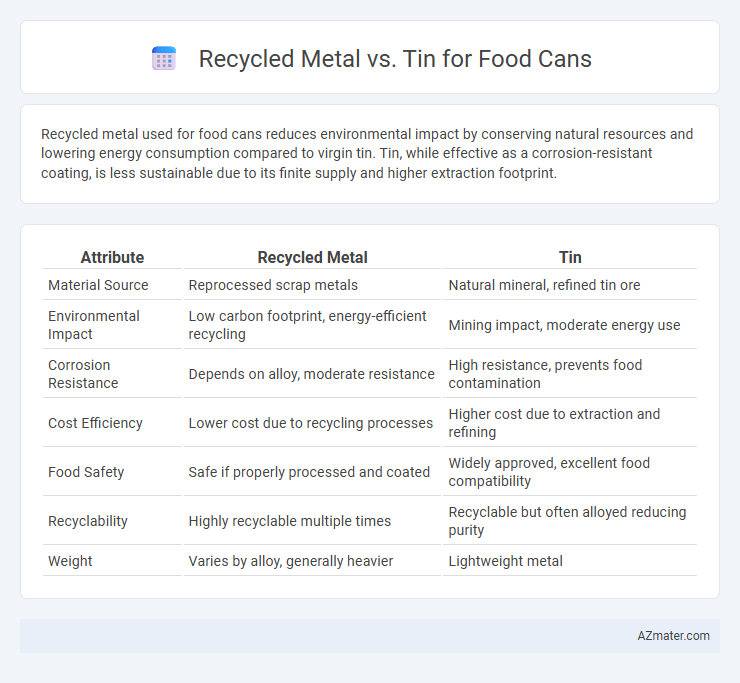
Recycled metal used for food cans reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources and lowering energy consumption compared to virgin tin. Tin, while effective as a corrosion-resistant coating, is less sustainable due to its finite supply and higher extraction footprint.
Table of Comparison
| Attribute | Recycled Metal | Tin |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Reprocessed scrap metals | Natural mineral, refined tin ore |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, energy-efficient recycling | Mining impact, moderate energy use |
| Corrosion Resistance | Depends on alloy, moderate resistance | High resistance, prevents food contamination |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost due to recycling processes | Higher cost due to extraction and refining |
| Food Safety | Safe if properly processed and coated | Widely approved, excellent food compatibility |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable multiple times | Recyclable but often alloyed reducing purity |
| Weight | Varies by alloy, generally heavier | Lightweight metal |
Overview of Food Can Materials: Recycled Metal vs Tin
Recycled metal and tin are common materials used in food can manufacturing, each offering distinct advantages in sustainability and durability. Recycled metal, primarily aluminum and steel, reduces environmental impact by conserving resources and lowering energy consumption during production, while maintaining corrosion resistance and strength essential for food preservation. Tin, often used as a protective coating over steel, prevents rust and extends shelf life, though it is less eco-friendly compared to recycled metals due to mining and refining processes.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Metal vs Traditional Tin
Recycled metal used in food cans significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional tin extraction and processing. Recycling metal saves up to 95% of the energy required to produce new tin from ore, minimizing resource depletion and landfill waste. This sustainable practice supports circular economy goals by decreasing pollution and preserving natural ecosystems through reduced mining activities.
Cost Differences in Food Can Production
Recycled metal significantly reduces raw material costs in food can production compared to tin, due to lower energy consumption and decreased mining expenses. Tin-plated steel cans incur higher costs from the tin coating process and reliance on volatile tin market prices. Utilizing recycled metal improves cost efficiency while maintaining quality and sustainability in food packaging.
Safety and Food Preservation Qualities
Recycled metal for food cans undergoes rigorous purification processes to eliminate contaminants, ensuring safety and compliance with FDA standards. Tin, often used as a coating on steel cans, provides a non-toxic barrier that prevents corrosion and preserves food quality over extended storage periods. The combination of recycled metal with tin plating enhances both structural integrity and food preservation by preventing metal leaching and maintaining a sterile environment.
Durability and Shelf Life Comparisons
Recycled metal used in food cans often retains similar durability to new tin, maintaining strength and resistance to corrosion essential for long-term food storage. Tin cans provide excellent shelf life by preventing contamination and preserving food quality, but recycled metals must undergo rigorous processing to meet these standards without compromising protective coatings. Studies indicate that when properly treated, recycled metal cans can match the shelf life and durability of traditional tin cans, supporting sustainable packaging without sacrificing performance.
Recycling and Sustainability Benefits
Recycled metal used in food cans significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions compared to primary metal production. Tin, commonly used as a coating for steel cans, enhances corrosion resistance but relies on sustainable sourcing to ensure minimal ecological footprint. Utilizing recycled metals in food packaging supports circular economy principles, conserving natural resources and promoting long-term sustainability in the industry.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
Recycled metal food cans gain consumer trust due to sustainability and environmental benefits, driving market demand for eco-friendly packaging solutions. Tin cans, valued for corrosion resistance and food safety, maintain steady popularity but face increased competition from recycled alternatives. Market trends indicate a shift towards recycled metal cans as consumers prioritize green products, influencing manufacturers to adopt circular economy practices.
Regulatory and Industry Standards
Recycled metal used in food cans must comply with stringent regulatory standards such as FDA's Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Title 21 to ensure safety and prevent contamination from heavy metals or toxic substances. Tin, often used as a coating for steel cans, meets industry standards specified by agencies like the International Tin Association and is regulated for purity and thickness to prevent corrosion and maintain food quality. Both materials undergo rigorous testing for migration limits and food contact safety, adhering to global guidelines including those from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to ensure consumer protection.
Manufacturing Processes: Efficiency and Challenges
Recycled metal in food can manufacturing enhances efficiency by reducing raw material extraction and energy consumption compared to primary tin production, leading to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Tin, often used for coating steel cans, requires energy-intensive refining and smelting processes but provides corrosion resistance and food safety benefits. Challenges in recycled metal include contamination control and variable material quality, while tin's sourcing faces supply constraints and environmental impacts from mining operations.
Future Prospects of Food Can Materials
Recycled metal offers significant environmental benefits and cost-efficiency in food can production, positioning it as a sustainable alternative to traditional tin cans. Innovations in alloy composition and coating technologies enhance the durability and safety of recycled metals, addressing corrosion and contamination concerns. Future prospects emphasize integrating advanced recycling processes with eco-friendly materials to reduce carbon footprints while maintaining food preservation standards.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Tin for Food can
 azmater.com
azmater.com