Smart metal offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional tin-based solder. Its advanced alloy composition improves joint reliability and reduces the risk of brittle fractures in electronic assemblies.
Table of Comparison
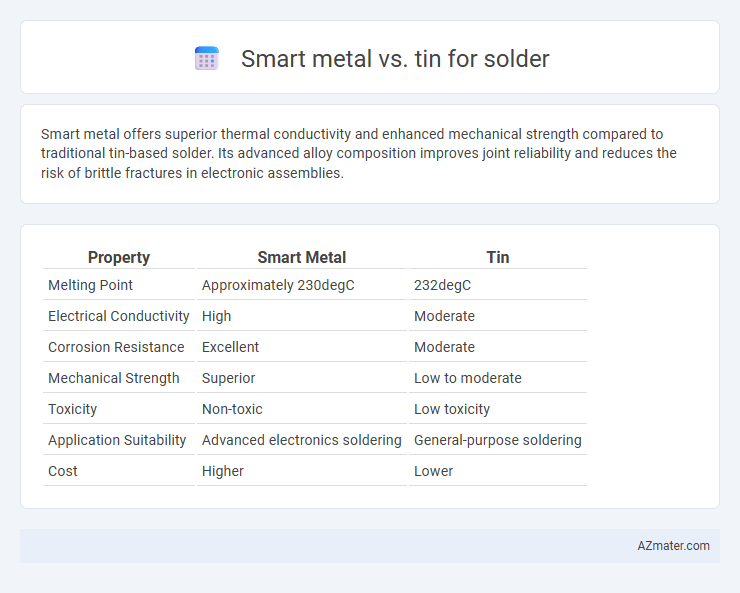
| Property | Smart Metal | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Melting Point | Approximately 230degC | 232degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Mechanical Strength | Superior | Low to moderate |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic | Low toxicity |
| Application Suitability | Advanced electronics soldering | General-purpose soldering |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to Smart Metal and Tin in Soldering
Smart metal in soldering refers to advanced alloys engineered for enhanced electrical conductivity and thermal stability, offering precise melting points and strong joint reliability. Tin, a traditional solder component, provides excellent corrosion resistance and low melting temperature, making it a staple in electronics assembly. Comparing the two, smart metals improve performance in high-demand applications, while tin remains favored for its ease of use and cost-effectiveness in general-purpose soldering.
Key Properties of Smart Metal vs Tin
Smart metal solder offers superior thermal conductivity and enhanced mechanical strength compared to traditional tin solder, resulting in more reliable and durable electronic connections. Its higher melting point ensures better performance in high-temperature applications, while improved corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of solder joints. Tin solder remains popular for its affordability and ease of use but lacks the advanced properties that smart metal provides for demanding industrial environments.
Melting Point Comparison
Smart metal solder typically features a melting point around 138-140degC, significantly lower than traditional tin solder, which melts at approximately 232degC. This lower melting point enhances workability and reduces thermal stress on components during soldering applications. Consequently, smart metal solder is preferred in precision electronics where temperature-sensitive parts require gentle heat exposure.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Smart metal solder alloys exhibit higher electrical conductivity compared to traditional tin-based solder, enhancing signal integrity in electronic circuits. The superior conductivity reduces resistance and power loss, critical for high-frequency and sensitive applications. Tin solders often contain impurities and alloying elements that lower conductivity, making smart metals a preferred choice for performance-driven soldering tasks.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Smart metal solder alloys typically offer superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to traditional tin-based solders, due to advanced formulations incorporating elements like silver, copper, and nickel. These metals improve tensile strength and resistance to thermal fatigue, making smart metal solders ideal for high-stress electronic applications. Tin solder, while cost-effective and widely used, generally exhibits lower mechanical strength and reduced longevity under mechanical and thermal cycling conditions.
Corrosion Resistance: Smart Metal vs Tin
Smart metal solder alloys exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to traditional tin-based solders, reducing the risk of oxidation and prolonging joint reliability in harsh environments. While tin solder tends to form tin whiskers and is prone to oxidation, smart metal compositions often include alloying elements that inhibit these degradation processes and enhance durability. This improved corrosion resistance makes smart metals ideal for high-performance electronic assemblies exposed to moisture and corrosive agents.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Smart metal solder, often containing non-toxic elements like silver or copper, reduces hazardous waste compared to traditional tin-lead solder, enhancing environmental sustainability. Tin solder, especially lead-based variants, poses significant health risks due to lead toxicity and environmental contamination during disposal. Choosing lead-free smart metal solder minimizes ecological damage and improves workplace safety by lowering exposure to toxic metals.
Cost and Availability
Smart metal solder typically costs more than traditional tin solder due to advanced alloy compositions designed for improved performance. Tin solder remains widely available and affordable, benefiting from established manufacturing and supply chains globally. Cost efficiency and ubiquitous availability make tin solder the preferred choice for general electronics assembly where budget constraints are critical.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Smart metal solder alloys offer superior thermal conductivity and mechanical strength compared to traditional tin-based solders, enhancing reliability in high-performance electronic devices. Applications in modern electronics such as smartphones, wearables, and automotive sensors benefit from smart metal's improved resistance to thermal cycling and oxidation. Tin solder remains cost-effective and widely used for general circuit assembly but often underperforms in environments requiring enhanced durability and electrical performance.
Future Trends in Soldering Materials
Smart metals, such as silver-based alloys and high-performance composites, are poised to revolutionize soldering by offering enhanced thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance compared to traditional tin-based solders. Future trends indicate a growing preference for lead-free and environmentally friendly smart metal formulations that improve joint reliability in advanced electronics and automotive applications. Emerging materials integrate nanotechnology and bio-based components to optimize soldering processes, reduce energy consumption, and meet stricter regulatory standards worldwide.
Infographic: Smart metal vs Tin for Solder
 azmater.com
azmater.com