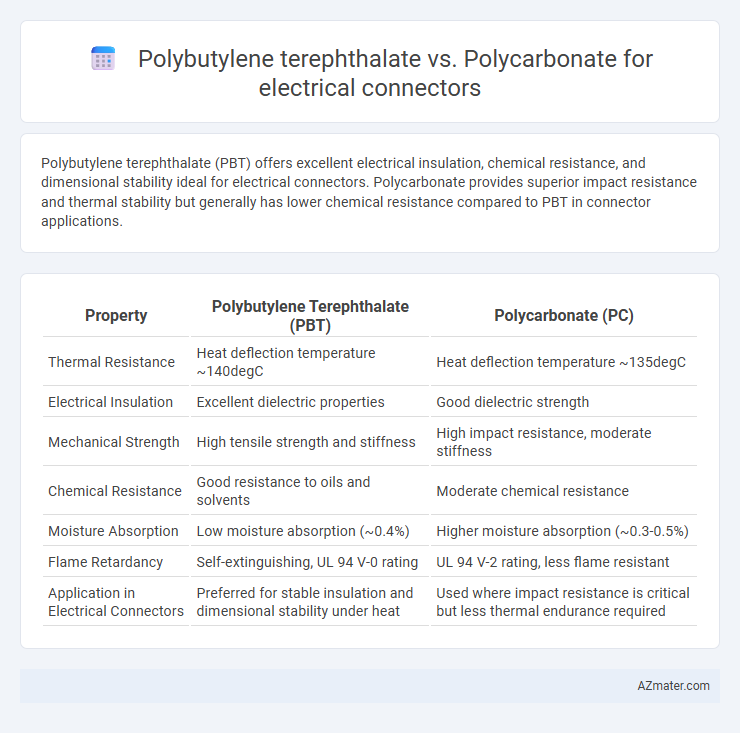
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability ideal for electrical connectors. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and thermal stability but generally has lower chemical resistance compared to PBT in connector applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) | Polycarbonate (PC) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Resistance | Heat deflection temperature ~140degC | Heat deflection temperature ~135degC |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric properties | Good dielectric strength |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength and stiffness | High impact resistance, moderate stiffness |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture absorption (~0.4%) | Higher moisture absorption (~0.3-0.5%) |
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishing, UL 94 V-0 rating | UL 94 V-2 rating, less flame resistant |
| Application in Electrical Connectors | Preferred for stable insulation and dimensional stability under heat | Used where impact resistance is critical but less thermal endurance required |
Introduction to Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) and Polycarbonate (PC)
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a thermoplastic polyester known for its excellent electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for electrical connector housings in automotive and industrial applications. Polycarbonate (PC) offers high impact resistance, toughness, and good electrical properties, frequently used when mechanical strength and transparency are required. Both polymers provide distinct advantages in electrical connector design, with PBT favored for thermal resistance and PC selected for durability under mechanical stress.
Material Composition and Properties
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is a semicrystalline thermoplastic polyester known for its high mechanical strength, excellent electrical insulation, and good resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for electrical connector housings. Polycarbonate (PC) is an amorphous, transparent thermoplastic with superior impact resistance, dimensional stability, and heat resistance, but it offers lower chemical resistance compared to PBT. The choice between PBT and PC for electrical connectors depends on performance requirements such as thermal stability, electrical insulation, and environmental resistance, with PBT excelling in chemical exposure and PC in impact toughness.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent mechanical strength and high resistance to wear and impact, making it ideal for electrical connectors requiring durability under thermal and mechanical stress. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior toughness and higher impact resistance but may exhibit lower dimensional stability compared to PBT in prolonged high-temperature environments. PBT's better resistance to chemicals and moisture combined with its stable mechanical properties ensures longer-lasting performance in demanding electrical connector applications.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent thermal stability with a melting point around 223degC, making it suitable for electrical connectors exposed to moderate heat. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior heat resistance, with a higher glass transition temperature near 147degC and better dimensional stability under thermal stress, ideal for connectors in environments requiring high impact strength and heat endurance. Selecting between PBT and PC depends on the operational temperature range and mechanical demands of the electrical connector application.
Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers superior electrical insulation properties with a high dielectric strength typically around 20-30 kV/mm, making it ideal for electrical connectors where high voltage resistance is critical. Polycarbonate (PC) also provides good insulation but generally exhibits lower dielectric strength and higher moisture absorption, which can reduce its electrical insulation performance over time. PBT's low dielectric constant and excellent dimensional stability under thermal stress enhance reliability and signal integrity in high-performance electrical connector applications.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Endurance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) exhibits superior chemical resistance against acids, alkalis, and solvents, making it highly suitable for electrical connectors exposed to harsh chemical environments. Polycarbonate (PC), while mechanically robust, tends to degrade in prolonged exposure to acids and some organic solvents, limiting its chemical resistance. In terms of environmental endurance, PBT withstands UV radiation and moisture better than PC, ensuring reliable performance in outdoor and high-humidity applications.
Processability and Molding Performance
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent processability with lower melting temperatures around 223degC, enabling faster cycle times and reduced thermal degradation during molding for electrical connectors. Polycarbonate (PC) requires higher molding temperatures near 270degC but provides superior impact resistance and dimensional stability, though it may exhibit increased shrinkage and warpage. PBT's superior flow properties and lower viscosity facilitate easier injection molding, making it a preferred choice for intricate connector geometries and high-volume production.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) typically offers a more cost-effective solution than polycarbonate (PC) for electrical connectors due to lower raw material and processing expenses. PBT's superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance reduce long-term maintenance and replacement costs, making it economically advantageous for large-scale manufacturing. Conversely, polycarbonate's higher upfront cost is often justified by its enhanced impact resistance and thermal performance in high-stress applications, but this increases the overall investment for connector production.
Typical Applications in Electrical Connectors
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) is widely used in electrical connectors due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, high dimensional stability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for automotive and consumer electronics connectors. Polycarbonate (PC) offers superior impact resistance and high heat deflection temperature, which suits connectors requiring enhanced mechanical strength and thermal endurance in industrial and telecommunications applications. Both materials provide reliable performance, but PBT is preferred for applications demanding long-term electrical insulation, while PC excels where mechanical toughness and thermal resistance are critical.
Choosing the Right Material: PBT vs PC for Electrical Connectors
Polybutylene terephthalate (PBT) offers excellent dimensional stability, chemical resistance, and high electrical insulation, making it ideal for electrical connectors that require durability in harsh environments. Polycarbonate (PC) provides superior impact resistance and thermal resistance but may be less resistant to certain chemicals compared to PBT. Selecting between PBT and PC depends on application-specific requirements such as mechanical stress, temperature range, and exposure to chemicals in electrical connector designs.
Infographic: Polybutylene terephthalate vs Polycarbonate for Electrical connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com