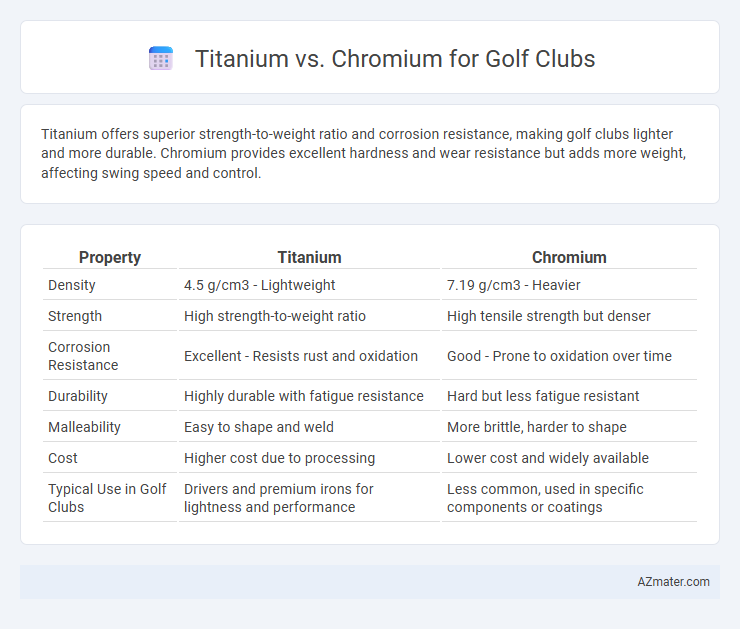
Titanium offers superior strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making golf clubs lighter and more durable. Chromium provides excellent hardness and wear resistance but adds more weight, affecting swing speed and control.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Chromium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cm3 - Lightweight | 7.19 g/cm3 - Heavier |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | High tensile strength but denser |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent - Resists rust and oxidation | Good - Prone to oxidation over time |
| Durability | Highly durable with fatigue resistance | Hard but less fatigue resistant |
| Malleability | Easy to shape and weld | More brittle, harder to shape |
| Cost | Higher cost due to processing | Lower cost and widely available |
| Typical Use in Golf Clubs | Drivers and premium irons for lightness and performance | Less common, used in specific components or coatings |
Introduction to Titanium and Chromium in Golf Clubs
Titanium and chromium are key materials used in golf club manufacturing due to their distinct properties. Titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for larger clubheads that improve forgiveness and distance. Chromium provides exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, often utilized in club shafts and irons to enhance longevity and performance.
Material Properties: Titanium vs Chromium
Titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, making golf club heads lighter and more durable compared to chromium. Chromium provides excellent hardness and wear resistance but is significantly heavier, which can impact swing speed and control. The superior fatigue resistance of titanium enhances the longevity and performance consistency of golf clubs under repetitive stress.
Weight Differences and Impact on Swing Speed
Titanium golf clubs are significantly lighter than chromium counterparts, contributing to increased swing speed and greater clubhead acceleration. The reduced weight of titanium allows for enhanced maneuverability and energy transfer, which can improve distance and control during swings. Chromium clubs, being heavier, may offer more stability but typically result in slower swing speeds, potentially limiting driving distance.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Titanium golf clubs offer superior durability due to their high strength-to-weight ratio, providing resistance to bending and corrosion over extended use. Chromium, often used as a coating on steel clubs, enhances surface hardness and corrosion resistance but lacks the overall resilience titanium alloys deliver. Golfers seeking long-lasting performance typically prefer titanium for its ability to maintain structural integrity and consistent playability across numerous rounds.
Performance Benefits on the Golf Course
Titanium golf clubs offer superior strength-to-weight ratio, providing enhanced swing speed and greater distance on drives. Chromium, while durable and corrosion-resistant, typically results in heavier clubheads that may reduce swing speed but improve control and accuracy. Golfers seeking maximum power benefit from titanium's lightweight properties, whereas those prioritizing precision might prefer chromium's stability.
Cost Analysis: Titanium vs Chromium Clubs
Titanium golf clubs typically cost significantly more than chromium clubs due to the higher material price and advanced manufacturing processes required for titanium. Chromium clubs, often more affordable, offer durability but lack the lightweight strength and flexibility of titanium, making them a budget-friendly choice without premium performance features. The investment in titanium clubs is justified by enhanced playability and long-term performance benefits despite the initial higher cost.
Feel and Feedback for Golfers
Titanium golf club heads offer a lightweight design that enhances swing speed and provides a solid, responsive feel, enabling golfers to better sense impact and ball flight. Chromium, often used in steel alloys, delivers a heavier, more stable clubhead with increased feedback, allowing skilled players to detect subtle variations in shot quality and trajectory. The choice between titanium and chromium directly impacts a golfer's tactile experience, influencing control and overall performance on the course.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance Needs
Titanium outperforms chromium in corrosion resistance due to its natural oxide layer that protects against rust and environmental damage, making it ideal for golf clubs used in varied weather conditions. Chromium, often used as a plating material, offers moderate corrosion resistance but may require more frequent maintenance to prevent wear and pitting over time. Golf clubs made from titanium demand less maintenance and retain their performance longer, providing durability and reliability with minimal upkeep.
Popular Golf Club Brands Using Titanium or Chromium
Titleist and Callaway lead in utilizing titanium for golf club heads due to its lightweight strength, enhancing swing speed and distance. Mizuno and TaylorMade incorporate chromium in their club designs to improve durability and corrosion resistance, favored for irons and wedges. The choice between titanium and chromium in popular golf clubs reflects a balance between performance benefits and material resilience tailored by manufacturers.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Playing Style
Titanium golf clubs offer superior strength-to-weight ratio, providing enhanced swing speed and distance for players seeking power and forgiveness. Chromium, often used in stainless steel clubs, delivers durability and a solid feel preferred by those prioritizing control and precision in their shots. Selecting between titanium and chromium depends on your playing style--opt for titanium for lightweight performance and increased distance, or chromium for robust feedback and accuracy.
Infographic: Titanium vs Chromium for Golf Club
 azmater.com
azmater.com