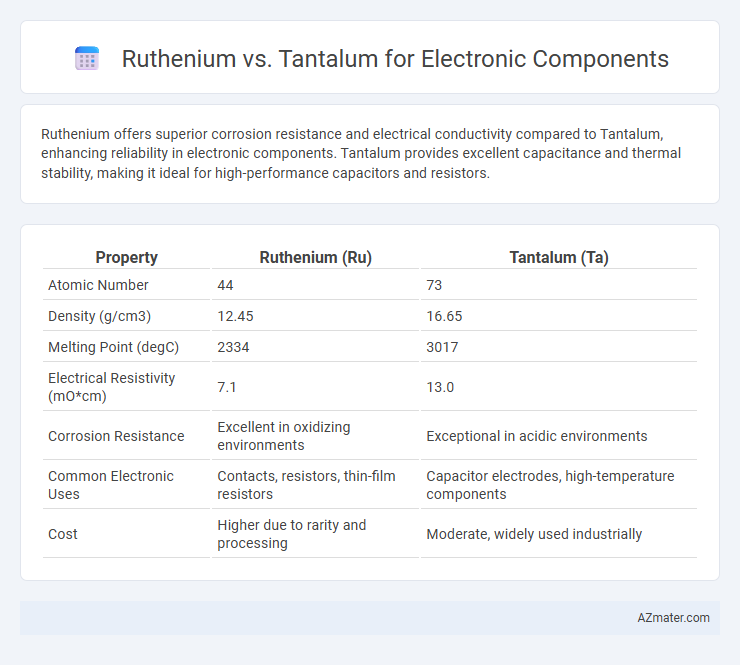
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to Tantalum, enhancing reliability in electronic components. Tantalum provides excellent capacitance and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance capacitors and resistors.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Tantalum (Ta) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 44 | 73 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 12.45 | 16.65 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2334 | 3017 |
| Electrical Resistivity (mO*cm) | 7.1 | 13.0 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent in oxidizing environments | Exceptional in acidic environments |
| Common Electronic Uses | Contacts, resistors, thin-film resistors | Capacitor electrodes, high-temperature components |
| Cost | Higher due to rarity and processing | Moderate, widely used industrially |
Introduction to Ruthenium and Tantalum in Electronics
Ruthenium and tantalum are critical materials in electronics due to their exceptional electrical properties and corrosion resistance. Ruthenium is commonly used in thin-film resistors and electrical contacts for its durability and stability under high temperatures. Tantalum is widely utilized in capacitors and high-performance electronic components because of its excellent capacitance and ability to maintain performance in harsh environments.
Material Properties: Ruthenium vs Tantalum
Ruthenium exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance and high hardness, making it ideal for thin-film resistors and contacts in electronic components, while tantalum is prized for its excellent capacitance stability and high melting point, suitable for capacitors and high-temperature applications. Ruthenium's higher electrical conductivity enhances efficiency in microelectronic circuits, whereas tantalum's superior dielectric properties support long-term reliability in energy storage devices. The choice between ruthenium and tantalum depends on specific performance requirements, such as wear resistance versus capacitance, influencing material selection in advanced electronics manufacturing.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Ruthenium exhibits excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it highly effective for thin-film resistors and contacts in electronic components. Tantalum offers superior capacitance stability and high dielectric constant, which is ideal for capacitors in power supply circuits. Ruthenium's lower resistivity enhances signal integrity, while tantalum's robust oxide layer ensures reliable performance under high voltage and temperature conditions.
Reliability and Longevity
Ruthenium exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and high conductivity, making it highly reliable for electronic components subjected to harsh environments. Tantalum offers outstanding capacitance stability and robust oxide layer formation, which enhances longevity in capacitors and high-frequency applications. Both metals provide superior thermal stability, but tantalum often dominates in long-term reliability for energy storage, while ruthenium excels in contact resistance and durability in switching devices.
Cost and Availability
Ruthenium, a rare platinum-group metal, generally commands a higher price due to limited availability and complex extraction processes, impacting its cost-effectiveness for electronic components. Tantalum, more abundant with established mining and refining infrastructure, offers a comparatively lower and more stable cost, making it a preferred choice in capacitors and high-performance electronics. Availability constraints of ruthenium contribute to supply risks, whereas tantalum benefits from broader sourcing options, ensuring more consistent market supply.
Applications in Modern Electronic Components
Ruthenium is extensively utilized in modern electronic components for its excellent corrosion resistance and superior conductivity, making it ideal for thin-film resistors, electrical contacts, and chip resistors in integrated circuits. Tantalum is predominantly applied in capacitors due to its high volumetric efficiency, stability, and reliability, enabling compact and durable devices in smartphones, automotive electronics, and aerospace systems. The choice between ruthenium and tantalum hinges on specific application requirements, with ruthenium favored for conductive and contact purposes and tantalum for energy storage and capacitance in miniaturized electronic components.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Ruthenium and Tantalum present distinct environmental and safety profiles in electronic components, with Ruthenium often favored for its corrosion resistance and lower toxicity, reducing hazardous waste during manufacturing. Tantalum's extraction, however, raises significant ethical and environmental concerns, including the disruption of conflict regions and high energy consumption in mining. Volatile exposure risks and recycling challenges highlight the need for careful handling and disposal regulations to mitigate potential environmental impacts for both metals.
Market Trends and Industry Adoption
Ruthenium and tantalum both play crucial roles in electronic components, with ruthenium gaining traction due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and conductivity in capacitors and resistors. Market trends indicate a growing preference for ruthenium in miniaturized devices and high-performance applications, driven by increasing demand for durability and efficiency in consumer electronics and automotive sectors. Industry adoption favors tantalum in capacitors for stable dielectric characteristics, but ruthenium's emerging use in thin-film resistors signals a shift toward advanced material integration in next-generation electronic components.
Technological Innovations and Future Outlook
Ruthenium, prized for its exceptional corrosion resistance and superior electrical conductivity, enhances the performance and longevity of electronic components such as resistors and contacts. Tantalum's high capacitance and stability under extreme conditions make it a critical material in advanced capacitors, particularly for aerospace and medical electronics. Innovations in nanostructured ruthenium coatings and tantalum capacitors with increased volumetric efficiency promise to drive future advancements in miniaturized, high-performance electronic devices.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Application
Ruthenium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and reliable performance in thin-film resistors and contacts, making it ideal for precision electronic components requiring durability at micro scales. Tantalum provides excellent capacitance, high melting point, and superior conductivity, commonly used in capacitors and high-temperature applications demanding stable electrical properties. Selecting between ruthenium and tantalum depends on the specific needs for corrosion resistance, capacitance, thermal stability, and conductivity in your electronic design.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Tantalum for Electronic Component
 azmater.com
azmater.com