Tungsten bearings offer superior hardness and wear resistance compared to bronze, making them ideal for high-stress and high-temperature environments. Bronze bearings provide excellent corrosion resistance and lubrication properties, suitable for moderate loads and lower-cost applications.
Table of Comparison
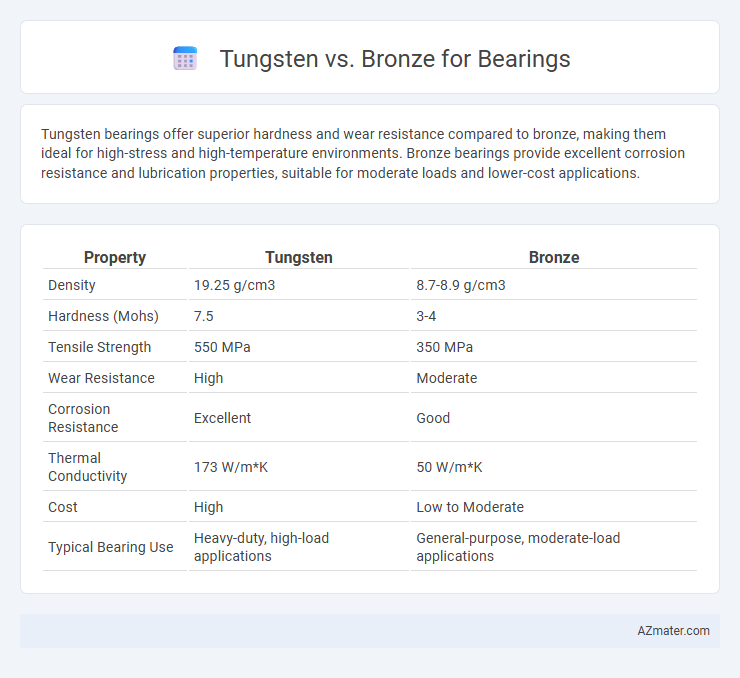
| Property | Tungsten | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 8.7-8.9 g/cm3 |
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7.5 | 3-4 |
| Tensile Strength | 550 MPa | 350 MPa |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Conductivity | 173 W/m*K | 50 W/m*K |
| Cost | High | Low to Moderate |
| Typical Bearing Use | Heavy-duty, high-load applications | General-purpose, moderate-load applications |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Bearing Material
Selecting the right bearing material is crucial for optimizing performance, durability, and cost-efficiency in mechanical applications. Tungsten bearings offer exceptional hardness, high melting points, and excellent wear resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature and high-load environments. Bronze bearings provide superior friction reduction, good corrosion resistance, and excellent machinability, which are advantageous for applications requiring smooth operation and moderate loads.
Overview of Tungsten Bearings
Tungsten bearings are renowned for their exceptional hardness and high resistance to wear, making them ideal for applications demanding long-lasting durability and minimal maintenance. Their high density contributes to excellent stability under heavy loads, while their resistance to corrosion ensures performance in harsh environments, including marine and chemical settings. Compared to bronze, tungsten bearings offer superior strength and lifespan, particularly in high-temperature and high-stress scenarios.
Overview of Bronze Bearings
Bronze bearings offer excellent corrosion resistance, high durability, and superior load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications with moderate speeds and pressures. Their alloy composition, typically a blend of copper, tin, and sometimes phosphorus or aluminum, provides excellent wear resistance and conformability against shaft materials. Bronze bearings perform well in lubricated environments, reducing friction and extending service life compared to other bearing materials like tungsten, which is harder but less forgiving under variable load conditions.
Mechanical Strength: Tungsten vs Bronze
Tungsten exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength than bronze, with tensile strengths often exceeding 1000 MPa compared to bronze's typical range of 200-500 MPa. This superior strength makes tungsten ideal for bearings subjected to extreme loads and high-stress conditions. Bronze offers better ductility and corrosion resistance but falls short in hardness and wear resistance when compared to tungsten-based bearings.
Wear Resistance and Durability Comparison
Tungsten bearings exhibit superior wear resistance due to their exceptional hardness and high melting point, making them ideal for high-stress, high-temperature applications. Bronze bearings offer good durability with excellent conformability and embedability, particularly suited for moderate loads and lower speed environments. Comparing both, tungsten outperforms bronze in wear longevity and resistance to deformation, ensuring longer service life under extreme conditions.
Lubrication Needs and Friction Properties
Tungsten bearings exhibit superior friction properties with low coefficients of friction, enabling smoother operation and reduced wear under high loads and speeds. Bronze bearings require consistent lubrication to maintain optimal performance, as their friction properties depend heavily on the lubrication film to prevent metal-to-metal contact and reduce heat buildup. Tungsten's inherent hardness and resistance to galling minimize lubrication needs, making it suitable for applications where maintenance intervals are critical.
Corrosion Resistance: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Tungsten exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making it an ideal material for bearings in harsh or chemically aggressive environments. Bronze, while offering good corrosion resistance in marine and freshwater applications, tends to degrade faster when exposed to acidic or alkaline conditions. The enhanced durability of tungsten bearings under corrosive stress results in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs.
Temperature Tolerance and Thermal Performance
Tungsten bearings exhibit superior temperature tolerance, maintaining structural integrity and performance at temperatures exceeding 1000degC, compared to bronze bearings which typically withstand up to 400degC before degrading. Tungsten's high thermal conductivity enables efficient heat dissipation, reducing the risk of overheating and prolonging bearing life in high-temperature applications. Bronze bearings, while more cost-effective, have lower thermal performance, making tungsten the preferred choice for extreme temperature environments and demanding industrial uses.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Tungsten bearings offer superior strength and corrosion resistance but come with a significantly higher cost due to complex extraction and processing, limiting widespread use. Bronze bearings provide a cost-effective alternative with good wear resistance and easier availability, making them ideal for general industrial applications. The abundant supply and lower manufacturing expenses of bronze contribute to its popularity in cost-sensitive projects.
Application Suitability: When to Use Tungsten or Bronze in Bearings
Tungsten bearings excel in high-load, high-temperature applications due to their exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery environments. Bronze bearings are preferred in low-speed, moderate-load, and abrasive conditions where good machinability and lubrication retention are critical, commonly used in agricultural equipment, marine applications, and general industrial machinery. Selecting tungsten or bronze bearings depends on operational parameters such as load capacity, temperature range, and environmental exposure to optimize performance and longevity.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Bronze for Bearing
 azmater.com
azmater.com