Tool steel offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heat-resistant parts exposed to mechanical stress. Nickel excels in high-temperature corrosion resistance and thermal stability, suitable for components in extreme heat environments.
Table of Comparison
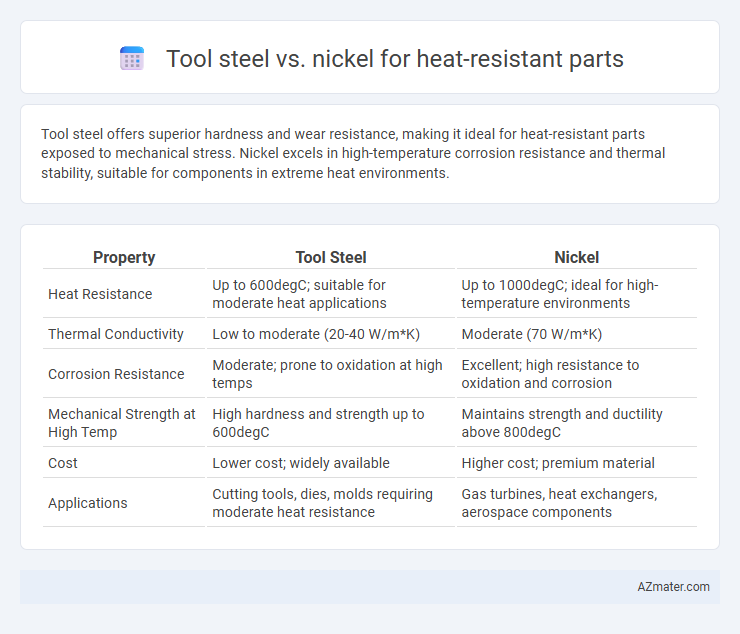
| Property | Tool Steel | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 600degC; suitable for moderate heat applications | Up to 1000degC; ideal for high-temperature environments |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low to moderate (20-40 W/m*K) | Moderate (70 W/m*K) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to oxidation at high temps | Excellent; high resistance to oxidation and corrosion |
| Mechanical Strength at High Temp | High hardness and strength up to 600degC | Maintains strength and ductility above 800degC |
| Cost | Lower cost; widely available | Higher cost; premium material |
| Applications | Cutting tools, dies, molds requiring moderate heat resistance | Gas turbines, heat exchangers, aerospace components |
Introduction to Heat-Resistant Materials
Heat-resistant materials such as tool steel and nickel alloys are essential in applications requiring high thermal stability and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. Tool steel offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for tooling and molds exposed to moderate heat, while nickel alloys provide superior corrosion resistance and maintain strength at extreme temperatures above 600degC. Selecting between tool steel and nickel depends on the specific operational temperature, mechanical load, and environmental conditions in heat-resistant applications.
Overview of Tool Steel
Tool steel is specially formulated for high hardness, wear resistance, and strength at elevated temperatures, making it a prime choice for heat-resistant parts exposed to mechanical stresses. Its alloying elements such as tungsten, molybdenum, and chromium enhance thermal stability and durability under cyclic heating conditions. Unlike nickel, tool steel offers superior machinability and hardness retention, which are critical for components requiring precision and long service life in heat-intensive applications.
Overview of Nickel Alloys
Nickel alloys exhibit exceptional heat resistance and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature applications such as heat-resistant parts. These alloys maintain strength and structural integrity at elevated temperatures, outperforming many tool steels in thermal stability and oxidation resistance. Common nickel alloys like Inconel and Hastelloy are widely used in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing industries where durability under extreme heat is critical.
Key Properties: Tool Steel vs Nickel
Tool steel offers exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature strength, making it ideal for cutting and forming heat-resistant parts. Nickel exhibits superior corrosion resistance, oxidation stability, and maintains toughness at elevated temperatures, suited for environments with extreme thermal cycling. Selecting between tool steel and nickel depends on application-specific requirements such as thermal conductivity, mechanical stress, and exposure to corrosive atmospheres.
Heat Resistance Comparison
Tool steel generally offers excellent heat resistance, withstanding temperatures up to 600degC depending on the grade, due to its high carbon and alloy content that maintains hardness at elevated temperatures. Nickel alloys, however, excel in extreme heat resistance, maintaining structural integrity and corrosion resistance at temperatures exceeding 900degC, making them ideal for high-temperature environments. The choice between tool steel and nickel for heat-resistant parts depends on the specific temperature requirements and mechanical stresses of the application.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Tool steel exhibits superior wear resistance and mechanical strength at elevated temperatures up to 600degC, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under thermal stress. Nickel alloys outperform tool steel in extreme high-temperature environments exceeding 700degC due to their excellent oxidation resistance and thermal stability. The choice between tool steel and nickel primarily depends on the specific temperature range and corrosion resistance required for the heat-resistant part.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Tool steel offers excellent wear resistance and mechanical strength but generally exhibits lower corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to nickel alloys. Nickel-based materials provide superior corrosion resistance in harsh chemical environments and maintain oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures, making them ideal for heat-resistant parts exposed to aggressive conditions. Selecting nickel alloys ensures enhanced durability and longevity in applications requiring sustained exposure to oxidizing atmospheres and corrosive media.
Applications in Heat-Resistant Parts
Tool steel is widely used in heat-resistant parts due to its excellent hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain strength at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for cutting tools, molds, and dies in high-temperature environments. Nickel alloys outperform tool steels in extreme heat resistance and corrosion resistance, commonly applied in aerospace engine components, gas turbines, and chemical processing equipment where stability at temperatures above 1000degF (540degC) is critical. The choice between tool steel and nickel depends on the specific thermal, mechanical, and environmental requirements of the heat-resistant application.
Cost and Availability
Tool steel offers a cost-effective solution for heat-resistant parts due to its widespread availability and lower raw material prices compared to nickel alloys. Nickel, while providing superior heat resistance and corrosion resistance, often incurs higher costs and faces supply chain constraints, impacting its availability. Choosing between tool steel and nickel requires balancing budget limitations with performance requirements in high-temperature environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Heat-Resistant Parts
Tool steel offers excellent wear resistance and hardness at high temperatures, making it suitable for heat-resistant parts subjected to mechanical stress and abrasion. Nickel alloys excel in corrosion resistance and maintain strength at extreme temperatures, ideal for environments with oxidative or chemical exposure. Selecting the right material depends on operating temperature, mechanical load, and environmental conditions to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Infographic: Tool steel vs Nickel for Heat-resistant part
 azmater.com
azmater.com