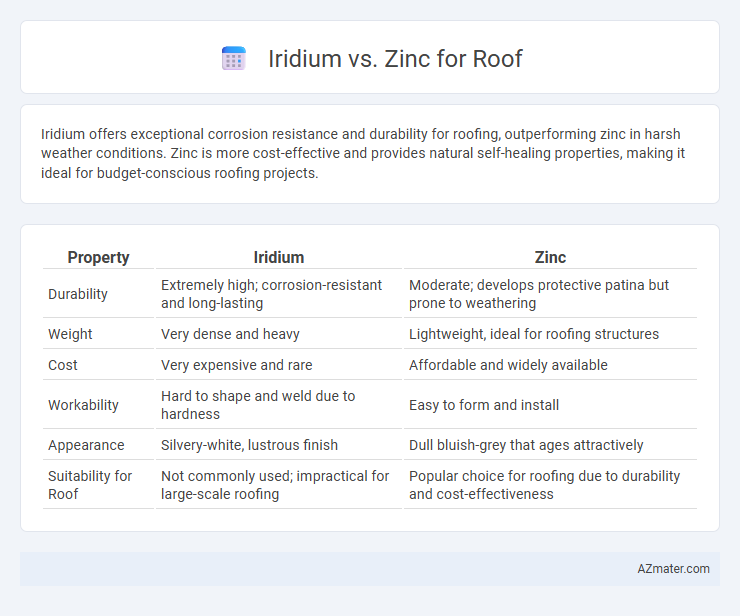
Iridium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and durability for roofing, outperforming zinc in harsh weather conditions. Zinc is more cost-effective and provides natural self-healing properties, making it ideal for budget-conscious roofing projects.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Iridium | Zinc |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Extremely high; corrosion-resistant and long-lasting | Moderate; develops protective patina but prone to weathering |
| Weight | Very dense and heavy | Lightweight, ideal for roofing structures |
| Cost | Very expensive and rare | Affordable and widely available |
| Workability | Hard to shape and weld due to hardness | Easy to form and install |
| Appearance | Silvery-white, lustrous finish | Dull bluish-grey that ages attractively |
| Suitability for Roof | Not commonly used; impractical for large-scale roofing | Popular choice for roofing due to durability and cost-effectiveness |
Introduction to Iridium and Zinc Roofing
Iridium roofing offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh weather conditions and long-term performance. Zinc roofing is favored for its natural self-healing properties, sustainability, and aesthetic versatility, commonly used in historic and modern architecture. Both materials provide energy efficiency and require minimal maintenance, but differ significantly in cost, appearance, and environmental impact.
Material Composition and Properties
Iridium and zinc differ significantly in material composition and properties relevant to roofing applications; iridium is a dense, corrosion-resistant precious metal with exceptional durability but is costly and rare, whereas zinc is a more affordable, lightweight metal known for its natural patina development and excellent resistance to corrosion through a protective oxide layer. Zinc's malleability and self-healing surface make it ideal for complex roof shapes and long-term weather resistance. Iridium's superior hardness and chemical inertness are less practical for large-scale roofing but beneficial in niche architectural accents requiring extreme durability.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Iridium roofing materials exhibit exceptional durability due to their resistance to corrosion, extreme weather, and UV radiation, significantly outperforming zinc in harsh environments. Zinc roofs offer good longevity, typically lasting 40 to 70 years, but Iridium roofing systems can extend beyond 80 years with minimal maintenance. The superior strength and non-corrosive properties of Iridium result in longer-lasting roofs that maintain structural integrity and aesthetic appeal over time.
Weather Resistance: Iridium vs Zinc
Iridium roofing offers superior weather resistance compared to zinc, with exceptional durability against extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and heavy rainfall due to its advanced alloy composition. Zinc is naturally corrosion-resistant and can develop a protective patina over time, but it is more susceptible to oxidation and erosion in harsh weather conditions. Iridium's enhanced strength and corrosion resistance make it ideal for environments with frequent storms and temperature fluctuations, ensuring longer roof lifespan and reduced maintenance.
Aesthetic Appeal and Design Options
Iridium roofing offers a sleek, modern aesthetic with a metallic sheen that enhances contemporary architectural designs, while zinc provides a more traditional, matte finish that naturally develops a protective patina over time, adding character and charm. Zinc's flexibility allows for intricate patterns and customized shapes, making it ideal for unique, artistic roof designs, whereas Iridium's rigidity supports bold, clean lines for minimalist and high-tech structures. Both materials boast durability and corrosion resistance, but zinc's evolving surface texture offers a dynamic visual appeal that changes with age, contrasting with the consistent polished look of Iridium.
Installation Process and Complexity
Iridium roofing materials offer a straightforward installation process due to their lightweight and flexible properties, reducing labor time and ensuring easier handling on rooftops. Zinc roofs require skilled professionals for installation because of their heavier weight and the need for precise technique in seaming and soldering to ensure durability and weather resistance. The complexity of zinc installation can increase overall project duration and cost, while Iridium's simpler application typically results in faster completion and lower labor expenses.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Iridium roofing materials generally have a higher upfront cost compared to zinc due to their advanced durability and corrosion resistance properties, which translate to reduced maintenance expenses over time. Zinc roofing offers a more affordable initial investment but may require more frequent repairs or replacements, increasing long-term costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses reveals that Iridium's premium pricing is often offset by its extended lifespan and lower upkeep, making it a cost-efficient choice for long-term roofing solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Iridium roofing offers superior environmental benefits due to its longevity and corrosion resistance, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing material waste. Zinc roofs are highly sustainable owing to their recyclability and low embodied energy, making them a popular eco-friendly choice in green building practices. Both materials support sustainable construction, but zinc's natural patina and recyclability provide a distinct ecological advantage over iridium's rarity and higher extraction impact.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifespan
Iridium roofing materials exhibit superior corrosion resistance with minimal maintenance, typically requiring inspections every 5 to 7 years, while zinc roofs need more frequent upkeep due to potential patina changes and can demand cleaning or treatment every 3 to 5 years. The lifespan of Iridium roof technology often exceeds 50 years, benefiting from its durable alloys and protective coatings, whereas zinc roofs generally last between 40 and 60 years depending on environmental exposure and maintenance routines. Choosing Iridium can reduce long-term maintenance costs and extend durability, making it a viable option for high-performance roofing solutions.
Final Verdict: Which Roofing Material is Best?
Iridium roofing offers exceptional durability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for harsh weather conditions, while zinc provides excellent longevity with a natural patina that enhances its protective layer over time. Zinc panels are lighter and more environmentally friendly, supporting sustainable building practices with easy recyclability. For homeowners prioritizing long-term performance and low maintenance, Iridium is best suited; however, zinc is preferable for eco-conscious projects demanding aesthetically aging roofing.
Infographic: Iridium vs Zinc for Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com