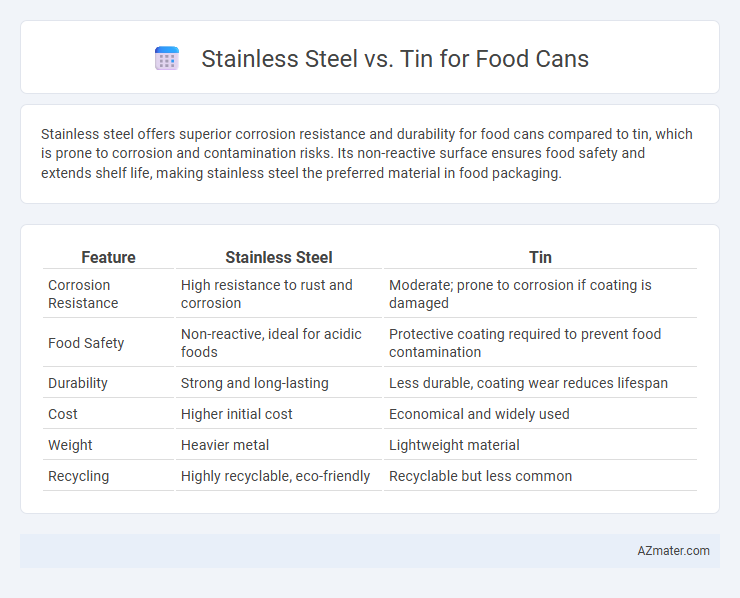
Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability for food cans compared to tin, which is prone to corrosion and contamination risks. Its non-reactive surface ensures food safety and extends shelf life, making stainless steel the preferred material in food packaging.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | High resistance to rust and corrosion | Moderate; prone to corrosion if coating is damaged |
| Food Safety | Non-reactive, ideal for acidic foods | Protective coating required to prevent food contamination |
| Durability | Strong and long-lasting | Less durable, coating wear reduces lifespan |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Economical and widely used |
| Weight | Heavier metal | Lightweight material |
| Recycling | Highly recyclable, eco-friendly | Recyclable but less common |
Introduction to Food Can Materials
Stainless steel and tin are widely used materials in food can manufacturing due to their corrosion resistance and ability to preserve food quality. Stainless steel offers superior strength and durability, making it ideal for long-term storage and high-pressure processing. Tin, often used as a coating on steel, prevents rust and provides an effective barrier against contamination, ensuring food safety and extended shelf life.
Overview of Stainless Steel Cans
Stainless steel cans for food storage offer superior corrosion resistance compared to tin cans, ensuring long-term preservation without leaching harmful substances. Featuring a durable, non-reactive surface, stainless steel maintains the integrity and flavor of food products while providing excellent protection against contaminants. Their robust construction supports repeated use and recycling, making them an environmentally sustainable choice in food packaging.
Overview of Tin-plated Cans
Tin-plated cans, also known as tin-coated steel cans, offer corrosion resistance and excellent food preservation by preventing direct contact between food and steel, thus minimizing contamination and rust. The thin layer of tin provides a non-toxic, airtight seal that extends shelf life and maintains flavor integrity, making them ideal for acidic or high-moisture foods. Compared to stainless steel, tin-plated cans are more cost-effective and widely used for mass food packaging due to their light weight and ease of manufacturing.
Material Composition and Properties
Stainless steel food cans are primarily composed of iron, chromium (usually around 10-12%), and nickel, offering high corrosion resistance, durability, and strength suitable for long-term food storage. Tin cans, typically made from thin steel sheets coated with tin, provide excellent corrosion prevention through the tin layer, which also acts as a safe barrier against food contamination. The stainless steel's chromium content forms a passive oxide layer that protects against rust, while tin coatings ensure non-reactivity and maintain food quality but generally lack the structural robustness of stainless steel.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to tin, making it ideal for long-term food storage and preventing contamination. Its chromium content forms a passive layer that protects against rust, while tin coatings can wear off over time, exposing the underlying metal to corrosion. This enhanced resistance ensures stainless steel cans maintain integrity and safety under various environmental conditions, unlike tin cans that may degrade faster when exposed to moisture or acidic foods.
Food Safety and Reactivity
Stainless steel offers superior food safety and low reactivity compared to tin, as it resists corrosion and does not leach harmful substances into food. Tin coatings can prevent metal corrosion but may react with acidic foods, potentially altering taste and safety. Choosing stainless steel cans ensures better preservation of food quality and reduces the risk of chemical contamination.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Stainless steel cans offer superior environmental benefits due to their high recyclability rate of up to 90%, reducing landfill waste and energy consumption compared to tin cans, which often rely on layers of tin coating over steel that complicate recycling processes. The production of stainless steel emits fewer greenhouse gases when using recycled content, promoting sustainable resource management relative to tin, which involves more intensive mining and refining practices that increase ecological footprints. Stainless steel's durability and resistance to corrosion extend the lifespan of food packaging, decreasing the frequency of replacement and contributing to a circular economy in food can manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Stainless steel cans offer superior durability and corrosion resistance but come with a higher initial cost compared to tin cans, which are more affordable due to cheaper raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Tin-plated steel, being lightweight and cost-effective, remains a popular choice for mass-produced food packaging, especially in budget-sensitive markets. Evaluating long-term affordability involves considering stainless steel's extended life span and reduced waste, potentially offsetting its upfront expense in sustainable packaging strategies.
Applications and Usage Scenarios
Stainless steel cans are widely used for storing acidic and high-temperature foods due to their corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for soups, sauces, and ready-to-eat meals. Tin-plated steel cans are commonly utilized for preserving low-acid foods such as vegetables and meats, benefiting from the tin coating that prevents rust and extends shelf life. Both materials are essential in the food industry, with stainless steel preferred for long-term storage and tin-plated steel favored for economical, large-scale food packaging.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Can Material
Choosing the right can material for food storage depends on factors such as corrosion resistance, food acidity, and cost. Stainless steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for acidic or long-term storage, while tin-coated steel provides a more economical option with adequate protection for less reactive foods. Evaluating the specific requirements of food preservation ensures optimal safety and shelf life.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Tin for Food can
 azmater.com
azmater.com