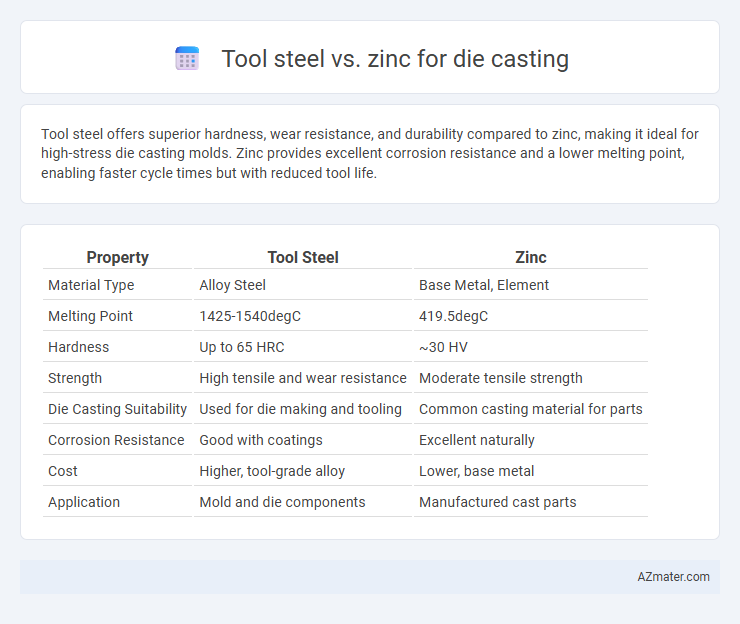
Tool steel offers superior hardness, wear resistance, and durability compared to zinc, making it ideal for high-stress die casting molds. Zinc provides excellent corrosion resistance and a lower melting point, enabling faster cycle times but with reduced tool life.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tool Steel | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Alloy Steel | Base Metal, Element |
| Melting Point | 1425-1540degC | 419.5degC |
| Hardness | Up to 65 HRC | ~30 HV |
| Strength | High tensile and wear resistance | Moderate tensile strength |
| Die Casting Suitability | Used for die making and tooling | Common casting material for parts |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good with coatings | Excellent naturally |
| Cost | Higher, tool-grade alloy | Lower, base metal |
| Application | Mold and die components | Manufactured cast parts |
Introduction to Die Casting Materials
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-volume die casting molds subjected to intense mechanical stress. Zinc excels in low melting temperature and excellent fluidity, allowing for quicker cycle times and precise detail reproduction in die-cast parts. The choice between tool steel and zinc depends on factors such as durability requirements, thermal conductivity, and production volume in die casting applications.
Overview of Tool Steel in Die Casting
Tool steel in die casting provides exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, making it ideal for producing durable and high-precision dies. Its alloy composition, including elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium, enhances strength and resistance to deformation under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions. This enables longer die life and consistent dimensional accuracy compared to materials like zinc, which soften rapidly at elevated temperatures.
Key Properties of Tool Steel
Tool steel is favored in die casting for its exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and high tensile strength, which ensure durability and precision under repeated thermal and mechanical stress. Its superior thermal conductivity and resistance to thermal fatigue reduce the risk of deformation and extend die life compared to zinc. Unlike zinc, tool steel maintains dimensional stability at elevated temperatures, making it ideal for complex and high-volume die casting applications.
Zinc as a Die Casting Material
Zinc offers excellent fluidity and low melting temperature, making it ideal for high-precision die casting with intricate details and thin walls. Its superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance contribute to durable, lightweight components, outperforming many tool steels in specific applications. Zinc's recyclability and cost-effectiveness further enhance its appeal in large-scale manufacturing of die-cast parts.
Key Properties of Zinc
Zinc for die casting offers excellent fluidity and low melting temperature around 419.5degC, enabling high precision and complex shapes with minimal thermal stress on molds. Its superior corrosion resistance and natural ability to withstand wear and abrasion enhance the durability of die-cast parts. Compared to tool steel, zinc provides faster cycle times and cost-effective production for small to medium-sized components requiring fine detail and surface finish.
Performance Comparison: Tool Steel vs Zinc
Tool steel offers superior wear resistance and thermal stability compared to zinc in die casting, enabling longer mold life and higher dimensional accuracy in high-volume production. Zinc provides excellent fluidity and faster cooling rates, resulting in shorter cycle times and fine surface finishes for intricate designs. The choice between tool steel and zinc depends on balancing durability requirements with production speed and detail precision.
Cost Analysis: Tool Steel vs Zinc
Tool steel incurs higher initial costs due to material price and machining complexity compared to zinc, which offers lower upfront tooling expenses. Zinc's shorter cycle times and ease of casting reduce overall production costs, making it more economical for high-volume runs. Despite higher durability and longer mold life in tool steel, zinc provides better cost efficiency for projects prioritizing fast turnaround and lower initial investment.
Application Suitability
Tool steel offers superior wear resistance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-volume die casting molds requiring long service life and dimensional precision. Zinc, with its low melting point and excellent fluidity, suits die casting applications demanding intricate shapes and faster production cycles but has lower strength and durability compared to tool steel. Selecting between tool steel and zinc depends on factors such as casting complexity, production volume, and expected mold lifespan.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Tool steel offers superior durability compared to zinc in die casting due to its high hardness and resistance to wear, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. Zinc, though easier to cast and less expensive, tends to wear faster and requires more frequent maintenance, especially under high-stress conditions. Maintenance of tool steel dies involves periodic heat treatment and polishing to extend lifespan, while zinc dies demand careful monitoring to prevent corrosion and deformation.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Die Casting Needs
Tool steel offers superior strength, hardness, and wear resistance compared to zinc, making it ideal for high-volume, high-precision die casting applications requiring durability and tight dimensional tolerances. Zinc excels in rapid heat dissipation and corrosion resistance, enabling shorter cycle times and cost-effective production for intricate, thin-walled components. Selecting the right material depends on production volume, component complexity, mechanical properties, and cost considerations to optimize die life and casting quality.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Zinc for Die casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com