Stainless steel cookware offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, while cast iron provides excellent heat retention and natural non-stick properties. Choosing between them depends on cooking style, maintenance preference, and desired heat performance.
Table of Comparison
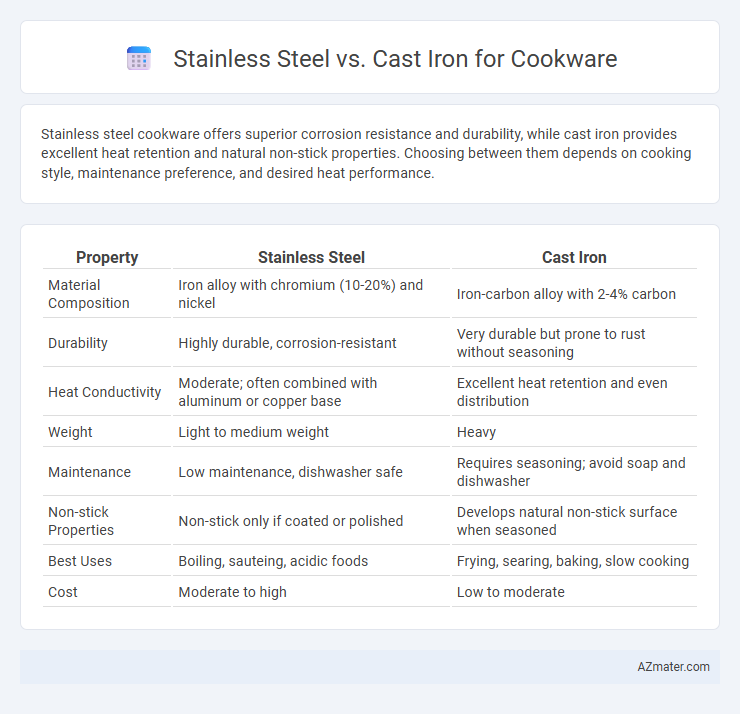
| Property | Stainless Steel | Cast Iron |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Iron alloy with chromium (10-20%) and nickel | Iron-carbon alloy with 2-4% carbon |
| Durability | Highly durable, corrosion-resistant | Very durable but prone to rust without seasoning |
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate; often combined with aluminum or copper base | Excellent heat retention and even distribution |
| Weight | Light to medium weight | Heavy |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe | Requires seasoning; avoid soap and dishwasher |
| Non-stick Properties | Non-stick only if coated or polished | Develops natural non-stick surface when seasoned |
| Best Uses | Boiling, sauteing, acidic foods | Frying, searing, baking, slow cooking |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Introduction to Stainless Steel and Cast Iron Cookware
Stainless steel cookware is prized for its durability, resistance to rust and corrosion, and non-reactive properties that maintain food flavor and color. Cast iron cookware excels in heat retention and even distribution, making it ideal for slow-cooking and searing, though it requires seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust. Both materials offer distinct benefits: stainless steel for versatility and ease of maintenance, and cast iron for superior heat performance and longevity.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Stainless steel cookware is composed primarily of iron, carbon, and chromium, offering corrosion resistance and durability through an alloying process, while cast iron consists mostly of iron with a higher carbon content, lending it superior heat retention and seasoning ability. Manufacturing stainless steel involves melting and molding the alloy, often polished for a smooth finish, whereas cast iron is made by pouring molten iron-carbon mixture into molds, resulting in a dense and porous structure that requires seasoning. The differing material compositions and manufacturing methods directly impact cookware performance, maintenance, and suitability for various cooking techniques.
Heat Retention and Distribution Comparison
Cast iron offers superior heat retention, maintaining consistent temperature for prolonged cooking, making it ideal for slow-cooking and searing. Stainless steel provides faster heat distribution, ensuring even cooking without hot spots, which is beneficial for precision tasks like sauteing. The choice depends on cooking style: cast iron excels in heat retention, while stainless steel ensures quick, uniform heat spread.
Durability and Longevity of Each Material
Stainless steel cookware offers exceptional durability due to its resistance to rust, corrosion, and staining, ensuring a longer lifespan even with frequent use. Cast iron is renowned for its longevity, often lasting generations if properly seasoned and maintained, with its ability to withstand high temperatures and repairability through re-seasoning. Both materials provide excellent durability, but stainless steel excels in ease of maintenance while cast iron delivers unmatched heat retention and resilience over time.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Stainless steel cookware requires less maintenance due to its resistance to rust, corrosion, and staining, making it easy to clean with ordinary dish soap or in a dishwasher. Cast iron demands regular seasoning to maintain its non-stick surface and prevent rust, requiring more effort during cleaning and drying to avoid moisture exposure. Proper upkeep of cast iron includes hand washing without soap and thorough drying, while stainless steel offers more convenience with its dishwasher-safe durability.
Cooking Performance and Versatility
Stainless steel cookware offers excellent heat distribution and retention, ensuring even cooking and precise temperature control, making it ideal for sauteing, searing, and deglazing. Cast iron excels in heat retention and develops a natural non-stick surface over time, perfect for slow-cooking, frying, and baking at high temperatures. Stainless steel is more versatile for acidic foods and dishwasher safe, while cast iron requires seasoning and careful maintenance to prevent rust.
Health and Safety Considerations
Stainless steel cookware offers excellent corrosion resistance and does not leach harmful metals into food, making it a safer choice for health-conscious cooking. Cast iron cookware maintains high heat retention but may release small amounts of iron, which can be beneficial or problematic depending on individual dietary needs. Both materials require proper maintenance; stainless steel resists rust and bacteria buildup, while cast iron must be seasoned regularly to prevent rust and ensure food safety.
Price and Value Analysis
Stainless steel cookware generally offers higher durability and corrosion resistance at a moderate price point, making it a cost-effective choice for long-term use. Cast iron pans are often more affordable upfront but require regular maintenance to prevent rust and maintain seasoning, impacting their overall value. Considering lifespan, heat retention, and maintenance costs, stainless steel provides better value for those seeking low upkeep, while cast iron suits budget-conscious cooks willing to invest time in care.
Common Uses and Best Recipe Matches
Stainless steel cookware excels in searing, sauteing, and boiling due to its durability and non-reactive surface, making it ideal for recipes like stir-fries, sauces, and soups. Cast iron retains heat exceptionally well, perfect for slow-cooking, frying, and baking dishes such as stews, cornbread, and seared steaks. Choosing between stainless steel and cast iron depends on cooking techniques and recipe requirements, with stainless steel preferred for quick, high-heat cooking and cast iron ideal for even heat distribution and retention.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Cookware for You
Selecting between stainless steel and cast iron cookware depends on cooking habits and maintenance preferences; stainless steel offers durability, non-reactivity, and low maintenance, ideal for searing and acidic foods. Cast iron excels in heat retention and even cooking, perfect for slow-cooking and achieving a natural non-stick surface with seasoning but requires more care to prevent rust. Consider factors like heat distribution, durability, and ease of cleaning to match cookware with your culinary needs.
Infographic: Stainless steel vs Cast iron for Cookware
 azmater.com
azmater.com