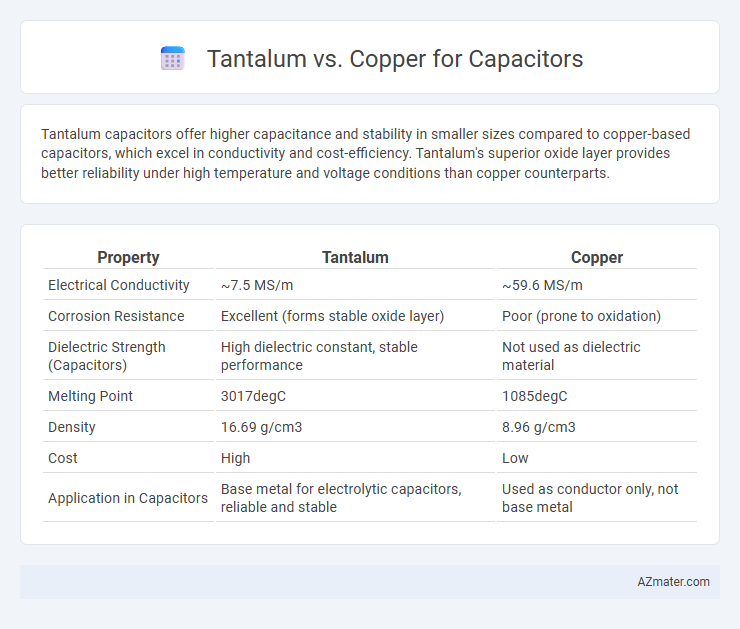
Tantalum capacitors offer higher capacitance and stability in smaller sizes compared to copper-based capacitors, which excel in conductivity and cost-efficiency. Tantalum's superior oxide layer provides better reliability under high temperature and voltage conditions than copper counterparts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | ~7.5 MS/m | ~59.6 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (forms stable oxide layer) | Poor (prone to oxidation) |
| Dielectric Strength (Capacitors) | High dielectric constant, stable performance | Not used as dielectric material |
| Melting Point | 3017degC | 1085degC |
| Density | 16.69 g/cm3 | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application in Capacitors | Base metal for electrolytic capacitors, reliable and stable | Used as conductor only, not base metal |
Introduction: The Role of Capacitors in Modern Electronics
Capacitors play a crucial role in modern electronics by storing and regulating electrical energy to ensure stable power delivery and signal filtering in devices. Tantalum capacitors, known for their high capacitance per volume and reliability, are preferred in space-constrained applications requiring long-term performance and low leakage current. Copper capacitors, often used as electrodes or in hybrid designs, offer excellent conductivity and cost efficiency but generally have lower capacitance density compared to tantalum counterparts.
Material Properties: Tantalum vs Copper
Tantalum exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, high melting point (2996degC), and superior capacitance per volume, making it ideal for compact, stable capacitors. Copper offers exceptional electrical conductivity (5.96 x 10^7 S/m) but lower corrosion resistance and melting point (1085degC), limiting its use primarily to capacitor leads and electrodes rather than dielectric material. The intrinsic properties of tantalum enable higher energy density and reliability in capacitors compared to copper components.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Tantalum capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency and better stability with lower Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) compared to copper-based film capacitors, resulting in superior frequency response and reduced power losses. Copper capacitors typically provide higher current handling and better thermal conductivity, which enhances heat dissipation in high-power electronics but may exhibit higher ESR and larger physical size than tantalum counterparts. The choice between tantalum and copper capacitors depends on specific electrical performance requirements, such as capacitance density, ripple current tolerance, and operating frequency.
Capacitance Density and Size Advantages
Tantalum capacitors offer significantly higher capacitance density compared to copper-based capacitors, enabling the creation of smaller, more compact components ideal for space-constrained electronic designs. The inherent electrochemical properties of tantalum allow for stable capacitance values with reduced equivalent series resistance (ESR), resulting in improved performance in miniaturized applications. Copper, while excellent for conductivity, does not match the volumetric efficiency of tantalum in capacitor fabrication, making tantalum the preferred choice where size and capacitance density are critical.
Reliability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors offer superior reliability and longer lifespan due to their stable oxide layer and high volumetric efficiency, making them ideal for critical applications requiring consistent performance. Copper capacitors, while cost-effective and having good electrical conductivity, generally exhibit shorter lifespans and lower reliability in high-stress environments due to susceptibility to corrosion and thermal degradation. Choosing tantalum capacitors enhances endurance and operational stability in demanding electronic circuits.
Cost Analysis: Tantalum vs Copper Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors typically have higher material and manufacturing costs compared to copper capacitors due to the rarity and expense of tantalum metal. Copper capacitors benefit from lower raw material costs and widespread availability, making them more cost-effective for large-scale production. Despite higher initial costs, tantalum capacitors offer superior performance in high-reliability applications, which can justify the investment depending on the use case.
Application Suitability in Consumer Electronics
Tantalum capacitors excel in consumer electronics requiring high volumetric efficiency and stable capacitance under varying temperatures, making them ideal for smartphones and laptops. Copper is primarily used in the capacitor's internal wiring and lead frames due to its superior electrical conductivity but does not serve as a dielectric or electrode material. For applications demanding miniaturization and reliable performance under stress, tantalum capacitors offer better suitability compared to copper-based capacitor components.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tantalum capacitors typically involve mining processes with higher environmental impact due to the extraction of conflict minerals and associated toxic waste, whereas copper is more abundant and recyclable, reducing ecological footprint. Safety concerns for tantalum capacitors include susceptibility to failure modes like thermal runaway and ignition under overload, while copper capacitors generally present lower risk of catastrophic failure. Choosing copper-based capacitors can enhance environmental sustainability and operational safety in electronic applications.
Market Trends and Future Developments
Tantalum capacitors dominate high-performance applications due to their superior volumetric efficiency and stability under extreme conditions, while copper capacitors gain traction in cost-sensitive markets owing to copper's excellent electrical conductivity and lower material costs. Market trends indicate a rising demand for miniaturized, high-reliability tantalum capacitors in automotive and aerospace sectors, driven by increasing electrification and IoT integration. Future developments focus on enhancing tantalum supply chain sustainability and advancing copper-based capacitor technology with improved thermal management and energy efficiency for consumer electronics.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Capacitor
Tantalum capacitors offer superior stability, higher volumetric efficiency, and excellent performance in low-voltage applications, making them ideal for compact, high-reliability circuits. Copper capacitors, primarily used as capacitor electrodes or in foil form, provide excellent conductivity and cost-effectiveness but lack the intrinsic dielectric properties of tantalum electrolytes. Selecting the right capacitor material depends on specific application requirements, with tantalum favored for miniaturization and long-term stability, while copper-based capacitors suit cost-sensitive and high-current scenarios.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Copper for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com