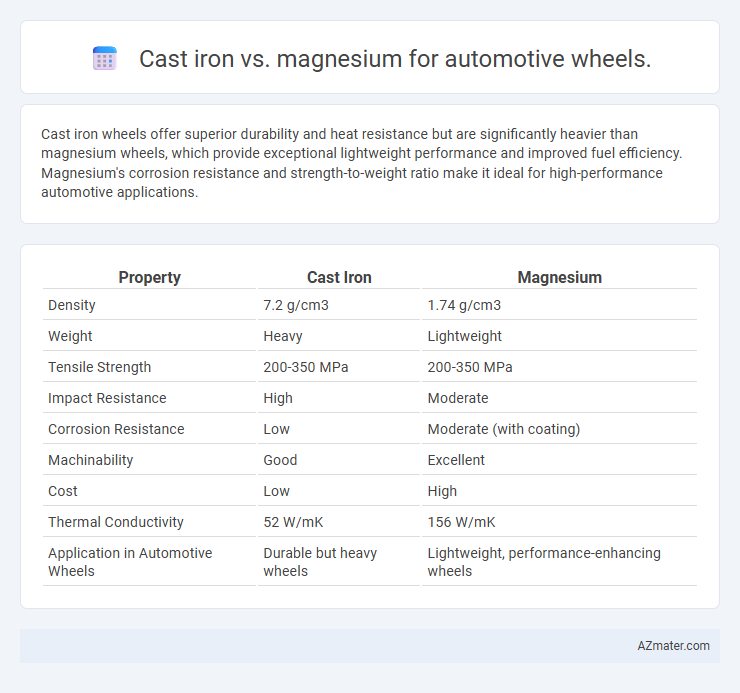
Cast iron wheels offer superior durability and heat resistance but are significantly heavier than magnesium wheels, which provide exceptional lightweight performance and improved fuel efficiency. Magnesium's corrosion resistance and strength-to-weight ratio make it ideal for high-performance automotive applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Cast Iron | Magnesium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.2 g/cm3 | 1.74 g/cm3 |
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Tensile Strength | 200-350 MPa | 200-350 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low | Moderate (with coating) |
| Machinability | Good | Excellent |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Thermal Conductivity | 52 W/mK | 156 W/mK |
| Application in Automotive Wheels | Durable but heavy wheels | Lightweight, performance-enhancing wheels |
Introduction to Automotive Wheel Materials
Automotive wheels are primarily manufactured using materials like cast iron and magnesium due to their distinct mechanical properties and performance benefits. Cast iron offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications, while magnesium provides a lightweight alternative with excellent weight-to-strength ratio, enhancing fuel efficiency and handling. Material selection impacts wheel longevity, vehicle dynamics, and manufacturing costs, driving innovation in alloy composition and processing techniques.
Overview of Cast Iron Wheels
Cast iron wheels are known for their exceptional strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty automotive applications. Their high density provides superior load-bearing capacity and resistance to wear, but this also results in increased weight compared to magnesium wheels. Cast iron's corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness contribute to its continued use despite the availability of lighter alternatives like magnesium alloy wheels.
Overview of Magnesium Wheels
Magnesium wheels offer a significant weight reduction compared to cast iron, improving vehicle performance by enhancing acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency. They exhibit excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance due to advanced alloy formulations, making them popular in high-performance and racing applications. Despite higher cost and susceptibility to surface damage, magnesium wheels contribute to overall vehicle agility and reduced unsprung mass, driving superior handling characteristics.
Weight Comparison: Cast Iron vs. Magnesium
Magnesium automotive wheels weigh approximately 35-50% less than cast iron wheels, significantly reducing unsprung mass and improving vehicle handling. Cast iron wheels typically weigh between 15-20 kg, whereas magnesium wheels can weigh as little as 8-12 kg for the same size. The lightweight nature of magnesium enhances fuel efficiency and acceleration, making it a preferred choice for performance and racing applications.
Strength and Durability Differences
Cast iron automotive wheels offer superior strength and exceptional durability due to their high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Magnesium wheels provide a lightweight alternative with impressive strength-to-weight ratios, but they are generally less durable and more susceptible to corrosion and fatigue compared to cast iron. The choice between cast iron and magnesium wheels hinges on balancing the need for maximum strength and long-term durability versus the priority of reduced weight for enhanced vehicle performance.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Magnesium automotive wheels offer superior corrosion resistance due to their natural oxide layer, which inhibits rust formation compared to cast iron wheels prone to rust in humid environments. Cast iron wheels require regular maintenance like painting or applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and extend lifespan. Magnesium wheels demand less maintenance, reducing overall upkeep costs and preserving appearance longer in automotive applications.
Performance and Handling Characteristics
Magnesium automotive wheels offer superior lightweight performance, reducing unsprung weight by up to 40% compared to cast iron, which enhances acceleration, braking, and overall handling precision. Cast iron wheels, while heavier and less responsive, provide exceptional durability and resistance to wear under harsh driving conditions. The reduced rotational mass of magnesium wheels significantly improves steering response and cornering agility, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles prioritizing handling dynamics.
Cost Analysis: Cast Iron vs. Magnesium Wheels
Cast iron wheels typically incur higher manufacturing costs due to their heavier weight and longer production cycle, whereas magnesium wheels offer cost advantages through reduced material usage and faster casting processes despite higher raw material prices. Maintenance expenses for cast iron wheels are generally lower given their durability and resistance to corrosion, contrasting with magnesium's need for protective coatings and more frequent upkeep. Over the vehicle's lifespan, the total cost of ownership may balance out depending on factors such as vehicle type, performance requirements, and environmental conditions impacting wheel longevity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cast iron automotive wheels have a higher carbon footprint due to energy-intensive smelting processes and heavier weight, which increases fuel consumption and emissions during vehicle operation. Magnesium wheels offer superior sustainability by being significantly lighter, reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency, while also enabling recycling with lower environmental impact. However, magnesium extraction and processing involve environmental concerns related to energy use and resource depletion, requiring advances in sustainable mining and production techniques.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Wheel Material
Magnesium wheels offer superior lightweight performance, enhancing vehicle acceleration and fuel efficiency, while cast iron wheels provide exceptional durability and cost-effectiveness. For high-performance and racing applications, magnesium is ideal due to its strength-to-weight ratio and heat dissipation properties. Cast iron remains the preferred choice for heavy-duty vehicles requiring robustness and low production costs.
Infographic: Cast iron vs Magnesium for Automotive wheel
 azmater.com
azmater.com