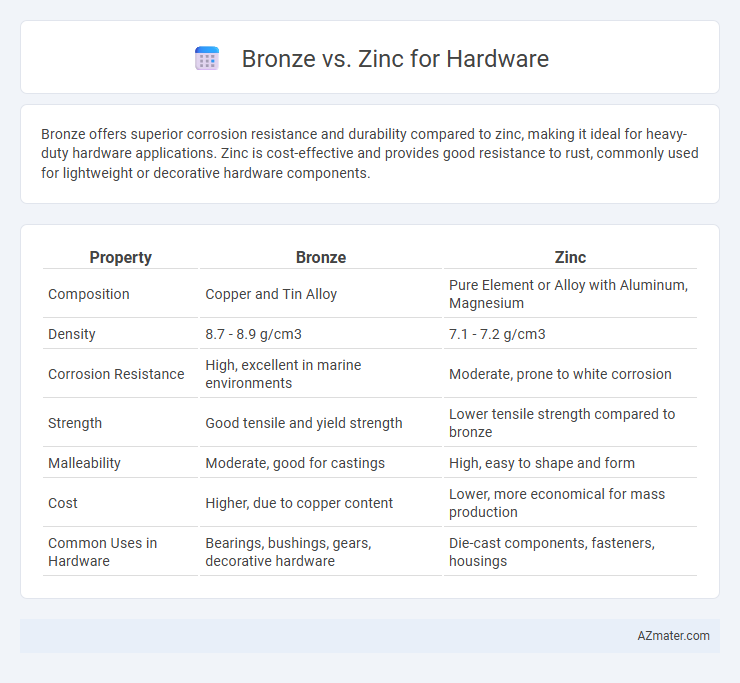
Bronze offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to zinc, making it ideal for heavy-duty hardware applications. Zinc is cost-effective and provides good resistance to rust, commonly used for lightweight or decorative hardware components.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and Tin Alloy | Pure Element or Alloy with Aluminum, Magnesium |
| Density | 8.7 - 8.9 g/cm3 | 7.1 - 7.2 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | High, excellent in marine environments | Moderate, prone to white corrosion |
| Strength | Good tensile and yield strength | Lower tensile strength compared to bronze |
| Malleability | Moderate, good for castings | High, easy to shape and form |
| Cost | Higher, due to copper content | Lower, more economical for mass production |
| Common Uses in Hardware | Bearings, bushings, gears, decorative hardware | Die-cast components, fasteners, housings |
Introduction to Bronze and Zinc Hardware
Bronze hardware, composed primarily of copper and tin, offers exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making it ideal for marine and outdoor applications. Zinc hardware, often alloyed with other metals like aluminum or copper, excels in cost-effectiveness and provides moderate strength with good resistance to rust and wear. Choosing between bronze and zinc depends on specific needs for longevity, appearance, and environmental exposure in various hardware projects.
Composition and Properties of Bronze
Bronze is primarily an alloy of copper and tin, often containing small amounts of other elements such as phosphorus, aluminum, or manganese to enhance its properties. Its composition results in high corrosion resistance, excellent strength, and superior wear resistance, making it ideal for hardware applications exposed to harsh environments. Bronze's low friction coefficient and ability to withstand high loads further distinguish it from zinc, which tends to be softer and more prone to corrosion.
Composition and Properties of Zinc
Zinc, primarily composed of approximately 98.5% zinc with small amounts of aluminum, copper, and magnesium, offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength in hardware applications. Its low melting point of around 420degC enables easy casting and molding, making it ideal for die-cast components requiring fine details. Compared to bronze, zinc provides superior malleability and electrical conductivity but generally lower tensile strength and durability.
Durability Comparison: Bronze vs. Zinc
Bronze hardware offers superior durability due to its high resistance to corrosion and wear, making it ideal for outdoor and heavy-duty applications. Zinc hardware, while more affordable and lightweight, tends to be less durable and more prone to corrosion over time, especially in harsh environments. Choosing bronze over zinc ensures longer-lasting performance and reduced maintenance costs in demanding hardware uses.
Corrosion Resistance: Which is Better?
Bronze exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc, making it more suitable for hardware exposed to harsh environments or marine conditions. Its copper-tin alloy composition forms a stable oxide layer that protects against rust and degradation. Zinc, while corrosion-resistant due to its sacrificial anode properties in galvanization, tends to corrode faster when used as a primary material in hardware without protective coatings.
Aesthetic Differences and Appearance
Bronze hardware offers a warm, rich patina that deepens over time, providing a classic and vintage aesthetic ideal for traditional or rustic designs. Zinc hardware presents a smoother, more uniform finish with a contemporary metallic sheen, often available in a variety of coatings such as brushed or polished, suitable for modern and industrial styles. The distinct color tones and aging characteristics make bronze a preferred choice for timeless elegance, while zinc complements sleek, minimalistic interiors.
Cost and Affordability Factors
Bronze hardware typically commands a higher price due to its durability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for long-term applications where cost-effectiveness is measured by lifespan. Zinc hardware offers a more affordable upfront cost, appealing for budget-sensitive projects, though it may require more frequent replacement due to lower resistance to wear and environmental factors. Evaluating the total cost of ownership favors bronze in scenarios demanding longevity, while zinc suits short-term or cost-constrained uses.
Applications in Hardware: When to Use Each
Bronze is ideal for hardware components requiring high corrosion resistance and durability, such as bearings, bushings, and gears used in marine and industrial applications. Zinc excels in cost-effective, die-cast parts like handles, locks, and fittings where moderate strength and good corrosion resistance are needed. Selecting bronze is preferable for heavy-duty, wear-resistant applications, while zinc suits lightweight, precision-molded hardware with intricate shapes.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze hardware, composed primarily of copper and tin, offers superior durability and corrosion resistance, reducing replacement frequency and minimizing environmental waste. Zinc, often recycled in manufacturing, has a lower melting point that conserves energy during production, contributing to reduced carbon emissions. Both metals support sustainability efforts, with bronze's longevity and zinc's recyclability playing crucial roles in eco-friendly hardware solutions.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Hardware Needs
Bronze and zinc possess distinct mechanical and corrosion-resistant properties essential for hardware applications, with bronze offering superior strength and durability, making it ideal for heavy-load or marine environments. Zinc excels in cost-effectiveness and provides excellent corrosion resistance in mild conditions, often used in die-cast hardware components where detail and finish are prioritized. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as load requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints, guiding optimal performance and longevity in your hardware projects.
Infographic: Bronze vs Zinc for Hardware
 azmater.com
azmater.com