Steel offers superior durability and corrosion resistance for outdoor sculptures, while bronze provides a classic aesthetic with excellent patina development and long-term aging qualities. Artists choose steel for modern, large-scale works and bronze for traditional, detailed sculptures emphasizing historical value.
Table of Comparison
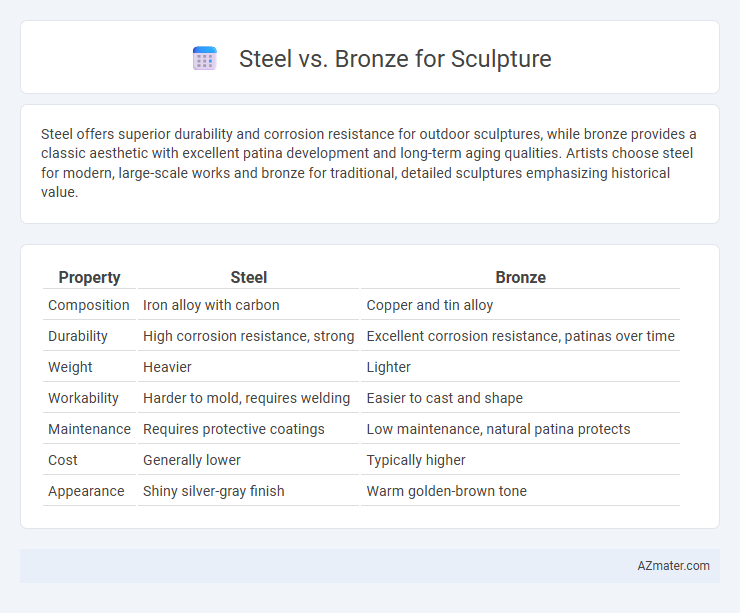
| Property | Steel | Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Iron alloy with carbon | Copper and tin alloy |
| Durability | High corrosion resistance, strong | Excellent corrosion resistance, patinas over time |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Workability | Harder to mold, requires welding | Easier to cast and shape |
| Maintenance | Requires protective coatings | Low maintenance, natural patina protects |
| Cost | Generally lower | Typically higher |
| Appearance | Shiny silver-gray finish | Warm golden-brown tone |
Overview: Steel vs Bronze in Sculpture
Steel offers durability, corrosion resistance, and a modern aesthetic, making it ideal for large, outdoor sculptures that require structural strength. Bronze, known for its timeless appeal and rich patina development, provides excellent detail resolution and is favored for traditional and intricate sculptural works. The choice between steel and bronze ultimately depends on factors like environmental exposure, desired finish, and artistic intent.
Historical Significance of Steel and Bronze Sculptures
Bronze sculptures have a rich historical significance, dating back to ancient civilizations such as Mesopotamia, Greece, and China, where bronze's durability and workability enabled detailed artistry and longevity. Steel sculptures emerged prominently during the 20th century, reflecting industrialization and modernism with their strength, scalability, and resistance to corrosion, enabling larger and more abstract forms. The shift from bronze to steel represents not only technological advancements but also changing artistic expressions influenced by cultural and material innovation.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Steel offers superior strength and exceptional durability compared to bronze, making it ideal for large-scale or outdoor sculptures exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Bronze provides moderate strength but excels in corrosion resistance and patina development, which enhances aesthetic appeal over time. The high tensile strength and resilience of steel ensure minimal deformation, while bronze's alloy composition allows for detailed work and longer-lasting surface integrity in humid environments.
Aesthetic Appeal: Color, Texture, and Finish
Steel sculptures boast a sleek, modern aesthetic with a smooth, reflective surface that enhances light interaction and highlights clean lines. Bronze offers a warm, rich color palette that develops a natural patina over time, adding depth and historical character to the artwork. The texture of bronze allows for intricate detailing, while steel's hardness supports sharp, geometric forms, making each material uniquely suited to different artistic expressions.
Workability and Sculpting Techniques
Steel offers high strength and durability, allowing sculptors to create large, intricate designs with greater structural integrity, but it requires welding, cutting, and grinding techniques that demand specialized tools and skills. Bronze, known for its excellent workability, allows detailed modeling through casting processes such as lost-wax casting, enabling fine textures and complex forms with relative ease. Sculptors often prefer bronze for detailed, delicate figurative works, while steel suits modern, abstract sculptures requiring bold, angular shapes and robust frameworks.
Cost Considerations: Bronze vs Steel
Bronze sculptures typically incur higher costs due to expensive raw materials and complex casting processes, often making them a premium choice for fine art installations. Steel, especially stainless or corten varieties, offers a more budget-friendly alternative with lower material expenses and simpler fabrication techniques like welding and laser cutting. Maintenance costs also vary, as bronze requires periodic patina treatments to preserve its appearance, whereas weathering steel forms a protective rust layer that minimizes upkeep.
Maintenance and Longevity
Steel sculptures require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion, especially when exposed to outdoor elements, with protective coatings extending their lifespan significantly. Bronze sculptures naturally develop a patina that acts as a protective layer, reducing the need for frequent upkeep and often enhancing their aesthetic appeal over time. In terms of longevity, bronze is highly durable and resistant to weathering, whereas steel's durability depends largely on the quality of its finish and environmental conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Steel offers greater durability and recyclability compared to bronze, significantly reducing long-term environmental impact through its high recycled content and efficient manufacturing processes. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, involves more energy-intensive mining and smelting operations, leading to higher carbon emissions and resource depletion. Choosing steel for sculptures aligns better with sustainable practices by minimizing habitat disruption and promoting circular material use in art production.
Famous Sculptures: Steel and Bronze Examples
Famous steel sculptures like Richard Serra's "Tilted Arc" showcase the medium's industrial strength and modern aesthetic, contrasting with the timeless elegance of bronze exemplified by Auguste Rodin's "The Thinker." Steel's durability allows for large-scale outdoor installations, while bronze offers intricate detailing and a warm patina that ages gracefully. Both materials remain iconic in sculpture history, influencing contemporary artistic expression and public monuments worldwide.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Sculpture
Steel offers exceptional durability and modern appeal for sculptures, making it ideal for outdoor installations that require resistance to weather and corrosion. Bronze provides a classic aesthetic with rich patina development and superior malleability, allowing intricate detailing for traditional or decorative sculptures. When choosing the right material, consider factors such as environmental exposure, desired texture, weight, and budget to ensure longevity and artistic expression in your sculpture.
Infographic: Steel vs Bronze for Sculpture
 azmater.com
azmater.com