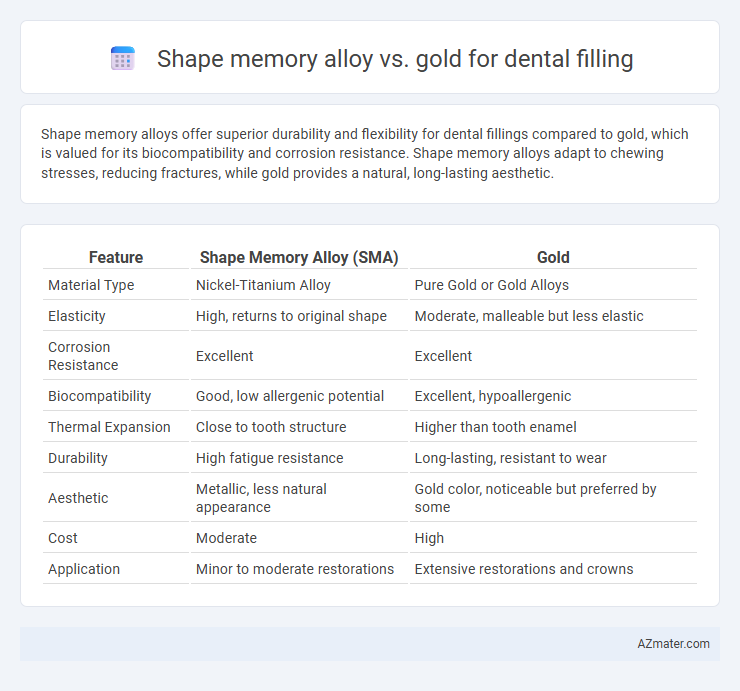
Shape memory alloys offer superior durability and flexibility for dental fillings compared to gold, which is valued for its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Shape memory alloys adapt to chewing stresses, reducing fractures, while gold provides a natural, long-lasting aesthetic.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shape Memory Alloy (SMA) | Gold |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Nickel-Titanium Alloy | Pure Gold or Gold Alloys |
| Elasticity | High, returns to original shape | Moderate, malleable but less elastic |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Biocompatibility | Good, low allergenic potential | Excellent, hypoallergenic |
| Thermal Expansion | Close to tooth structure | Higher than tooth enamel |
| Durability | High fatigue resistance | Long-lasting, resistant to wear |
| Aesthetic | Metallic, less natural appearance | Gold color, noticeable but preferred by some |
| Cost | Moderate | High |
| Application | Minor to moderate restorations | Extensive restorations and crowns |
Introduction to Dental Fillings: Material Choices
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) and gold are two distinct materials commonly used for dental fillings, each offering unique benefits in durability and biocompatibility. SMAs provide superior adaptability and resilience due to their elasticity and ability to return to original shape after deformation, making them ideal for stress-prone occlusal surfaces. Gold fillings excel in corrosion resistance, longevity, and minimal wear on opposing teeth, making them a premium choice for patients prioritizing durability and aesthetics in dental restorations.
Overview of Shape Memory Alloys in Dentistry
Shape memory alloys (SMAs), primarily nickel-titanium (NiTi), offer exceptional flexibility, biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for dental applications such as orthodontic wires and endodontic instruments. Unlike gold, which is prized for its malleability and aesthetic appeal in dental fillings, SMAs provide adaptive mechanical properties that enable better stress distribution and reduced risk of microfractures. The unique ability of SMAs to return to their original shape after deformation enhances durability and patient comfort in dental restorations and appliances.
Gold as a Traditional Dental Filling Material
Gold has been a traditional dental filling material renowned for its exceptional durability, biocompatibility, and resistance to corrosion, often lasting 15 to 30 years or more in restorations. Compared to shape memory alloys, gold offers superior malleability and adaptability to tooth contours, ensuring a precise fit and reduced risk of microleakage. Despite advances in alternative materials, gold's proven longevity and minimal wear on opposing teeth maintain its status as a preferred choice for high-quality dental restorations.
Biocompatibility: Shape Memory Alloy vs Gold
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) exhibit excellent biocompatibility due to their ability to withstand oral environment stresses and resist corrosion, minimizing allergic reactions. Gold, as a noble metal, is highly biocompatible, non-toxic, and inert, which makes it less likely to cause adverse tissue responses. While gold remains the gold standard for dental fillings in terms of biocompatibility, modern SMAs offer promising alternative properties with satisfactory tissue integration and durability.
Mechanical Properties and Longevity
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) exhibit superior elasticity, enabling them to withstand cyclic stresses without permanent deformation, which is advantageous for dental fillings subjected to repetitive chewing forces. Gold offers exceptional corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, with a proven track record of lasting over 20 years in oral environments due to its stable mechanical properties and minimal wear. While gold fillings provide long-term durability and reliable mechanical strength, SMAs introduce innovative flexibility but lack extensive longevity data compared to the established performance of gold in dental restorations.
Aesthetic Considerations for Dental Restorations
Shape memory alloys, commonly composed of nickel-titanium, offer excellent durability but lack the natural tooth color, making them less favorable for aesthetic dental restorations compared to gold. Gold fillings provide a warm, metallic sheen that can be polished to a high luster, blending more harmoniously with certain dental hues and enhancing the restoration's visual appeal. While gold alloys are highly biocompatible and corrosion-resistant, their color still contrasts with natural enamel, requiring careful placement in less conspicuous areas for optimal aesthetics.
Cost Comparison: Shape Memory Alloy vs Gold Fillings
Shape memory alloys used for dental fillings typically cost significantly less than gold fillings, making them a more budget-friendly option for patients seeking durable restorations. Gold fillings are known for their longevity and biocompatibility but come with a higher price tag due to the precious metal content and complex fabrication process. Dentists often recommend shape memory alloys when cost efficiency is prioritized without substantially compromising functional performance.
Clinical Performance and Patient Outcomes
Shape memory alloys (SMAs) in dental fillings offer superior elasticity and durability, adapting to occlusal forces and reducing microleakage compared to traditional gold restorations. Gold fillings provide excellent biocompatibility and long-term stability but lack the flexibility of SMAs, potentially leading to marginal gaps over time. Clinical studies highlight improved patient outcomes with SMAs through enhanced comfort, reduced post-operative sensitivity, and better preservation of tooth structure relative to gold fillings.
Advances in Dental Technology: Future Trends
Shape memory alloys (SMA) offer superior adaptability and durability in dental fillings compared to traditional gold, responding dynamically to oral temperature changes and reducing microleakage risks. Advances in nanotechnology and biomaterials enhance SMA's biocompatibility and mechanical strength, positioning them as a future trend in minimally invasive dentistry. Emerging research focuses on integrating smart alloys with digital dentistry techniques to improve precision, longevity, and patient comfort over conventional gold restorations.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Dental Filling Material
Shape memory alloys offer superior elasticity and durability for dental fillings, adapting closely to tooth structure and reducing microleakage. Gold remains a premium choice due to its exceptional biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and long-term stability. Optimal selection depends on balancing mechanical performance, aesthetics, and patient-specific clinical factors to ensure longevity and oral health.
Infographic: Shape memory alloy vs Gold for Dental filling
 azmater.com
azmater.com