Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance and high thermal stability, making it suitable for capacitor dielectrics in harsh environments. Tantalum provides superior capacitance per volume and reliable performance in miniaturized capacitors, favored in high-performance electronic circuits.
Table of Comparison
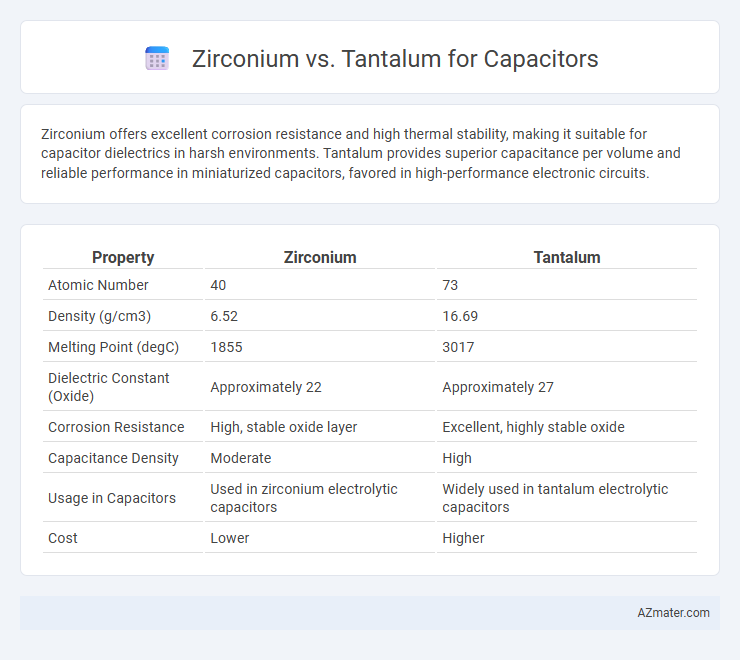
| Property | Zirconium | Tantalum |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 40 | 73 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 6.52 | 16.69 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 1855 | 3017 |
| Dielectric Constant (Oxide) | Approximately 22 | Approximately 27 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, stable oxide layer | Excellent, highly stable oxide |
| Capacitance Density | Moderate | High |
| Usage in Capacitors | Used in zirconium electrolytic capacitors | Widely used in tantalum electrolytic capacitors |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Zirconium and Tantalum Capacitors
Zirconium and tantalum capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for their high capacitance and reliability. Tantalum capacitors, known for their superior volumetric efficiency and stable electrical performance, are often preferred in miniaturized devices. Zirconium capacitors offer excellent high-frequency characteristics and better thermal stability, making them suitable for aerospace and military applications.
Material Properties: Zirconium vs Tantalum
Zirconium and tantalum exhibit distinct material properties impacting capacitor performance; zirconium offers a high dielectric constant and excellent corrosion resistance, while tantalum provides superior stability and higher capacitance per volume. Zirconium oxides enable capacitors with strong thermal stability but lower conductivity compared to tantalum oxide. Tantalum capacitors are preferred for high-reliability applications due to their robust electrochemical characteristics and longer lifecycle under stress.
Capacitance and Performance Comparison
Zirconium capacitors exhibit higher dielectric constant values, enabling greater capacitance density compared to tantalum capacitors, which typically provide lower capacitance per volume. Tantalum capacitors offer superior reliability and stability under high temperature and voltage stress, making them ideal for critical performance applications. Performance-wise, zirconium-based capacitors may suffer from higher leakage currents and lower endurance, while tantalum capacitors deliver lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) and improved long-term capacitance retention.
Electrical Conductivity and Efficiency
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior electrical conductivity compared to zirconium-based capacitors, resulting in lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and improved efficiency in high-frequency applications. Zirconium capacitors may offer robust thermal stability but generally have higher internal resistance, reducing overall performance in low-loss circuits. The conductivity advantage of tantalum enhances energy density and charge-discharge cycles, making it more efficient for demanding electronic components.
Voltage Ratings and Stability
Zirconium-based capacitors typically offer moderate voltage ratings around 25-50V with excellent thermal stability, making them suitable for applications requiring consistent performance under temperature fluctuations. Tantalum capacitors provide higher voltage ratings, often ranging from 10V up to 125V or more, and exhibit superior stability with low ESR and high reliability in demanding environments. The choice between zirconium and tantalum capacitors depends on the required voltage rating and stability, with tantalum favored for higher voltage and long-term stability, while zirconium is preferred for moderate voltage and robust thermal performance.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors are renowned for their exceptional reliability and long lifespan, often exceeding 10,000 hours of operation at rated conditions due to their stable oxide layer and high melting point. Zirconium capacitors, while less common, offer good performance but generally have lower reliability and shorter lifespan compared to tantalum because of less stable oxide formation and susceptibility to failure under stress. In high-reliability applications, tantalum capacitors are preferred for their superior endurance and consistent capacitance retention over time.
Cost Analysis: Zirconium vs Tantalum Capacitors
Zirconium capacitors generally offer a more cost-effective solution than tantalum capacitors due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes. Tantalum capacitors tend to be more expensive because of the rarity and high demand of tantalum metal, impacting supply chain costs significantly. In applications requiring high capacitance and reliability, the higher price of tantalum capacitors is often justified, though zirconium capacitors provide a budget-friendly alternative with acceptable performance in less critical environments.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Zirconium-based capacitors excel in high-frequency circuits due to their superior dielectric properties and thermal stability, making them ideal for telecommunications and RF applications. Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and reliable performance in low-voltage, energy-dense environments, which is critical for portable electronics and medical devices. Both materials support miniaturization trends, but tantalum's resilience to electrical stress enhances longevity in demanding consumer electronics and aerospace systems.
Environmental and Sourcing Considerations
Zirconium and tantalum differ significantly in environmental and sourcing impacts when used in capacitors. Tantalum mining often raises concerns due to its association with conflict minerals and environmental degradation in regions like Central Africa, leading to complex ethical and supply chain challenges. Zirconium, derived mainly from abundant mineral sands, presents fewer sourcing conflicts and lower ecological risks, making it a more sustainable and environmentally friendly choice for capacitor manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: Zirconium or Tantalum?
Zirconium capacitors offer excellent corrosion resistance and stable capacitance under high-frequency conditions, making them suitable for applications requiring long-term reliability. Tantalum capacitors provide higher volumetric efficiency and superior capacitance per volume but are more sensitive to voltage spikes and require careful derating. Choosing between zirconium and tantalum capacitors depends on the balance between performance stability, size constraints, and voltage tolerance specific to the electronic circuit demands.
Infographic: Zirconium vs Tantalum for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com