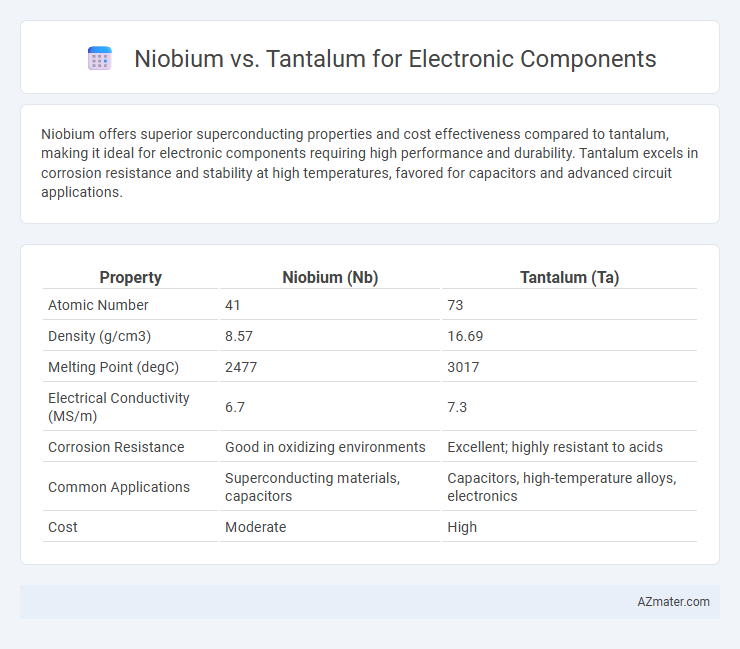
Niobium offers superior superconducting properties and cost effectiveness compared to tantalum, making it ideal for electronic components requiring high performance and durability. Tantalum excels in corrosion resistance and stability at high temperatures, favored for capacitors and advanced circuit applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Tantalum (Ta) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 41 | 73 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.57 | 16.69 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2477 | 3017 |
| Electrical Conductivity (MS/m) | 6.7 | 7.3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in oxidizing environments | Excellent; highly resistant to acids |
| Common Applications | Superconducting materials, capacitors | Capacitors, high-temperature alloys, electronics |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Niobium and Tantalum in Electronics
Niobium and tantalum are critical metals widely used in electronic components for their exceptional capacitance and corrosion resistance. Tantalum is renowned for its high dielectric constant and stability in capacitors, making it a preferred choice in high-performance circuits. Niobium offers similar properties with cost advantages and is increasingly adopted in capacitors and superalloys for electronic applications.
Material Properties Overview
Niobium offers excellent superconducting properties and high corrosion resistance, making it ideal for capacitors and semiconductors in electronic components. Tantalum features superior thermal stability and exceptional capacitance per volume, often preferred for high-performance capacitors in miniaturized devices. Both metals exhibit high melting points and chemical inertness, but tantalum's enhanced dielectric properties provide a critical advantage in energy storage applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Niobium and tantalum are critical materials used in electronic components, where their electrical conductivity significantly influences performance. Niobium exhibits a conductivity of approximately 6.7 x 10^6 S/m, while tantalum offers slightly lower conductivity around 7.5 x 10^6 S/m, making tantalum marginally superior in this aspect. The choice between niobium and tantalum depends on balancing conductivity with other factors like corrosion resistance and thermal stability.
Capacitor Applications: Niobium vs Tantalum
Niobium and tantalum are critical materials in capacitor applications, with tantalum offering superior volumetric efficiency and higher capacitance per volume, making it ideal for miniaturized electronics. Niobium capacitors provide enhanced thermal stability and lower cost, which benefits high-temperature environments and cost-sensitive applications. Performance trade-offs include tantalum's susceptibility to dielectric breakdown versus niobium's relatively lower capacitance density but improved safety profile in harsh conditions.
Reliability and Performance in Circuits
Niobium and tantalum both play critical roles in electronic components, with tantalum capacitors favored for high reliability and stable performance in circuits subjected to high temperatures and voltages. Niobium capacitors offer similar characteristics but generally provide improved environmental friendliness and cost-effectiveness, albeit with slightly lower volumetric efficiency compared to tantalum. The choice between niobium and tantalum depends on specific circuit requirements, balancing factors such as capacitance stability, equivalent series resistance (ESR), and long-term reliability under electrical stress.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Niobium offers a cost advantage over tantalum due to its more abundant global supply, primarily sourced from Brazil and Canada, which reduces price volatility for electronic component manufacturers. Tantalum's limited availability, concentrated in conflict-prone regions like the Democratic Republic of Congo, often leads to higher prices and supply chain risks in capacitors and high-performance electronic applications. Choosing niobium can ensure better cost predictability and steady availability, making it a strategic material for scalable electronics production.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Niobium offers significant environmental advantages over tantalum in electronic components due to its higher abundance and more efficient recycling capabilities, reducing the demand for environmentally damaging mining practices. Tantalum mining often involves conflict minerals and labor issues, whereas niobium extraction is generally less associated with ethical concerns and has a lower carbon footprint. Sustainable production of niobium supports greener electronics by lowering toxic waste and enabling longer component lifecycles through enhanced material properties.
Manufacturing and Process Compatibility
Niobium and tantalum both serve crucial roles in electronic component manufacturing, with niobium offering superior thermal conductivity and cost-effectiveness, while tantalum excels in corrosion resistance and capacitance stability. Niobium's compatibility with existing semiconductor manufacturing processes allows for easier integration in soldering and thin-film deposition, whereas tantalum requires specialized handling due to its higher melting point and oxidation sensitivity. Manufacturers must weigh niobium's process adaptability against tantalum's performance benefits to optimize electronic component reliability and production efficiency.
Industry Adoption and Trends
Niobium and tantalum are critical materials in electronic components, with tantalum dominating capacitor manufacturing due to its high capacitance and stability under extreme conditions. Niobium, gaining traction for its cost-effectiveness and comparable conductivity, is increasingly adopted in emerging flexible electronics and energy storage devices. Industry trends reveal a gradual diversification toward niobium-tantalum alloy use, driven by supply chain considerations and the push for sustainable sourcing in semiconductor production.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Niobium and tantalum both offer exceptional corrosion resistance and high capacitance, making them ideal for electronic components such as capacitors and resistors. Niobium is often favored for applications requiring cost-effectiveness and moderate performance, while tantalum provides superior stability and reliability in high-temperature and high-frequency environments. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors like budget, operating conditions, and electrical requirements to optimize component efficiency and lifespan.
Infographic: Niobium vs Tantalum for Electronic Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com