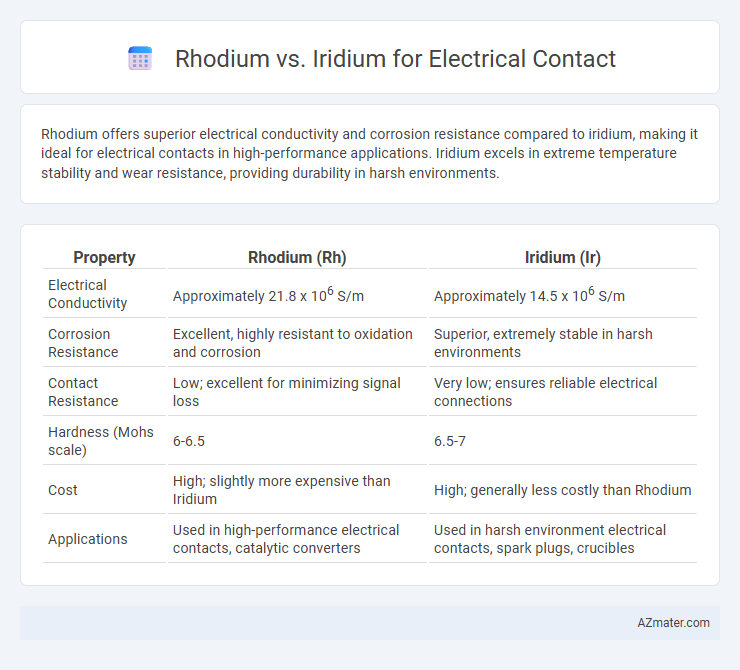
Rhodium offers superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to iridium, making it ideal for electrical contacts in high-performance applications. Iridium excels in extreme temperature stability and wear resistance, providing durability in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium (Rh) | Iridium (Ir) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Approximately 21.8 x 106 S/m | Approximately 14.5 x 106 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion | Superior, extremely stable in harsh environments |
| Contact Resistance | Low; excellent for minimizing signal loss | Very low; ensures reliable electrical connections |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 6-6.5 | 6.5-7 |
| Cost | High; slightly more expensive than Iridium | High; generally less costly than Rhodium |
| Applications | Used in high-performance electrical contacts, catalytic converters | Used in harsh environment electrical contacts, spark plugs, crucibles |
Introduction to Rhodium and Iridium in Electrical Contacts
Rhodium and iridium are both precious metals widely used in electrical contacts due to their exceptional corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity. Rhodium offers superior hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-performance contacts in harsh environments. Iridium provides excellent stability at high temperatures and maintains conductivity under extreme conditions, ensuring reliable electrical performance.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher electrical conductivity compared to iridium, making it ideal for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Iridium exhibits exceptional hardness and melting point, providing enhanced durability and resistance to wear under high-temperature conditions. Both metals resist oxidation effectively, but rhodium's lower density and better surface reflectivity contribute to improved performance in precision connectors.
Electrical Conductivity: Rhodium vs Iridium
Rhodium exhibits higher electrical conductivity compared to iridium, making it a preferred choice for electrical contact applications requiring efficient current transfer. Iridium, while offering superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, has lower conductivity which may reduce performance in high-current environments. The electrical resistivity of rhodium is approximately 4.5 uO*cm, whereas iridium's resistivity is around 5.3 uO*cm, highlighting rhodium's advantage in minimizing energy loss.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Rhodium offers superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to iridium, making it highly effective for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Its ability to maintain conductivity and minimize surface degradation under high-temperature and oxidative conditions extends the lifespan of electrical components. Iridium, while corrosion-resistant, tends to oxidize more readily at elevated temperatures, reducing its long-term reliability in electrical contact applications.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
Rhodium exhibits high hardness and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for electrical contacts requiring durability and resistance to wear and deformation. Iridium, although slightly softer than rhodium, offers superior toughness and resistance to impact, enhancing contact longevity under mechanical stress. Both metals provide outstanding corrosion resistance, but rhodium's combination of hardness and strength makes it preferable for applications with high mechanical demands.
Contact Wear and Lifespan
Rhodium and iridium are both durable materials used for electrical contacts, with rhodium offering superior corrosion resistance that significantly reduces contact wear in harsh environments. Iridium exhibits exceptional hardness and high melting point, contributing to extended lifespan by resisting deformation under high current loads. Studies indicate rhodium contacts maintain lower contact resistance over time, whereas iridium's mechanical stability ensures longevity in abrasive or high-stress applications.
Cost and Availability of Rhodium and Iridium
Rhodium, significantly rarer than iridium, commands higher prices due to constrained supply and intense demand in automotive and electrical industries. Iridium offers greater availability and slightly lower cost, making it a more common choice for electrical contacts where budget constraints exist. Both metals provide excellent corrosion resistance and conductivity, but cost and accessibility often determine their application.
Industrial and Application-Specific Uses
Rhodium and iridium are rare platinum-group metals widely used in electrical contacts due to their excellent corrosion resistance and high melting points. Rhodium offers superior electrical conductivity and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-reliability industrial switches, automotive spark plugs, and precision connectors. Iridium's exceptional hardness and stability under extreme temperatures suit aerospace components, medical devices, and high-current electrical contacts where durability and longevity are critical.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical contacts in harsh environments, while its extraction and refinement have a moderate environmental impact. Iridium, known for its exceptional durability and high melting point, provides reliable performance in high-temperature applications but involves more energy-intensive mining processes that pose greater environmental concerns. Both metals require careful handling due to their rarity and potential health risks during processing, emphasizing the need for sustainable sourcing and strict workplace safety protocols.
Choosing the Right Metal for Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in harsh environments. Iridium provides exceptional hardness and wear resistance, which ensures durability in heavy-duty applications requiring frequent switching. Selecting the right metal depends on balancing conductivity and longevity requirements, with rhodium preferred for low-resistance connections and iridium suited for extreme durability and mechanical stress.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Iridium for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com