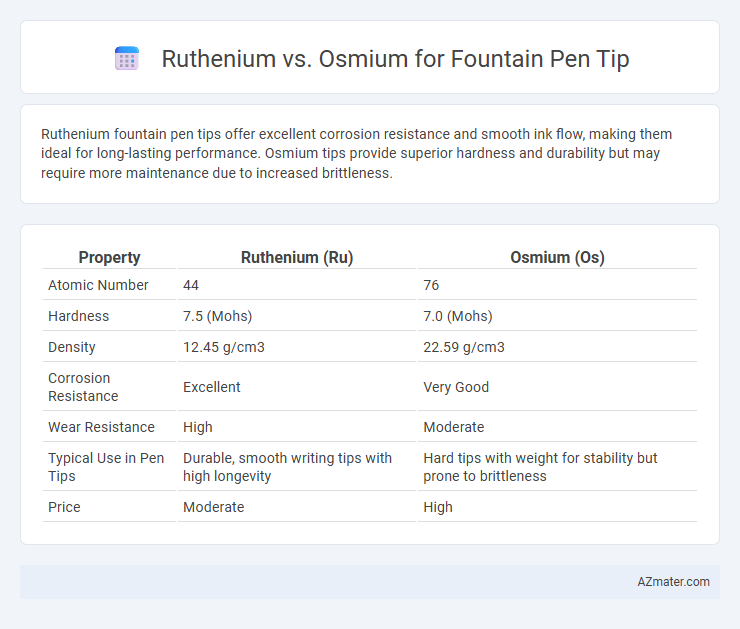
Ruthenium fountain pen tips offer excellent corrosion resistance and smooth ink flow, making them ideal for long-lasting performance. Osmium tips provide superior hardness and durability but may require more maintenance due to increased brittleness.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Osmium (Os) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 44 | 76 |
| Hardness | 7.5 (Mohs) | 7.0 (Mohs) |
| Density | 12.45 g/cm3 | 22.59 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Wear Resistance | High | Moderate |
| Typical Use in Pen Tips | Durable, smooth writing tips with high longevity | Hard tips with weight for stability but prone to brittleness |
| Price | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Fountain Pen Tipping Materials
Ruthenium and Osmium are two of the rarest and hardest platinum-group metals used in fountain pen tips, prized for their durability and corrosion resistance. Ruthenium offers excellent wear properties and smooth writing due to its hardness and ability to form a thin, durable layer on nibs. Osmium, while denser and harder than Ruthenium, is less commonly used due to its brittleness and the difficulty of handling it in thin tip applications.
Overview of Ruthenium and Osmium
Ruthenium and Osmium are both platinum group metals prized for their exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for fountain pen tips. Ruthenium offers superior scratch resistance and a slightly lower density, which contributes to a smoother writing experience and longer tip durability. Osmium, the densest naturally occurring element, provides unmatched wear resistance and a distinctive dark hue, enhancing the pen's aesthetics along with its functional lifespan.
Historical Use of Metals in Pen Tips
Ruthenium and osmium have both played significant roles in the evolution of fountain pen tips, with osmium historically favored due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance, ensuring durability and smooth writing. Ruthenium, as a member of the platinum group metals, gained attention for its corrosion resistance and moderate hardness, making it a valuable alternative in pen nib alloys during the 20th century. The transition from osmium-tipped pens to ruthenium-alloyed tips reflects advances in metallurgy aimed at enhancing nib longevity and writing performance.
Physical Properties: Ruthenium vs Osmium
Ruthenium and osmium, both members of the platinum group metals, exhibit exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, crucial for fountain pen tips. Ruthenium has a hardness of about 6.5 on the Mohs scale and offers greater wear resistance, enhancing durability under frequent writing conditions. Osmium ranks higher in density (22.59 g/cm3) and hardness (around 7 on the Mohs scale), but its brittleness can affect longevity and flexibility in the delicate nib structure.
Hardness and Durability Comparison
Ruthenium and osmium are platinum-group metals known for exceptional hardness and durability, essential for fountain pen tips. Osmium is the hardest naturally occurring element with a Mohs hardness of about 7, offering superior wear resistance and long-lasting performance under constant ink flow. Ruthenium, while slightly softer with a Mohs hardness around 6, provides excellent corrosion resistance and flexibility, making it a durable yet slightly more resilient option for fountain pen nib tips.
Corrosion Resistance in Fountain Pen Tips
Ruthenium and osmium, both platinum-group metals, exhibit exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for fountain pen tips exposed to varying ink chemistries. Ruthenium demonstrates superior resistance to oxidizing and acidic conditions commonly found in inks, which prevents tip degradation and ensures long-term durability. Osmium, though highly dense and hard, is more prone to surface oxidation, potentially affecting its performance over extended use in fountain pen applications.
Writing Experience: Smoothness and Feedback
Ruthenium fountain pen tips offer exceptional smoothness and a moderate amount of feedback, making them ideal for writers who appreciate fluid strokes with subtle tactile sensation. Osmium tips provide a slightly firmer writing experience with increased feedback, favored by those seeking precision and control during long writing sessions. Both metals boast excellent durability and resistance to wear, enhancing the overall lifespan of the fountain pen nib.
Manufacturing and Availability
Ruthenium and Osmium are both platinum-group metals used for fountain pen tips due to their exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, but Ruthenium is preferred in manufacturing because it is more readily available and easier to alloy with other metals. Osmium, while harder and denser, presents challenges in processing due to its brittleness and scarcity, making it less practical for mass production of pen nibs. Availability of Ruthenium, sourced primarily from South African and Russian mines, ensures more consistent supply chains compared to the limited and expensive Osmium reserves, impacting overall cost-efficiency in fountain pen tip manufacturing.
Cost Considerations for Pen Makers and Users
Ruthenium and osmium are both platinum group metals used in fountain pen tips, with ruthenium generally being more affordable due to its relatively greater abundance and lower market price. Pen makers often choose ruthenium for cost-effective manufacturing while maintaining durability and corrosion resistance essential for smooth writing. Osmium, though offering superior hardness and longevity, commands a higher price, making it a premium choice for luxury pens aimed at users willing to invest in lasting quality.
Choosing the Best Metal for Fountain Pen Tips
Ruthenium and osmium are both dense, corrosion-resistant platinum-group metals commonly used in high-quality fountain pen tips for durability and smooth writing. Osmium, known for its extreme hardness and high wear resistance, offers superior longevity and a consistently smooth ink flow, making it ideal for frequent writers. Ruthenium provides excellent scratch resistance and a slightly softer feel, preferred by those seeking balanced durability with a more responsive writing experience.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Osmium for Fountain Pen Tip
 azmater.com
azmater.com