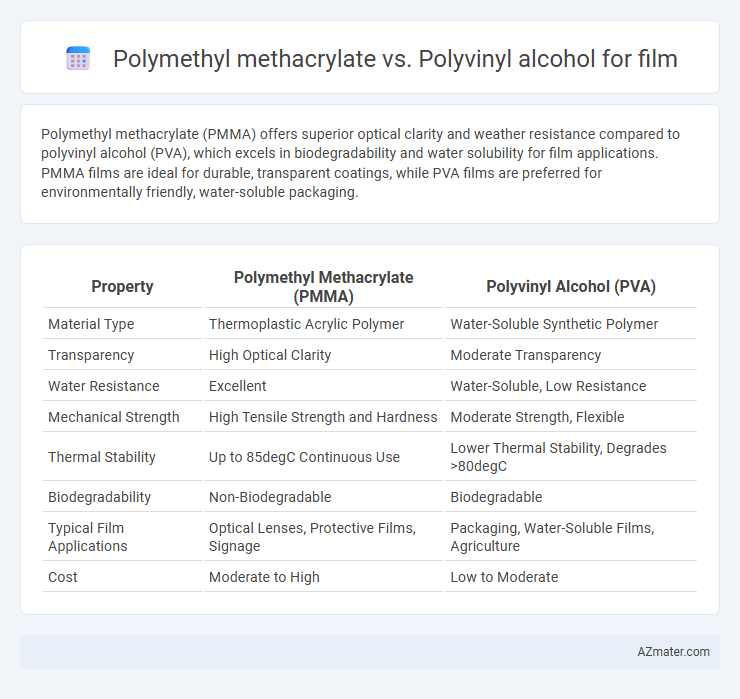
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and weather resistance compared to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), which excels in biodegradability and water solubility for film applications. PMMA films are ideal for durable, transparent coatings, while PVA films are preferred for environmentally friendly, water-soluble packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA) | Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic Acrylic Polymer | Water-Soluble Synthetic Polymer |
| Transparency | High Optical Clarity | Moderate Transparency |
| Water Resistance | Excellent | Water-Soluble, Low Resistance |
| Mechanical Strength | High Tensile Strength and Hardness | Moderate Strength, Flexible |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 85degC Continuous Use | Lower Thermal Stability, Degrades >80degC |
| Biodegradability | Non-Biodegradable | Biodegradable |
| Typical Film Applications | Optical Lenses, Protective Films, Signage | Packaging, Water-Soluble Films, Agriculture |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
Introduction to Film Materials: PMMA vs PVA
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) are prominent polymers used in film applications, each exhibiting distinct properties tailored for specific uses. PMMA offers excellent optical clarity, UV resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for transparent protective films and displays. PVA, known for its water solubility, strong film-forming ability, and biodegradability, is commonly employed in packaging films and water-soluble applications.
Chemical Structure Comparison: Polymethyl Methacrylate and Polyvinyl Alcohol
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) features a rigid, hydrophobic carbon backbone with methyl methacrylate side groups, providing high transparency and mechanical strength ideal for film applications. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) possesses a flexible, hydrophilic polymer chain with abundant hydroxyl (-OH) groups, enhancing film flexibility and water solubility. The contrasting chemical structures of PMMA and PVA define their distinct physical properties and suitability for various film uses in industries such as packaging, coatings, and biomedical devices.
Mechanical Properties of PMMA and PVA Films
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) films exhibit high tensile strength and excellent rigidity, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and dimensional stability. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) films offer superior flexibility and higher elongation at break but have lower tensile strength compared to PMMA. The mechanical properties of PMMA contribute to its resistance to deformation under stress, while PVA's mechanical behavior favors applications needing pliability and water solubility.
Optical Clarity and Transparency Differences
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits superior optical clarity and transparency compared to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), making it ideal for high-quality optical films and lenses. PMMA offers a higher light transmittance rate, typically exceeding 90%, with minimal haze and excellent resistance to yellowing over time. In contrast, PVA films exhibit lower transparency and can absorb moisture, leading to reduced clarity and potential optical distortions in humid conditions.
Water Resistance and Solubility Characteristics
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits excellent water resistance due to its hydrophobic nature, making it ideal for durable, moisture-resistant films. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), in contrast, is highly water-soluble, which limits its use in humid or wet environments but offers advantages in biodegradable or easily removable film applications. The choice between PMMA and PVA for film production depends on the specific requirements for water resistance and solubility, with PMMA favored for long-term water stability and PVA preferred for environmentally sensitive uses.
Film-Forming Abilities and Processes
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) exhibits superior film-forming abilities due to its excellent transparency, rigidity, and resistance to environmental degradation, making it ideal for durable, high-quality films used in optical and protective applications. Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) offers good film-forming properties with strong adhesion, flexibility, and water solubility, suitable for biodegradable or water-soluble films in packaging and pharmaceutical industries. The film formation process for PMMA typically involves solution casting or spin coating, requiring organic solvents, whereas PVA films often form through aqueous solution drying, enabling eco-friendly and cost-effective manufacturing.
Durability and Environmental Stability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior durability and environmental stability compared to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) when used in film applications, owing to its high resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and chemical exposure. PMMA films maintain clarity and mechanical strength over prolonged outdoor use, while PVA films tend to degrade quickly in humid or wet conditions due to their water-solubility and lower resistance to environmental stressors. The enhanced weatherability and aging resistance of PMMA make it a preferred choice for long-term film applications requiring sustained performance.
Applications in Industry: PMMA vs PVA Films
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) films excel in optical clarity, UV resistance, and weatherability, making them ideal for applications in automotive glazing, electronic displays, and protective screens. In contrast, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) films offer exceptional water solubility, biodegradability, and gas barrier properties, which suit packaging, agricultural mulch films, and medical wound dressings. The choice between PMMA and PVA films depends on the required durability, transparency, and environmental impact for specific industrial uses.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and durability but comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), which is more affordable and widely accessible for film applications. PVA films excel in biodegradability and water solubility, making them cost-effective for short-term or disposable uses, while PMMA is preferred for long-lasting, high-performance films despite its premium price. Supply chain stability favors PVA due to its established production scale, whereas PMMA's specialized manufacturing processes can lead to supply constraints and increased investment.
Future Trends in Film Technology: PMMA and PVA
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) are advancing film technology with PMMA offering superior optical clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for high-performance displays and protective coatings. PVA's biodegradability and excellent barrier properties position it as a leading material in sustainable and flexible packaging films. Emerging trends include integrating PMMA with nanomaterials for enhanced durability and developing PVA-based films with improved mechanical strength for eco-friendly applications.
Infographic: Polymethyl methacrylate vs Polyvinyl alcohol for Film
 azmater.com
azmater.com