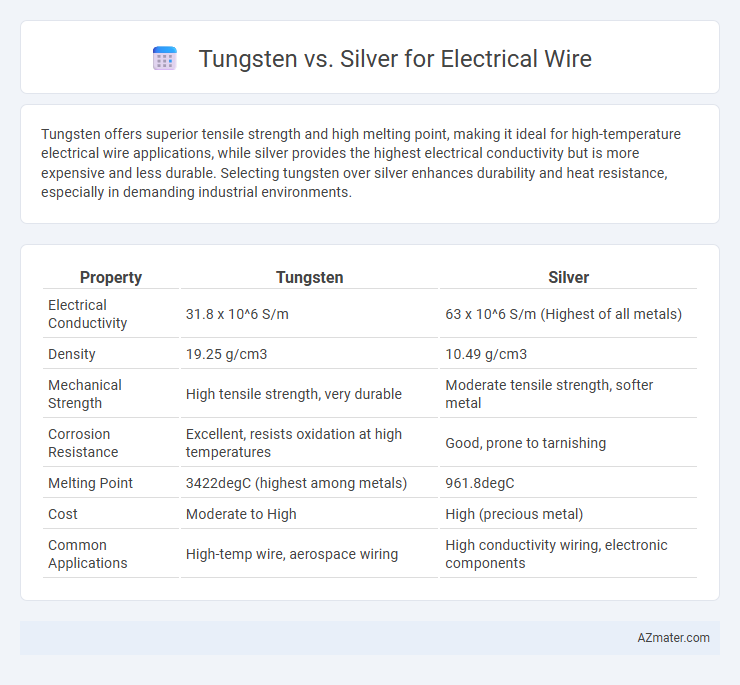
Tungsten offers superior tensile strength and high melting point, making it ideal for high-temperature electrical wire applications, while silver provides the highest electrical conductivity but is more expensive and less durable. Selecting tungsten over silver enhances durability and heat resistance, especially in demanding industrial environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tungsten | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 31.8 x 10^6 S/m | 63 x 10^6 S/m (Highest of all metals) |
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 10.49 g/cm3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, very durable | Moderate tensile strength, softer metal |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation at high temperatures | Good, prone to tarnishing |
| Melting Point | 3422degC (highest among metals) | 961.8degC |
| Cost | Moderate to High | High (precious metal) |
| Common Applications | High-temp wire, aerospace wiring | High conductivity wiring, electronic components |
Introduction: Comparing Tungsten and Silver as Electrical Wires
Tungsten and silver are two metals often compared for electrical wiring due to their distinct conductivity and mechanical properties. Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among metals, making it highly efficient for current transmission, while tungsten offers exceptional strength and high melting point, enhancing durability in extreme conditions. Choosing between tungsten and silver depends on balancing conductivity needs with mechanical resilience and cost considerations.
Electrical Conductivity: Tungsten vs Silver
Silver boasts the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, approximately 63 million Siemens per meter, making it the most efficient material for electrical wire. Tungsten's electrical conductivity is significantly lower, around 18 million Siemens per meter, roughly 30% of silver's conductivity, which results in higher resistance and energy loss when used as wiring. Despite tungsten's superior mechanical strength and high melting point, silver remains the preferred choice for applications prioritizing minimal electrical resistance and maximum conductivity.
Thermal Conductivity Differences
Tungsten and silver differ significantly in thermal conductivity, with silver exhibiting one of the highest thermal conductivities among metals at approximately 429 W/m*K, making it exceptional for dissipating heat in electrical wiring. Tungsten's thermal conductivity, around 173 W/m*K, is considerably lower but remains notable for high-temperature applications due to its superior melting point and mechanical strength. Choosing silver wire enhances heat dissipation and reduces resistive losses, while tungsten wire offers thermal stability and durability in extreme environments.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Tungsten exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to silver, making it highly resistant to deformation and wear in electrical wire applications. Its high tensile strength and low thermal expansion contribute to maintaining stable conductivity under extreme mechanical stress and temperature variations. Despite silver's excellent conductivity, tungsten's robust mechanical properties ensure longer lifespan and reliability in demanding industrial environments.
Corrosion Resistance in Wiring Applications
Tungsten exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to silver in electrical wiring applications, making it ideal for environments prone to oxidation and chemical exposure. Silver, while an excellent conductor, tarnishes quickly when exposed to air and sulfur compounds, which can degrade electrical performance over time. The inherently robust oxide layer on tungsten wires enhances long-term reliability and minimizes maintenance needs in corrosive conditions.
Cost and Availability of Tungsten and Silver
Tungsten offers lower cost and greater availability compared to silver, making it a budget-friendly option for electrical wiring. Silver, while highly conductive, is significantly more expensive and less abundant, limiting its use in large-scale applications. The economic advantage and more stable supply of tungsten contribute to its preferred use where cost and material availability are critical factors.
Common Uses in Electrical Engineering
Tungsten wires are commonly used in high-temperature and high-wear electrical applications such as vacuum tubes, light bulb filaments, and aerospace components due to their excellent thermal resistance and mechanical strength. Silver wires, known for their superior electrical conductivity, are frequently utilized in high-frequency and low-resistance connections, including RF connectors, printed circuit boards, and advanced electronic devices. Both metals serve specialized roles in electrical engineering, with tungsten favored for durability under extreme conditions and silver prioritized for optimal electrical performance.
Suitability for High-Temperature Environments
Tungsten excels in high-temperature electrical wiring due to its exceptional melting point of 3,422degC, making it highly resistant to thermal degradation and ideal for extreme environments such as aerospace and industrial furnaces. Silver, while offering superior electrical conductivity, has a much lower melting point of 961.8degC, limiting its use in high-temperature applications where thermal stability is critical. Tungsten's low thermal expansion and durability under intense heat ensure reliable performance in electrical components exposed to severe thermal conditions.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Tungsten offers higher melting point and better thermal stability compared to silver, reducing fire hazards and enhancing safety in electrical wiring applications. Silver, while highly conductive, is prone to oxidation and environmental degradation, which may compromise wire integrity over time. The sustainable extraction and lower environmental impact of tungsten mining further establish it as a safer choice for eco-conscious electrical infrastructure.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for Your Electrical Needs
Tungsten offers high tensile strength and excellent heat resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and high-temperature performance, while silver provides superior electrical conductivity, ensuring minimal energy loss in sensitive circuits. For standard electrical wiring, silver's efficiency and conductivity make it the preferred choice, despite its higher cost, whereas tungsten is suited for specialized environments such as high-stress or high-temperature conditions. Selecting between tungsten and silver depends on balancing conductivity needs with environmental factors and mechanical strength requirements for optimal electrical performance.
Infographic: Tungsten vs Silver for Electrical Wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com