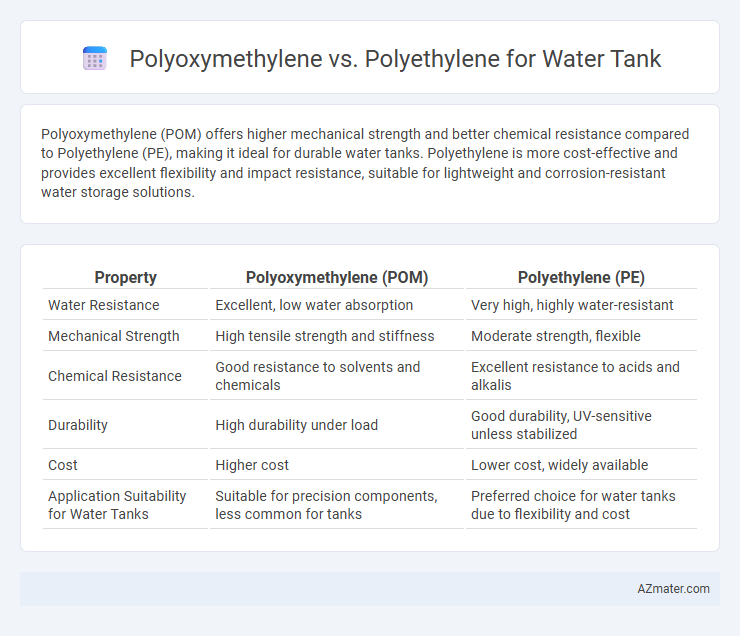
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers higher mechanical strength and better chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for durable water tanks. Polyethylene is more cost-effective and provides excellent flexibility and impact resistance, suitable for lightweight and corrosion-resistant water storage solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyoxymethylene (POM) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Water Resistance | Excellent, low water absorption | Very high, highly water-resistant |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | Moderate strength, flexible |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and chemicals | Excellent resistance to acids and alkalis |
| Durability | High durability under load | Good durability, UV-sensitive unless stabilized |
| Cost | Higher cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Application Suitability for Water Tanks | Suitable for precision components, less common for tanks | Preferred choice for water tanks due to flexibility and cost |
Introduction to Polyoxymethylene and Polyethylene
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a highly crystalline thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for precision components in water tanks. Polyethylene (PE), particularly high-density polyethylene (HDPE), is widely used in water tank manufacturing due to its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and affordability, providing durability and leak-proof performance. Both materials serve distinct roles, with POM offering superior rigidity and dimensional stability, while PE excels in impact resistance and ease of fabrication.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Polyoxymethylene (POM) is a thermoplastic polymer with a repeating -CH2-O- unit, giving it a highly crystalline structure and strong carbon-oxygen bonds that provide excellent chemical resistance and rigidity. Polyethylene (PE) consists of -CH2- repeating units, resulting in a more flexible, less dense polymer with varying density grades like HDPE and LDPE that influence its chemical resistance and mechanical properties. The distinct chemical structures make POM more suitable for precision components requiring stiffness and chemical resilience, while PE's composition offers better impact resistance and suitability for large, flexible water tanks.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior tensile strength and stiffness compared to Polyethylene (PE), making it ideal for water tanks requiring high mechanical durability and resistance to deformation. POM exhibits higher impact resistance and better dimensional stability under temperature variations, enhancing the tank's structural integrity. In contrast, polyethylene's flexibility and lower strength may lead to easier deformation under load, though it provides better chemical resistance and cost-effectiveness for less demanding applications.
Durability and Lifespan in Water Tanks
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior durability and dimensional stability compared to polyethylene (PE) due to its higher resistance to wear, chemicals, and UV radiation, making it ideal for long-term water tank applications. Polyethylene, while cost-effective and corrosion-resistant, has a shorter lifespan when exposed to environmental stressors and may degrade faster under prolonged sunlight exposure. The inherent mechanical strength and low moisture absorption of polyoxymethylene result in water tanks with enhanced longevity and reduced maintenance requirements.
Resistance to Chemicals and Corrosion
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it highly suitable for water tanks exposed to harsh substances. Polyethylene (PE), while also resistant to many acids and alkalis, can degrade more quickly under prolonged exposure to certain solvents and oxidizing agents. POM's molecular structure provides enhanced corrosion resistance compared to PE, ensuring greater durability and longevity in chemically aggressive water storage environments.
Impact on Water Quality and Safety
Polyoxymethylene (POM) exhibits superior chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, reducing the risk of contaminants leaching into stored water, thus enhancing water quality and safety in water tanks. Polyethylene (PE), widely used due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, may allow slight permeability and potential microbial growth if not properly treated, potentially impacting water purity. Choosing POM for water tanks ensures better long-term water safety by minimizing chemical interactions, while PE requires specific food-grade grades and additives to maintain water quality.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance compared to Polyethylene (PE), but it comes at a higher material and production cost, making it less economical for large-scale water tank manufacturing. Polyethylene, widely available in various grades like HDPE and LDPE, provides excellent cost-effectiveness and accessibility due to its extensive global supply chain and lower raw material prices. For water tanks, HDPE's affordability and sufficient durability often outweigh POM's enhanced performance, defining PE as the preferred choice in terms of cost-efficiency and material availability.
Manufacturing Process and Ease of Fabrication
Polyoxymethylene (POM) boasts high stiffness and low friction, making it ideal for precision water tank components but requires controlled processing temperatures due to its thermal sensitivity during injection molding. Polyethylene (PE), especially high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offers excellent chemical resistance and ease of fabrication through extrusion and rotational molding, facilitating seamless tank manufacturing with less stringent temperature control. The manufacturing process of POM demands greater precision and drying, while PE's versatility in fabrication methods allows for cost-effective and scalable water tank production.
Environmental Considerations and Recyclability
Polyoxymethylene (POM) offers superior mechanical strength and chemical resistance for water tanks but has limited recyclability compared to polyethylene (PE), which is widely recycled through established systems. Polyethylene's lower environmental impact arises from its easier recycling process and broader acceptance in municipal recycling programs, reducing landfill contributions. Choosing polyethylene supports circular economy practices and minimizes ecological footprints, while POM's production and disposal pose greater environmental challenges due to its complex polymer structure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Water Tanks
Polyoxymethylene (POM) outperforms polyethylene (PE) in water tank applications due to its superior mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to chemical degradation. Polyethylene tanks offer cost-effective, lightweight solutions with excellent corrosion resistance but lack the rigidity and long-term durability of POM. Selecting the right material requires balancing budget constraints with performance needs, where POM is ideal for high-stress, long-lasting water tanks, while PE suits less demanding, budget-sensitive projects.
Infographic: Polyoxymethylene vs Polyethylene for Water Tank
 azmater.com
azmater.com