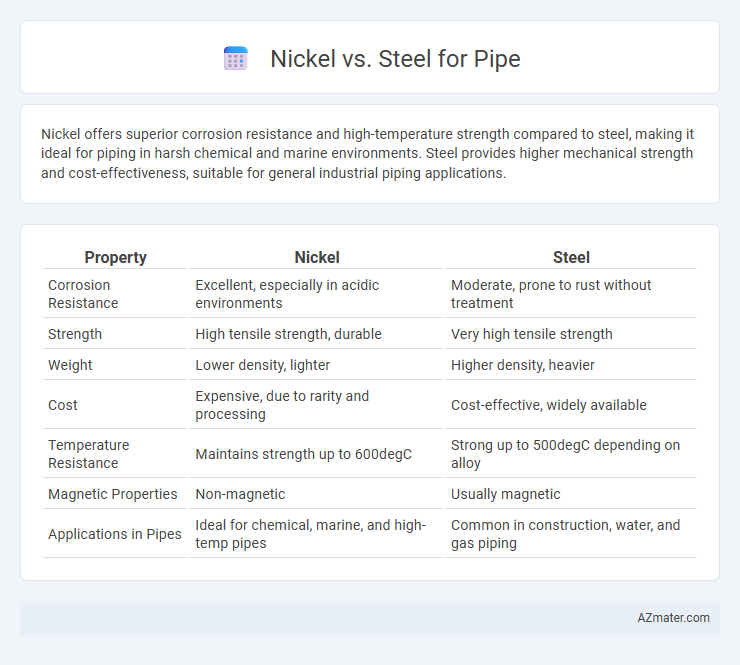
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to steel, making it ideal for piping in harsh chemical and marine environments. Steel provides higher mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness, suitable for general industrial piping applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nickel | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, especially in acidic environments | Moderate, prone to rust without treatment |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Very high tensile strength |
| Weight | Lower density, lighter | Higher density, heavier |
| Cost | Expensive, due to rarity and processing | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Temperature Resistance | Maintains strength up to 600degC | Strong up to 500degC depending on alloy |
| Magnetic Properties | Non-magnetic | Usually magnetic |
| Applications in Pipes | Ideal for chemical, marine, and high-temp pipes | Common in construction, water, and gas piping |
Introduction to Nickel and Steel Pipes
Nickel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance, high-temperature strength, and excellent durability, making them ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Steel pipes, particularly carbon and stainless steel varieties, provide high mechanical strength, cost-effectiveness, and versatility in construction and industrial use. Understanding the distinctions between nickel and steel pipes is crucial for selecting materials based on environmental conditions and performance requirements.
Chemical Composition Differences
Nickel pipes primarily consist of high nickel content, usually above 60%, providing superior corrosion resistance, especially in acidic environments, due to nickel's stable passive oxide layer. In contrast, steel pipes contain significant iron with varying amounts of carbon, manganese, and trace elements, which affect strength but make them more susceptible to rust and chemical degradation without protective coatings. The chemical composition shifts between these metals directly influence their suitability for different industrial applications, with nickel alloys favored for harsh chemical resistance and steel preferred for structural strength and cost efficiency.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nickel alloys generally exhibit higher tensile strength and better corrosion resistance compared to standard carbon steel, making them suitable for high-stress environments and extreme temperatures. Steel pipes, especially those made from stainless steel grades like 304 or 316, offer excellent mechanical strength and toughness but may underperform compared to nickel in resistance to thermal expansion and fatigue. Selecting between nickel and steel for piping depends on specific mechanical property requirements such as yield strength, elongation, and operating conditions.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
Nickel offers superior corrosion resistance compared to steel, particularly in harsh environments with acidic, alkaline, or saline conditions, thanks to its stable oxide layer that prevents surface degradation. Steel, especially carbon steel, is prone to rust and corrosion unless treated or alloyed with elements like chromium to form stainless steel. Stainless steel pipes, containing nickel and chromium, provide enhanced corrosion resistance but typically cannot match the pure nickel's resilience against highly aggressive media such as sulfuric acid or seawater.
Temperature Tolerance Performance
Nickel pipes exhibit superior temperature tolerance compared to steel, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 1000degF (538degC), whereas steel typically withstands up to 800degF (427degC) before compromising strength. Nickel's high melting point of around 2470degF (1354degC) and excellent oxidation resistance make it ideal for high-temperature applications in chemical processing and power generation. In contrast, steel may suffer from thermal fatigue and scaling under prolonged heat exposure, limiting its performance in extreme thermal environments.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Nickel pipes generally have a higher initial cost compared to steel pipes due to the expense of raw nickel material and specialized manufacturing processes. Steel pipes offer a more economical option for large-scale projects because of their lower price and widespread availability, making them cost-effective for standard applications. Long-term economic considerations include nickel's superior corrosion resistance, which can reduce maintenance and replacement costs in harsh environments, potentially offsetting its higher upfront price.
Fabrication and Welding Comparison
Nickel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and flexibility during fabrication, making them ideal for complex or high-temperature applications, while steel pipes provide greater strength and are more cost-effective for standard pressure environments. Welding nickel requires specialized techniques and filler materials to prevent cracking and preserve its corrosion-resistant properties, whereas steel welding is more straightforward with widely available equipment and expertise. The choice depends on the application's environmental and mechanical demands, with nickel preferred for harsh chemical exposure and steel favored for structural strength and economic fabrication.
Lifespan and Durability Factors
Nickel pipes offer superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to steel pipes, especially in harsh chemical or high-temperature environments. Steel pipes, while strong and cost-effective, are prone to rust and degradation over time when exposed to moisture or corrosive elements, reducing their durability. The enhanced alloy composition in nickel increases resistance to oxidation and mechanical wear, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring extended service life and minimal maintenance.
Common Applications in Industry
Nickel pipes are widely used in chemical processing, aerospace, and marine industries due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Steel pipes, particularly carbon and stainless steel, dominate in oil and gas, construction, and water supply systems because of their durability, cost-effectiveness, and mechanical strength. The choice between nickel and steel pipes depends on specific application requirements such as exposure to corrosive environments and temperature thresholds.
Choosing the Right Material for Pipes
Nickel alloys offer superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength compared to steel, making them ideal for chemical processing and extreme environments. Steel pipes provide excellent mechanical strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of fabrication, suitable for water distribution and structural applications. Selecting between nickel and steel pipes depends on factors like environmental conditions, required durability, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Nickel vs Steel for Pipe
 azmater.com
azmater.com