Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, higher elasticity, and excellent resistance to UV radiation compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which provides greater flame retardancy and chemical resistance for cable insulation. EVA is favored for lightweight, eco-friendly applications, while PVC remains preferred for cost-effective, durable insulation in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
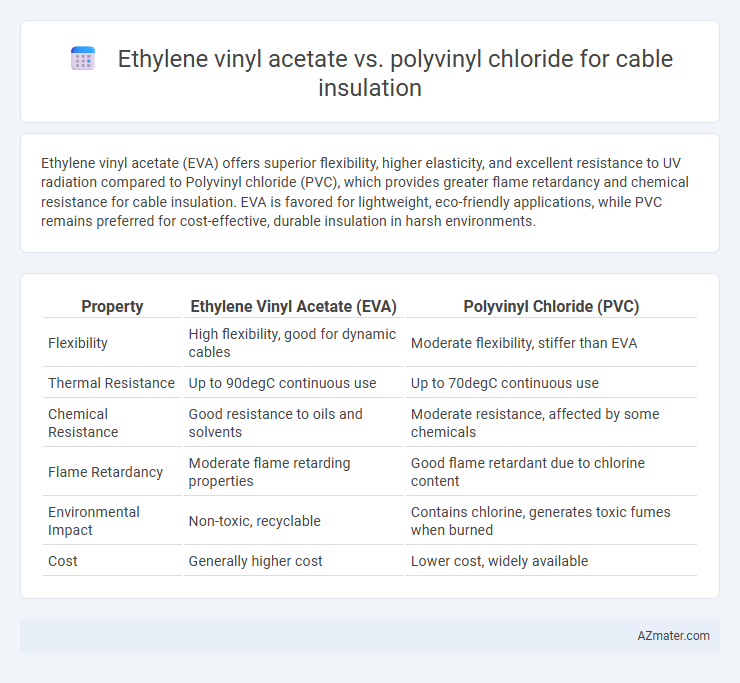
| Property | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | High flexibility, good for dynamic cables | Moderate flexibility, stiffer than EVA |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 90degC continuous use | Up to 70degC continuous use |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Moderate resistance, affected by some chemicals |
| Flame Retardancy | Moderate flame retarding properties | Good flame retardant due to chlorine content |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, recyclable | Contains chlorine, generates toxic fumes when burned |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Lower cost, widely available |
Introduction to Cable Insulation Materials
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are widely used materials for cable insulation due to their distinct properties. EVA offers flexibility, good thermal stability, and low-temperature performance, making it suitable for environments requiring elasticity and durability. PVC provides excellent flame retardancy, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness, commonly used in general-purpose electrical cable insulation applications.
What is Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA)?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) is a copolymer produced by combining ethylene and vinyl acetate, widely used in cable insulation for its flexibility, durability, and excellent electrical properties. EVA offers superior resistance to cracking, UV radiation, and low temperatures compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), making it ideal for outdoor and harsh environment applications. Its low density and chemical resistance contribute to better insulation performance and longer cable life in demanding electrical installations.
Understanding Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is widely used for cable insulation due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. PVC's inherent flame retardancy and cost-effectiveness make it ideal for power cables and telecommunications wiring, ensuring durability in various environmental conditions. Its ability to withstand temperature variations between -40degC to 105degC further enhances its performance in industrial and residential applications.
Key Properties of EVA in Cable Insulation
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers excellent flexibility, high dielectric strength, and superior resistance to cracking and cold temperatures, making it ideal for cable insulation applications. Its low-temperature flexibility and good elongation properties improve mechanical durability and reduce the risk of insulation failure under thermal and mechanical stress. EVA also provides enhanced moisture resistance and excellent electrical insulation performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), ensuring reliable and long-lasting cable protection.
Key Properties of PVC in Cable Insulation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers excellent flame retardancy, high mechanical strength, and good chemical resistance, making it a reliable choice for cable insulation. Its superior dielectric properties ensure stable electrical performance, while flexibility and durability under various environmental conditions contribute to long service life. PVC's cost-effectiveness combined with ease of processing supports widespread application in both residential and industrial cable installations.
Thermal Performance: EVA vs PVC
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior thermal performance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its higher melting point and better heat resistance, enabling cable insulation to withstand elevated temperatures without degradation. EVA's enhanced thermal stability allows for greater flexibility and durability in high-temperature environments, reducing the risk of insulation failure. In contrast, PVC tends to soften and lose mechanical integrity at lower temperatures, limiting its effectiveness in demanding thermal conditions.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and elongation properties compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), enhancing cable durability under mechanical stress. PVC provides higher tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring robust physical protection. The choice between EVA and PVC for cable insulation hinges on balancing EVA's elasticity with PVC's rigidity to meet specific mechanical strength demands.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior environmental benefits over polyvinyl chloride (PVC) due to its lower toxicity and better recyclability, reducing hazardous waste and the release of dioxins during disposal. EVA's non-chlorinated composition results in fewer harmful emissions during combustion, enhancing safety for both manufacturers and end-users. In contrast, PVC contains chlorine, which can generate toxic gases and persistent pollutants when burned, making EVA a safer and more eco-friendly choice for cable insulation.
Cost Effectiveness and Market Availability
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility and environmental resistance compared to polyvinyl chloride (PVC), with moderate cost benefits that make it a competitive option for cable insulation in specialized applications. PVC remains the dominant market choice due to its low cost, widespread availability, and excellent flame-retardant properties, driving large-scale adoption in residential and industrial cable manufacturing. Market availability of PVC is extensive, supported by robust supply chains and recycling infrastructure, whereas EVA supply is more limited, impacting large-volume cost-effectiveness despite its performance advantages.
Choosing the Right Material: EVA or PVC?
Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) offers superior flexibility, excellent low-temperature performance, and good resistance to UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor cable insulation. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) provides better fire resistance, chemical stability, and cost-effectiveness, often preferred for indoor and general-purpose cables. Selecting between EVA and PVC depends on environmental conditions, mechanical requirements, and regulatory compliance within specific cable applications.
Infographic: Ethylene vinyl acetate vs Polyvinyl chloride for Cable insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com