Steel pipes offer superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, which are prone to corrosion and pose significant health risks due to lead toxicity. Using steel pipes in plumbing systems ensures long-term safety and compliance with modern building standards.
Table of Comparison
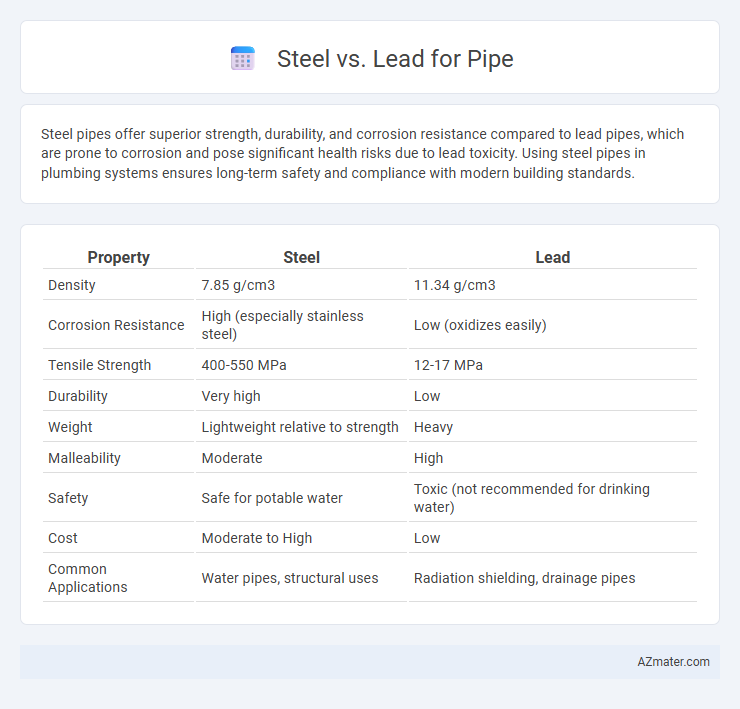
| Property | Steel | Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 7.85 g/cm3 | 11.34 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (especially stainless steel) | Low (oxidizes easily) |
| Tensile Strength | 400-550 MPa | 12-17 MPa |
| Durability | Very high | Low |
| Weight | Lightweight relative to strength | Heavy |
| Malleability | Moderate | High |
| Safety | Safe for potable water | Toxic (not recommended for drinking water) |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low |
| Common Applications | Water pipes, structural uses | Radiation shielding, drainage pipes |
Introduction to Pipe Materials: Steel vs Lead
Steel pipes offer superior strength, durability, and corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, making them a preferred choice in modern plumbing and construction. Lead pipes, historically used due to their malleability, pose significant health risks from lead leaching and are generally banned in new installations. The transition from lead to steel piping enhances water quality, structural integrity, and regulatory compliance in residential and industrial applications.
Historical Use of Steel and Lead Pipes
Steel pipes gained prominence in the early 20th century due to their strength and durability, gradually replacing lead pipes that were commonly used in ancient Rome and early modern plumbing systems. Lead pipes, valued for their malleability and ease of installation, posed significant health risks which led to regulatory bans and the adoption of safer materials like steel. By mid-1900s, steel became the preferred material in water delivery systems, offering superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity compared to lead.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Steel pipes exhibit superior strength and durability compared to lead pipes, making them ideal for high-pressure environments and long-term use. Steel's tensile strength ranges from 400 to 550 MPa, significantly higher than lead's approximate 18 MPa, which translates to better resistance against deformation and cracking. Furthermore, steel is highly corrosion-resistant when properly coated, extending its lifespan far beyond that of lead, which is prone to corrosion and contamination.
Corrosion Resistance: Steel vs Lead
Steel pipes, especially those made from stainless steel, exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to lead pipes, which are prone to corrosion and lead leaching into water supplies. Lead pipes can deteriorate over time due to oxidation and acidic water conditions, posing significant health risks. Steel's durability and resistance to rust through protective coatings or alloying elements make it a safer and longer-lasting choice for plumbing systems.
Health and Safety Concerns
Steel pipes offer superior health and safety benefits compared to lead pipes, primarily due to lead's toxicity and risk of causing lead poisoning when used in water systems. Steel is corrosion-resistant and does not leach harmful substances, ensuring safer drinking water quality and reducing potential exposure to heavy metals. Regulatory agencies such as the EPA have banned lead pipes in plumbing to mitigate health hazards, making steel a preferred and safer alternative for potable water systems.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Steel pipes offer greater environmental sustainability due to their recyclability and longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing landfill waste. Lead pipes pose significant environmental hazards as lead is toxic, contaminating water supplies and soil, necessitating costly and energy-intensive remediation efforts. Using steel instead of lead aligns with sustainable infrastructure goals by promoting safer water quality and lowering ecological risks.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Steel pipes require professional welding or threading during installation, demanding specialized tools and skills, while lead pipes are easier to shape and join but pose significant health risks, limiting their current use. Maintenance for steel pipes involves regular inspection for corrosion and potential rust treatment or replacement, whereas lead pipes necessitate complete removal due to toxicity concerns and are not recommended for potable water systems. Choosing steel ensures durability and compliance with modern plumbing codes, whereas lead is largely obsolete and banned in many regions.
Cost Comparison: Steel vs Lead Pipes
Steel pipes generally cost more upfront than lead pipes due to higher material expenses and manufacturing complexity. Lead pipes, while cheaper initially, pose significant health and environmental risks that increase long-term costs through maintenance and replacement. Considering durability, corrosion resistance, and regulatory compliance, steel pipes offer better overall cost efficiency despite the higher initial investment.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Steel pipes adhere to stringent regulatory standards such as ASTM A53, A106, and API 5L, ensuring high strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for high-pressure applications. Lead pipes face significant compliance restrictions due to health hazards associated with lead leaching, with regulations like the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) in the US mandating phase-outs and replacements. Regulatory agencies prioritize steel pipes for potable water and gas distribution systems because of their durability, safety, and compliance with environmental and health standards.
Future Trends in Pipe Material Selection
Future trends in pipe material selection show a growing preference for steel over lead due to steel's superior corrosion resistance, durability, and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Advances in steel manufacturing and coating technologies enhance its lifespan and reduce maintenance costs, making it ideal for sustainable infrastructure projects. Lead pipes are increasingly phased out globally because of health risks associated with lead contamination in water systems, driving demand for safer alternatives like stainless steel and galvanized steel pipes.
Infographic: Steel vs Lead for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com