Tungsten spark plugs offer superior durability and high melting point, enhancing engine performance under extreme conditions. Iridium spark plugs provide better ignition efficiency and longer lifespan due to their fine electrode tip and corrosion resistance.
Table of Comparison
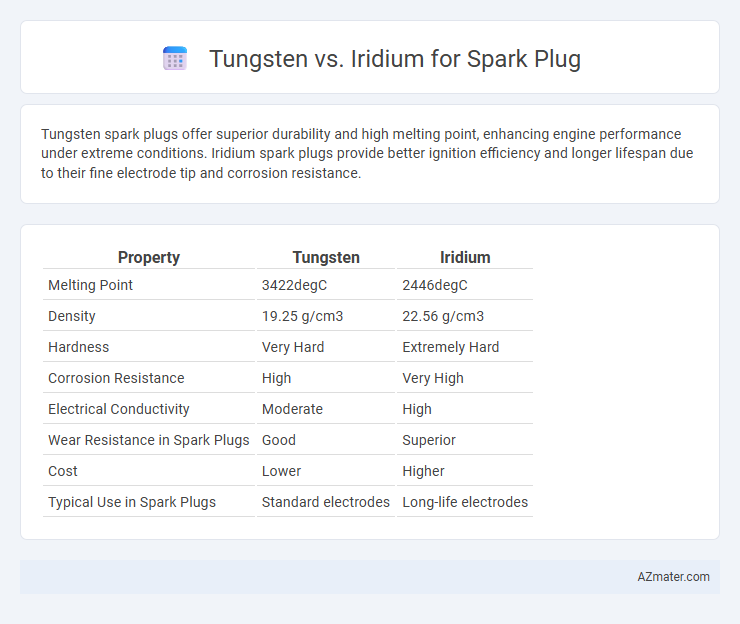
| Property | Tungsten | Iridium |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | 3422degC | 2446degC |
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 22.56 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | Very Hard | Extremely Hard |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Very High |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate | High |
| Wear Resistance in Spark Plugs | Good | Superior |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Use in Spark Plugs | Standard electrodes | Long-life electrodes |
Introduction to Spark Plug Materials
Spark plug materials significantly influence engine performance, with tungsten and iridium being prominent choices due to their high melting points and durability. Tungsten offers excellent wear resistance and thermal conductivity, enhancing spark efficiency in harsh conditions. Iridium, being more corrosion-resistant and having superior electrical conductivity, provides longer lifespan and consistent ignition even under extreme engine stress.
Chemical and Physical Properties: Tungsten vs Iridium
Tungsten and iridium both serve as critical materials for spark plug electrodes due to their exceptional chemical stability and physical robustness at high temperatures. Tungsten exhibits a high melting point of 3422degC and excellent wear resistance, enabling it to withstand extreme combustion conditions, while its density of 19.25 g/cm3 contributes to durability. Iridium surpasses tungsten with an even higher melting point of 2446degC and significantly greater corrosion resistance, along with a density of 22.56 g/cm3, making it ideal for producing long-lasting spark plugs with superior ignition performance.
Conductivity and Heat Resistance Comparison
Tungsten and iridium both exhibit excellent conductivity, but tungsten's electrical conductivity measures around 31.6 MS/m, slightly lower than iridium's approximately 21.2 MS/m, influencing spark efficiency. Tungsten offers superior heat resistance with a melting point of 3,422degC compared to iridium's 2,447degC, enabling it to withstand higher combustion chamber temperatures. This enhanced thermal durability makes tungsten spark plugs more resistant to wear and electrode erosion under extreme engine conditions.
Durability and Lifespan of Tungsten and Iridium Spark Plugs
Iridium spark plugs offer superior durability and lifespan compared to tungsten, with iridium's melting point of 2446degC providing enhanced wear resistance and extended service intervals often exceeding 60,000 miles. Tungsten spark plugs, while harder than traditional materials, have a lower melting point around 3422degC but tend to degrade faster due to lower oxidation resistance, resulting in shorter useful life typically between 20,000 to 30,000 miles. The fine-wire iridium electrode design reduces gap erosion, ensuring consistent spark performance and longer intervals between replacements, making iridium the preferred choice for high-performance and long-lasting ignition systems.
Performance Impact: Engine Efficiency and Power
Tungsten spark plugs provide superior durability and high melting points, enhancing engine efficiency by maintaining consistent electrode shape and minimizing wear under extreme combustion conditions. Iridium spark plugs, known for their fine tips and excellent conductivity, improve ignition performance, resulting in better combustion and increased power output. The choice between tungsten and iridium directly affects engine responsiveness and fuel economy by optimizing spark energy and durability in varying operational environments.
Cost Analysis: Price Differences and Value
Tungsten spark plugs generally cost less than iridium spark plugs due to the lower price of tungsten compared to iridium, a rare and precious metal. While iridium plugs have a higher upfront price, their superior durability and better performance can offer greater long-term value, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. Cost analysis reveals that tungsten plugs are economical for budget-focused consumers, but iridium spark plugs provide enhanced longevity and efficiency, justifying their premium price for high-performance or extended-use applications.
Compatibility with Modern and Classic Engines
Tungsten spark plugs provide excellent wear resistance and are highly compatible with modern engines that require precise ignition performance and durability under high RPM conditions. Iridium spark plugs, known for their superior ignition efficiency and longevity, are ideal for both modern and classic engines, offering enhanced combustion and better fuel economy across various engine types. Choosing between tungsten and iridium depends on engine specifications, with iridium often preferred for advanced electronic ignition systems and tungsten favored for robust, high-stress applications.
Maintenance, Fouling, and Replacement Frequency
Tungsten spark plugs offer high durability and resist fouling better than conventional plugs, but iridium spark plugs outperform tungsten in terms of longevity and fouling resistance due to their finer electrode tip and higher melting point. Iridium plugs require less frequent replacement, often lasting up to 100,000 miles, reducing maintenance needs compared to tungsten plugs, which typically need replacement between 30,000 and 50,000 miles. Both materials improve engine performance and efficiency, but iridium's enhanced resistance to wear and fouling makes it the preferred choice for longer service intervals.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tungsten spark plugs offer greater environmental benefits due to their high durability, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing waste. Iridium spark plugs, while also durable, require more energy-intensive mining processes that contribute to higher ecological footprints. Choosing tungsten spark plugs supports sustainability by lowering resource consumption and reducing metal extraction impacts.
Choosing the Right Spark Plug: Tungsten or Iridium?
Choosing the right spark plug depends on the electrode material, where tungsten offers excellent wear resistance and conductivity but iridium provides superior durability and a higher melting point, making it ideal for high-performance engines. Iridium spark plugs last longer and maintain a stable spark under extreme conditions, improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions compared to tungsten. For everyday driving, tungsten spark plugs are cost-effective and reliable, but iridium plugs deliver enhanced ignition performance and longevity for demanding applications.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Iridium for Spark Plug
 azmater.com
azmater.com