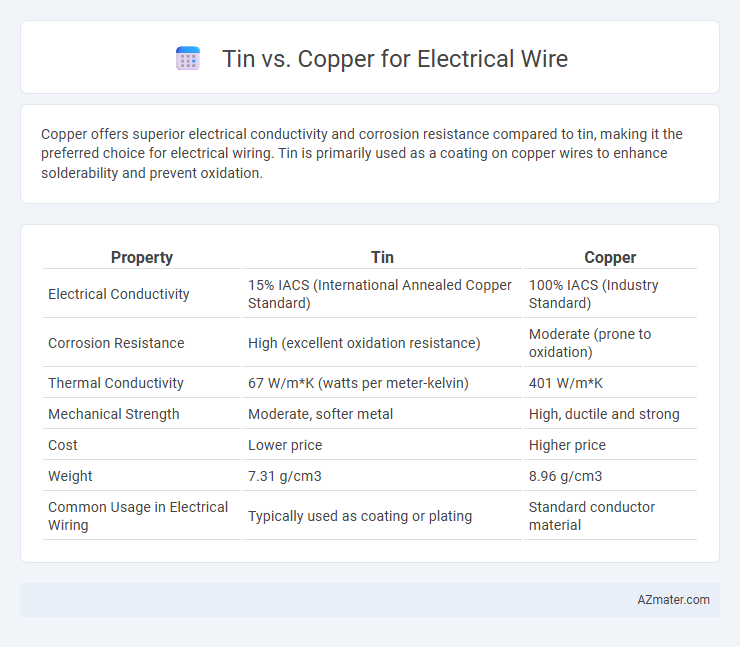
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to tin, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring. Tin is primarily used as a coating on copper wires to enhance solderability and prevent oxidation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tin | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 15% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) | 100% IACS (Industry Standard) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (excellent oxidation resistance) | Moderate (prone to oxidation) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 67 W/m*K (watts per meter-kelvin) | 401 W/m*K |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate, softer metal | High, ductile and strong |
| Cost | Lower price | Higher price |
| Weight | 7.31 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Common Usage in Electrical Wiring | Typically used as coating or plating | Standard conductor material |
Overview: Tin vs Copper in Electrical Wiring
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity, making it the standard choice for wiring in residential and industrial applications. Tin, often used as a coating for copper wires, enhances corrosion resistance without significantly affecting conductivity. The combination of copper's high conductivity and tin's protective qualities ensures durable, efficient electrical wiring solutions.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity at approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to minimal resistance and efficient current flow. Tin, with a much lower conductivity around 9.17 x 10^6 S/m, is often used as a coating on copper wires to prevent oxidation rather than as a primary conductor. The notable difference in conductivity directly impacts energy loss and heat generation, positioning copper as the optimal material for high-performance electrical applications.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Tin-coated copper wires offer superior corrosion resistance compared to bare copper, preventing oxidation and extending the wire's lifespan in harsh environments. Copper's natural conductivity is slightly reduced by tin plating but significantly enhances protection against moisture, salt, and other corrosive agents. This combination ensures tin-coated copper wires maintain electrical performance and durability over time, making them ideal for marine and industrial applications where longevity is critical.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Tin-coated copper wires offer enhanced corrosion resistance but come at a higher initial cost compared to pure copper wires, which remain more affordable due to widespread production and demand. Copper's abundant availability and superior electrical conductivity make it the preferred choice for most electrical wiring applications despite price fluctuations influenced by global mining and supply chain factors. The total cost of ownership favors copper when considering its longevity and efficiency, whereas tin-coated options serve niche markets requiring extra durability in harsh environments.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Copper offers superior mechanical strength and excellent flexibility, making it highly durable for electrical wiring in demanding environments. Tin-plated copper wires provide added corrosion resistance but slightly reduce the overall tensile strength compared to pure copper. Flexibility differences are minimal; however, copper remains the preferred choice for applications requiring a balance of strength and pliability.
Solderability and Ease of Installation
Tin-plated copper wires offer superior solderability due to the tin coating preventing copper oxidation, resulting in smoother solder joints and improved electrical conductivity. Pure copper wires, while highly conductive, are prone to surface oxidation that complicates soldering and requires additional flux or cleaning. Tin plating also enhances ease of installation by reducing the risk of brittle joints and ensuring consistent mechanical bonding in electrical connections.
Weight and Suitability for Applications
Tin-coated copper wire offers a balance between weight and corrosion resistance, making it slightly heavier than pure copper wire due to the tin layer but more suitable for marine and industrial applications exposed to moisture. Pure copper wire is lighter and exhibits superior electrical conductivity, ideal for most residential and commercial wiring where weight savings and performance are critical. Considering weight and application, tin-coated copper excels in durability and corrosion protection, while pure copper optimizes electrical efficiency and lightweight design.
Safety and Thermal Performance
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity and thermal performance compared to tin, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and reducing the risk of overheating in electrical wires. Tin coatings on copper wires primarily enhance corrosion resistance without significantly impacting thermal stability or safety under normal operating conditions. Choosing pure copper wires improves overall safety by minimizing electrical resistance and maintaining stable thermal characteristics during high current loads.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Tin-coated copper wire offers enhanced corrosion resistance, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing electronic waste in comparison to pure copper wire. Copper is highly recyclable with a recovery rate exceeding 90%, making it environmentally advantageous due to lower energy consumption in recycling processes. The tin coating, while beneficial for durability, requires specialized recycling methods to separate metals efficiently, impacting overall recyclability and environmental footprint.
Industry Standards and Common Uses
Tin-coated copper wire meets industry standards such as ASTM B33 and IEC 60228, providing enhanced corrosion resistance and solderability for marine, aerospace, and industrial applications. Pure copper wire, compliant with standards like ASTM B3 and UL 758, offers superior electrical conductivity ideal for residential, commercial, and automotive wiring. The choice between tin and copper wiring depends on environmental conditions and application requirements, with tin-coated copper preferred for harsh environments and pure copper favored for maximum conductivity.
Infographic: Tin vs Copper for Electrical Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com