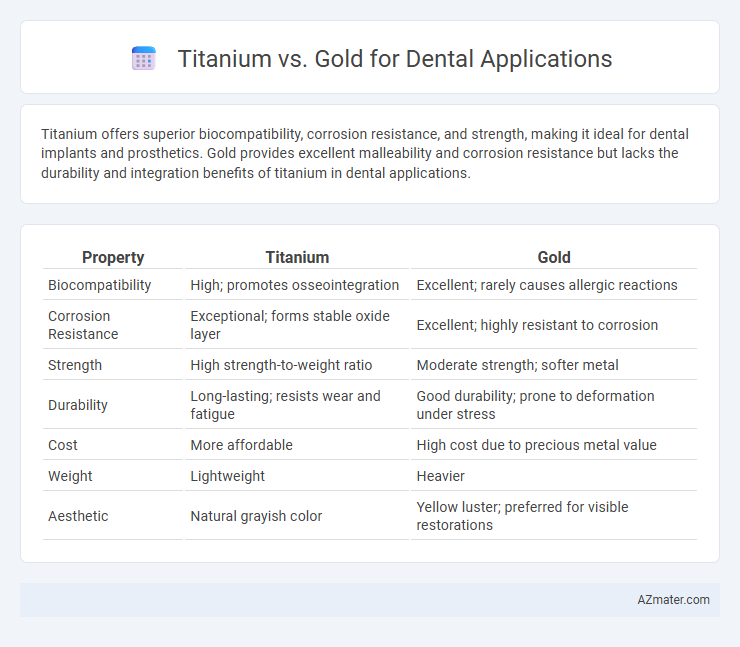
Titanium offers superior biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength, making it ideal for dental implants and prosthetics. Gold provides excellent malleability and corrosion resistance but lacks the durability and integration benefits of titanium in dental applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Titanium | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility | High; promotes osseointegration | Excellent; rarely causes allergic reactions |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional; forms stable oxide layer | Excellent; highly resistant to corrosion |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Moderate strength; softer metal |
| Durability | Long-lasting; resists wear and fatigue | Good durability; prone to deformation under stress |
| Cost | More affordable | High cost due to precious metal value |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavier |
| Aesthetic | Natural grayish color | Yellow luster; preferred for visible restorations |
Introduction to Titanium and Gold in Dentistry
Titanium is highly favored in dental applications due to its exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength, making it ideal for implants and prosthetics. Gold's longstanding use in dentistry is attributed to its durability, resistance to tarnish, and compatibility with oral tissues, often utilized in crowns, bridges, and inlays. Both metals offer unique benefits, with titanium excelling in osseointegration and gold providing superior malleability for precise dental restorations.
Material Properties of Titanium and Gold
Titanium exhibits exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and a high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for dental implants that require durability and osseointegration. Gold offers excellent malleability, corrosion resistance, and non-reactivity, ensuring precise fit and longevity in dental crowns and bridges. While titanium's lightweight and strength enable robust implant frameworks, gold's softness allows for detailed customization and superior wear resistance in restorative dentistry.
Biocompatibility: Titanium vs Gold
Titanium exhibits exceptional biocompatibility due to its ability to form a stable oxide layer that prevents corrosion and promotes osseointegration with bone tissue, making it ideal for dental implants. Gold, known for its inert properties, offers excellent compatibility with soft tissues and minimal allergic reactions but lacks the osteoconductive benefits seen with titanium. The choice between titanium and gold depends on the specific dental application, balancing titanium's superior integration with hard tissues and gold's favorable interaction with surrounding oral mucosa.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Titanium exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, making it highly durable for dental implants under long-term oral conditions. Gold, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, offers lower tensile strength and is more prone to deformation under heavy masticatory forces compared to titanium. Titanium's superior mechanical properties and ability to osseointegrate ensure greater longevity and stability in dental applications relative to gold.
Corrosion Resistance in Oral Environments
Titanium exhibits superior corrosion resistance in oral environments compared to gold due to the formation of a stable, protective oxide layer (TiO2) that prevents metal ion release and degradation. Gold is inherently resistant to corrosion but can suffer from surface wear and galvanic interactions when used in conjunction with other metals. The biocompatibility and passivation properties of titanium make it the preferred choice for dental implants and restorations exposed to fluctuating pH and saliva composition.
Aesthetics and Visual Appeal
Titanium offers exceptional strength and biocompatibility but has a metallic gray color that can be visually unappealing in dental restorations. Gold, although softer and less durable than titanium, provides a warm, natural luster that enhances the aesthetic appeal of crowns and bridges. For patients prioritizing aesthetic and visual appeal, gold remains a preferred material due to its ability to blend seamlessly with natural teeth.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Titanium offers a cost-effective solution for dental implants due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses compared to gold, making it more accessible for a broader patient base. Gold, while biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, generally incurs higher costs driven by fluctuating precious metal prices and complex alloying processes. The affordability of titanium supports widespread use in dental restoration, balancing durability and budget constraints effectively.
Allergic Reactions and Safety Considerations
Titanium is widely favored in dental applications due to its exceptional biocompatibility and minimal allergic reactions, making it a safe choice for implants and prosthetics. Gold, while also biocompatible, carries a higher risk of allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to metal alloys, especially those containing nickel or other trace metals. Safety considerations favor titanium for long-term dental use, as it exhibits superior corrosion resistance and osseointegration, reducing complications related to hypersensitivity and implant failure.
Clinical Applications: Implants vs Restorations
Titanium is predominantly used for dental implants due to its exceptional biocompatibility, osseointegration capabilities, and mechanical strength, ensuring long-term stability and support for prosthetic teeth. Gold, while less common in implants, excels in dental restorations such as crowns and bridges because of its corrosion resistance, malleability, and superior wear properties, providing precise fit and durability. Clinical outcomes indicate titanium implants offer predictable bone integration, whereas gold restorations optimize occlusal function and aesthetic longevity in dental rehabilitation.
Summary and Recommendations
Titanium offers exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength, making it the preferred choice for dental implants and prosthetics. Gold, while biocompatible and malleable, is primarily used for crowns and inlays due to its aesthetic appeal and ease of customization but lacks the structural robustness required for implants. For long-term dental restorations, titanium is recommended for implants and frameworks, whereas gold remains suitable for high-quality restorative work focused on durability and appearance.
Infographic: Titanium vs Gold for Dental Application
 azmater.com
azmater.com