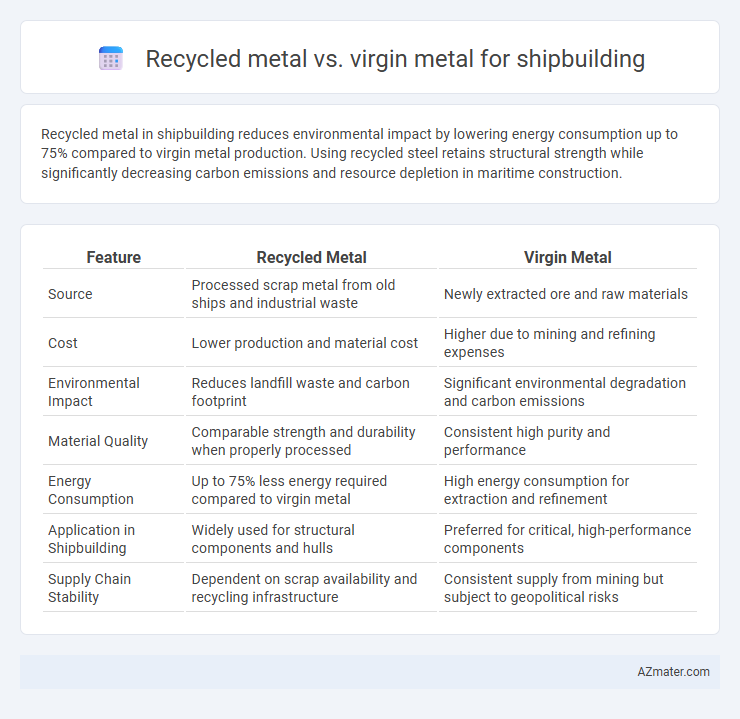
Recycled metal in shipbuilding reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption up to 75% compared to virgin metal production. Using recycled steel retains structural strength while significantly decreasing carbon emissions and resource depletion in maritime construction.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled Metal | Virgin Metal |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Processed scrap metal from old ships and industrial waste | Newly extracted ore and raw materials |
| Cost | Lower production and material cost | Higher due to mining and refining expenses |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces landfill waste and carbon footprint | Significant environmental degradation and carbon emissions |
| Material Quality | Comparable strength and durability when properly processed | Consistent high purity and performance |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 75% less energy required compared to virgin metal | High energy consumption for extraction and refinement |
| Application in Shipbuilding | Widely used for structural components and hulls | Preferred for critical, high-performance components |
| Supply Chain Stability | Dependent on scrap availability and recycling infrastructure | Consistent supply from mining but subject to geopolitical risks |
Introduction to Metal Choices in Shipbuilding
Recycled metal and virgin metal both play critical roles in shipbuilding, with recycled metal offering environmental benefits and cost efficiency, while virgin metal ensures higher purity and structural integrity. Shipbuilders often assess strength, corrosion resistance, and availability when choosing between these metals to meet strict maritime safety standards. Advances in recycling technology have improved the quality of recycled metals, making them a viable alternative in many ship hull and structural applications.
Overview of Recycled Metal in Ship Construction
Recycled metal in ship construction offers sustainable advantages by reducing the demand for virgin metal extraction and lowering energy consumption during production. The use of recycled steel and aluminum maintains essential structural integrity while promoting environmental benefits such as decreased carbon emissions. Shipbuilders increasingly prioritize recycled metals to meet regulatory standards and support circular economy goals within the maritime industry.
Virgin Metal: Definition and Applications in Shipbuilding
Virgin metal refers to raw metal extracted directly from ore, characterized by its high purity and consistent properties essential for structural integrity in shipbuilding. In ship construction, virgin metals such as steel, aluminum, and copper are preferred for critical components like hulls, frames, and propulsion systems to ensure strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. The superior mechanical properties and traceability of virgin metals make them indispensable for meeting stringent maritime safety standards and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact: Recycled vs Virgin Metal
Recycled metal in shipbuilding significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to virgin metal production, which involves intensive mining and ore processing. The use of recycled metals conserves natural resources and decreases landfill waste, contributing to a more sustainable shipbuilding industry. Life cycle assessments show that recycled steel can cut carbon emissions by up to 58%, making it a more eco-friendly choice for marine construction.
Cost Comparison: Recycled Metal vs Virgin Metal
Recycled metal for shipbuilding often reduces raw material costs by 20-40% compared to virgin metal due to lower extraction and processing expenses. Virgin metal incurs higher costs from intensive mining, refining, and transportation processes, increasing overall ship production budgets. Choosing recycled metal supports cost-efficiency while maintaining structural integrity and adherence to maritime industry standards.
Mechanical Properties and Performance
Recycled metal in shipbuilding offers comparable mechanical properties to virgin metal, including tensile strength, ductility, and fatigue resistance, when processed with advanced refining techniques. Performance-wise, recycled metals maintain structural integrity under marine stressors such as corrosion and impact, ensuring long-term durability. Utilizing recycled metal reduces environmental impact and material costs without compromising the ship's safety and operational efficiency.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Recycled metal in shipbuilding offers comparable durability to virgin metal when properly processed, ensuring structural integrity under marine conditions. Corrosion resistance in recycled metals depends on alloy composition and treatment methods, with high-quality recycling processes achieving similar protection against saltwater and environmental exposure. Selecting recycled metals with certified corrosion-resistant coatings enhances longevity and reduces maintenance costs for maritime vessels.
Supply Chain and Material Availability
Recycled metal offers a more sustainable and cost-effective supply chain solution with reduced lead times compared to virgin metal, which depends heavily on mining and refining processes vulnerable to geopolitical and environmental disruptions. The availability of recycled metal fluctuates with scrap market dynamics but benefits from established collection and processing infrastructure near shipbuilding hubs. Virgin metal supply faces longer production cycles and higher carbon footprints, impacting project timelines and material sourcing reliability.
Regulatory Standards for Shipbuilding Metals
Recycled metal in shipbuilding must adhere to strict regulatory standards such as those outlined by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and classification societies like ABS and Lloyd's Register, ensuring it meets durability, corrosion resistance, and structural integrity requirements equivalent to virgin metal. Virgin metals typically provide more consistent material properties, making compliance with standards like ISO 9001 and IMO's SOLAS easier to verify during material certification. Regulatory frameworks prioritize traceability, quality control, and environmental impact, influencing the choice between recycled and virgin metals in ship construction for safety and sustainability compliance.
Future Trends: Sustainability in Shipbuilding Materials
Recycled metal plays a pivotal role in advancing sustainability within shipbuilding, reducing reliance on energy-intensive virgin metal extraction and lowering carbon emissions by up to 60%. Emerging trends highlight the integration of high-quality recycled alloys that maintain structural integrity while promoting circular economy principles. Innovations in sorting technology and metallurgical processes are expected to enhance the scalability and cost-effectiveness of recycled metal usage, driving greener ship construction.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Virgin metal for Shipbuilding
 azmater.com
azmater.com