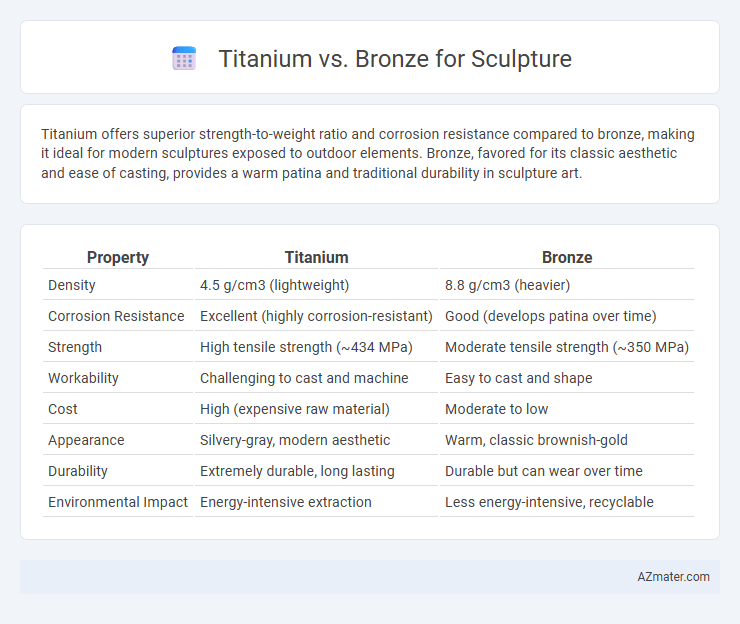
Titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making it ideal for modern sculptures exposed to outdoor elements. Bronze, favored for its classic aesthetic and ease of casting, provides a warm patina and traditional durability in sculpture art.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3 (lightweight) | 8.8 g/cm3 (heavier) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (highly corrosion-resistant) | Good (develops patina over time) |
| Strength | High tensile strength (~434 MPa) | Moderate tensile strength (~350 MPa) |
| Workability | Challenging to cast and machine | Easy to cast and shape |
| Cost | High (expensive raw material) | Moderate to low |
| Appearance | Silvery-gray, modern aesthetic | Warm, classic brownish-gold |
| Durability | Extremely durable, long lasting | Durable but can wear over time |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-intensive extraction | Less energy-intensive, recyclable |
Introduction to Titanium and Bronze in Sculpture
Titanium offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and a lightweight profile, making it ideal for large-scale outdoor sculptures that require durability with minimal maintenance. Bronze, a traditional alloy of copper and tin, has been favored for centuries due to its excellent casting properties, warm patina, and ability to capture fine details in sculptural works. Sculptors choose titanium for modern, innovative projects and bronze for classic, timeless aesthetics, reflecting distinct material qualities and artistic intentions.
Historical Use of Bronze vs Titanium
Bronze has been a cornerstone material in sculpture since ancient civilizations, prized for its durability, malleability, and rich patina that enhances artistic detail over time. Titanium, a modern alternative, offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance but lacks the extensive historical pedigree bronze holds in classical and Renaissance artworks. The enduring legacy of bronze sculptures, from the Greeks to the Renaissance masters, underscores its historical and cultural significance compared to the relatively recent adoption of titanium in contemporary sculptural practices.
Physical Properties Compared
Titanium exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior corrosion resistance compared to bronze, making it ideal for large outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh environments. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, offers excellent castability and traditional patina development but is denser and more prone to oxidation. While titanium's high melting point and tensile strength provide greater durability, bronze remains favored for its historic aesthetic qualities and ease of detailed molding.
Aesthetic Qualities and Surface Finish
Titanium offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a naturally grayish-silver hue that resists corrosion and maintains a matte to slightly glossy surface finish without patination. Bronze, renowned for its classic warmth and rich golden-brown tones, develops a unique patina over time, enhancing its depth and historical appeal through oxidation. Surface finishes on bronze can range from highly polished to textured, often used to emphasize intricate details, while titanium's surface is typically smoother, emphasizing contemporary minimalism in sculptures.
Durability and Longevity
Titanium offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh weather conditions. Bronze, a traditional material, ages gracefully by developing a natural patina that protects against further corrosion while maintaining structural integrity. Both metals provide longevity, but titanium's superior strength-to-weight ratio ensures minimal maintenance and extended lifespan in demanding environments.
Workability and Fabrication Techniques
Titanium offers superior corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio compared to bronze, making it ideal for complex, lightweight sculptural designs. Despite its hardness demanding advanced fabrication techniques like CNC machining, welding with inert gas shielding, and plasma cutting, titanium allows finer detailing and greater structural integrity. Bronze, being softer and more malleable, supports traditional methods such as casting, chasing, and welding, enabling artists to achieve intricate textures and patinas with relatively simpler tools.
Cost Analysis: Titanium vs Bronze
Titanium sculptures typically cost 20-30% more than bronze due to higher raw material prices and specialized fabrication techniques. Bronze remains more budget-friendly, with established casting methods contributing to lower production expenses and shorter lead times. Maintenance costs are lower for titanium, as its corrosion resistance reduces long-term conservation expenses compared to bronze's periodic patina treatment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Titanium offers a significantly lower environmental impact than bronze due to its corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Bronze production involves intensive mining and smelting processes that emit high levels of greenhouse gases and contribute to resource depletion. Choosing titanium supports sustainability by minimizing waste and energy consumption throughout the sculpture's lifecycle.
Popular Examples in Modern Sculptures
Titanium and bronze are prominent materials in modern sculpture, with titanium favored for its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and ability to produce sharp, intricate details. Notable examples include Anish Kapoor's "Cloud Gate" in Chicago, which uses highly polished stainless steel with titanium alloys to create a reflective surface. In contrast, bronze remains a classic choice, showcased in works like Henry Moore's abstract forms, valued for its durability and traditional patina.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sculpture
Titanium offers exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh environments. Bronze, with its classic aesthetic, excellent durability, and ease of casting, remains a popular choice for detailed and traditional sculpture work. Choosing between titanium and bronze depends on factors like environmental exposure, desired finish, weight considerations, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Titanium vs Bronze for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com