92 g/cm3 | 1.13 - 1.15 g/cm3 |
| Moisture Absorption | Low (hydrophobic) | High (absorbs moisture) |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, less abrasion resistance | High abrasion resistance, strong tensile strength |
| Flexibility & Softness | Stiffer, less elastic | Flexible, soft hand feel |
| Thermal Resistance | Melting point ~160degC | Melting point ~215-265degC (varies by type) |
| Common Uses in Fabric | Activewear, upholstery, industrial fabrics | Wear-resistant clothing, hosiery, outdoor gear |
| UV Resistance | Good | Poor to moderate |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polypropylene and Polyamide Fabrics
Polypropylene fabrics are lightweight, moisture-wicking, and resistant to chemicals and abrasion, making them ideal for activewear and outdoor applications. Polyamide fabrics, commonly known as nylon, offer high strength, elasticity, and durability, along with excellent resistance to wear and UV exposure. Both materials provide distinct performance benefits, with polypropylene excelling in moisture management and polyamide favored for its toughness and versatility in textile manufacturing.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polypropylene consists of a linear hydrocarbon chain with repeating propylene units, making it a highly non-polar and hydrophobic polymer with excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, features amide groups (-CONH-) in its backbone, which introduces polarity and hydrogen bonding capabilities, resulting in higher moisture absorption and greater tensile strength. The contrasting chemical structures influence fabric properties, with polypropylene offering superior chemical inertness and lighter weight, while polyamide provides enhanced durability and elasticity due to its polar amide linkages.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Polypropylene fabric is produced primarily through melt spinning, which offers energy efficiency, faster production rates, and lower manufacturing costs compared to polyamide. Polyamide, commonly Nylon, requires a more complex polycondensation process and higher processing temperatures during melt spinning, resulting in increased energy consumption and longer production cycles. These differences influence fabric qualities and industrial scalability, with polypropylene favored for cost-effective mass production and polyamide preferred for applications needing strength and elasticity.
Durability and Strength Differences
Polypropylene fabrics exhibit high resistance to moisture, chemical exposure, and abrasion, making them exceptionally durable for outdoor and industrial applications. Polyamide (nylon) offers superior tensile strength and elasticity, providing enhanced durability under repeated stress and strain. While polypropylene excels in lightweight durability and chemical resistance, polyamide delivers greater mechanical strength and resilience, ideal for performance-intensive fabrics.
Moisture Resistance and Absorption
Polypropylene fabric exhibits superior moisture resistance with low moisture absorption rates around 0.01%, making it highly effective for quick-drying and water-repellent applications. Polyamide (nylon) absorbs more moisture, approximately 4-5%, which can lead to longer drying times but provides better breathability and comfort in activewear fabrics. Choosing between polypropylene and polyamide depends on prioritizing water repellency and drying speed versus moisture management and fabric softness.
Comfort and Skin Sensitivity
Polypropylene fabric offers excellent moisture-wicking properties and is lightweight, making it highly breathable and comfortable for active wear, but it can sometimes cause static buildup and may not be ideal for sensitive skin. Polyamide (nylon) fibers provide a softer, smoother texture that feels gentle against the skin, enhancing comfort for individuals with skin sensitivities while maintaining durability and flexibility. Both materials are engineered for performance, yet polyamide's hypoallergenic qualities often make it the preferred choice for those prioritizing skin comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polypropylene fabric offers low environmental impact due to its energy-efficient production and recyclability, but it is derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions. Polyamide, while more durable and biodegradable under specific conditions, involves higher water consumption and chemical use during synthesis, raising concerns about pollution. Sustainable alternatives include bio-based polyamides and recycled polypropylene, reducing ecological footprints and enhancing circular economy integration.
Cost and Market Availability
Polypropylene fabric offers a significantly lower cost compared to polyamide, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications. Its widespread production ensures abundant market availability, especially in sportswear and outdoor gear sectors. Polyamide fibers, although more expensive due to higher manufacturing costs, provide superior durability and elasticity, maintaining steady demand in high-performance and luxury textile markets.
Common Applications in Textile Industry
Polypropylene is widely used in activewear and sportswear due to its moisture-wicking properties and lightweight nature, making it ideal for performance fabrics. Polyamide, commonly known as nylon, is favored in hosiery, lingerie, and swimwear for its elasticity, durability, and smooth texture. Both fibers serve distinct roles in the textile industry, with polypropylene excelling in technical and outdoor fabrics while polyamide dominates in fashion and intimate apparel.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fabric
Polypropylene excels in moisture-wicking and lightweight durability, ideal for activewear and outdoor fabrics needing quick-drying properties. Polyamide offers superior strength, elasticity, and abrasion resistance, making it the preferred choice for high-performance sportswear and luxury textiles. Selecting the right fabric depends on the primary use--polypropylene suits moisture management and cost efficiency, while polyamide delivers enhanced comfort and durability in demanding applications.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Polyamide for Fabric
 azmater.com
azmater.com