Rare earth metals offer superior magnetic and phosphorescent properties essential for high-performance electronics, while silver provides unmatched electrical conductivity and thermal efficiency. Selecting rare earth metals enhances device miniaturization and durability, whereas silver is preferred in circuit wiring and contacts for optimal signal transmission.
Table of Comparison
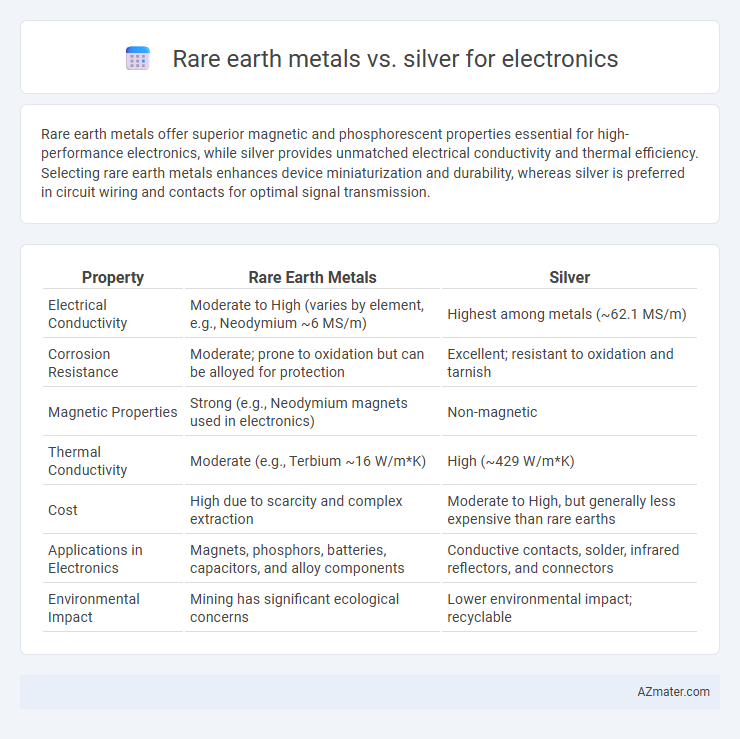
| Property | Rare Earth Metals | Silver |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate to High (varies by element, e.g., Neodymium ~6 MS/m) | Highest among metals (~62.1 MS/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; prone to oxidation but can be alloyed for protection | Excellent; resistant to oxidation and tarnish |
| Magnetic Properties | Strong (e.g., Neodymium magnets used in electronics) | Non-magnetic |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (e.g., Terbium ~16 W/m*K) | High (~429 W/m*K) |
| Cost | High due to scarcity and complex extraction | Moderate to High, but generally less expensive than rare earths |
| Applications in Electronics | Magnets, phosphors, batteries, capacitors, and alloy components | Conductive contacts, solder, infrared reflectors, and connectors |
| Environmental Impact | Mining has significant ecological concerns | Lower environmental impact; recyclable |
Introduction to Rare Earth Metals and Silver in Electronics
Rare earth metals such as neodymium, dysprosium, and praseodymium are critical for manufacturing powerful magnets, essential in electronic devices like smartphones, hard drives, and electric vehicles due to their superior magnetic and conductive properties. Silver, known for its exceptional electrical conductivity and thermal stability, is widely used in electronic components including connectors, switches, and printed circuit boards to enhance performance and reliability. While rare earth metals contribute to the miniaturization and efficiency of modern electronics, silver remains indispensable for optimal conductivity and durability in electrical contacts and circuitry.
Composition and Properties: Rare Earth Metals vs Silver
Rare earth metals consist primarily of 17 elements with unique magnetic, phosphorescent, and catalytic properties that enhance electronic device performance, especially in components like magnets, batteries, and display screens. Silver, a precious metal known for its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, is widely used in electronic contacts and conductive inks due to its low resistivity and stability. The composition of rare earth metals offers superior magnetic and catalytic functionalities, whereas silver excels in electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making each material critical for distinct electronic applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Silver exhibits the highest electrical conductivity among all metals, making it exceptionally efficient for electronic applications where minimal resistance is crucial. Rare earth metals, while offering unique magnetic and optical properties, generally possess lower electrical conductivity compared to silver, limiting their use in high-performance electrical components. For circuits and connectors demanding optimal current flow, silver remains the preferred choice due to its superior conductive efficiency.
Availability and Supply Chain Issues
Rare earth metals are crucial for electronics due to their unique magnetic and conductive properties, but their availability is limited by concentrated extraction in a few countries, leading to supply chain vulnerabilities and geopolitical risks. Silver, while more abundant and widely distributed globally, faces challenges in supply due to high demand in multiple industries and environmentally intensive mining processes. Both materials experience supply chain disruptions, but rare earth metals are more susceptible due to fewer substitutes and complex refining requirements.
Cost Analysis: Rare Earth Metals vs Silver
Rare earth metals, despite their critical role in advanced electronics, generally have a higher cost per kilogram than silver due to limited supply and complex extraction processes. Silver, valued for its superior electrical conductivity and relative abundance, offers a more cost-effective option for many electronic applications, especially in large-scale manufacturing. However, the volatility in rare earth metal prices driven by geopolitical factors and environmental regulations can significantly impact overall production costs in electronics where these materials are essential.
Applications of Rare Earth Metals in Modern Electronics
Rare earth metals like neodymium, europium, and yttrium play critical roles in modern electronics by enabling powerful magnets, phosphors for display screens, and efficient catalysts, which silver cannot fully replace. Neodymium magnets are essential in compact, high-performance devices such as hard drives, microphones, and electric motors, whereas europium and yttrium contribute to the vivid colors in LED and LCD screens. Although silver remains valuable for its superior electrical conductivity in circuits and contacts, rare earth metals' unique magnetic and optical properties drive innovations in miniaturized and energy-efficient electronic components.
Role of Silver in Electronic Devices
Silver plays a crucial role in electronic devices due to its unmatched electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance circuits, contacts, and connectors. Unlike rare earth metals, which are primarily used for their magnetic and phosphorescent properties in components like magnets and displays, silver enhances signal integrity and reduces resistance in printed circuit boards and conductive inks. Its superior thermal conductivity also aids in heat dissipation, ensuring device reliability and longevity in advanced electronics.
Environmental Impact and Recycling Potential
Rare earth metals, essential in advanced electronics for magnets and batteries, pose significant environmental challenges due to energy-intensive mining and toxic waste production. Silver, commonly used in conductive components, offers higher recycling rates because of its well-established recovery infrastructure and lower environmental footprint during recycling. Both materials require improved sustainable practices, but silver's recycling potential currently surpasses that of rare earth metals, reducing electronic waste and environmental harm.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Rare earth metals like neodymium and dysprosium are increasingly favored over silver in electronics due to their superior magnetic and conductive properties, enabling more efficient miniaturization of components in smartphones and electric vehicles. Innovations in recycling rare earth elements from electronic waste enhance sustainability and supply chain security, addressing critical shortages in global markets. Emerging trends also highlight the development of hybrid materials combining rare earth metals with silver to improve thermal management and conductivity in advanced circuit designs.
Future Prospects in Electronics Manufacturing
Rare earth metals are critical for future electronics manufacturing due to their unique magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties that enable advanced components like permanent magnets and phosphors. Silver excels in conductivity and antimicrobial applications but faces limitations from high cost and supply risks compared to the more abundant rare earth elements. Innovations in rare earth recycling and sustainable extraction methods will drive increased adoption, positioning rare earth metals as essential materials in next-generation electronics.
Infographic: Rare earth metal vs Silver for Electronics
 azmater.com
azmater.com