Lead roofing offers superior corrosion resistance and malleability, making it ideal for complex roof shapes, while steel provides higher tensile strength and cost-effectiveness for large, flat roof surfaces. Lead's longevity can exceed 100 years, whereas steel typically lasts 40-60 years with proper maintenance.
Table of Comparison
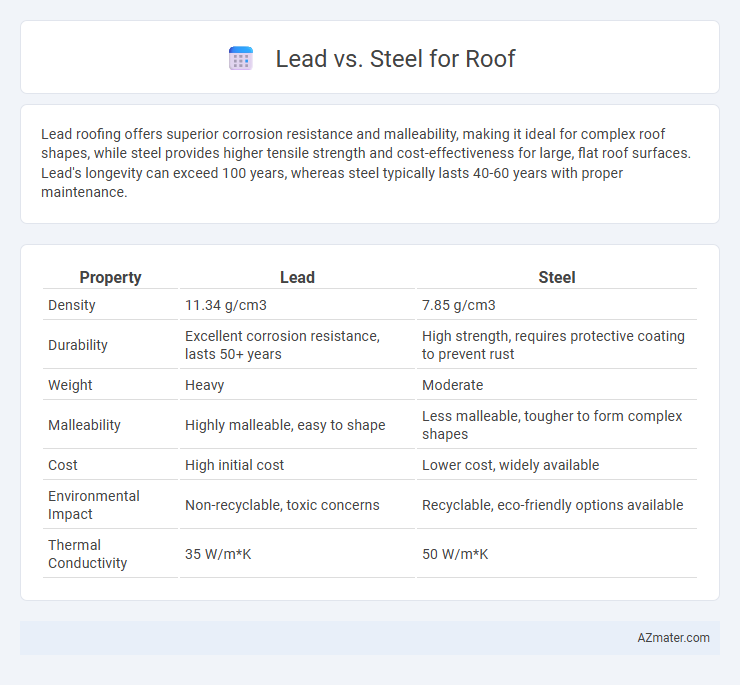
| Property | Lead | Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 11.34 g/cm3 | 7.85 g/cm3 |
| Durability | Excellent corrosion resistance, lasts 50+ years | High strength, requires protective coating to prevent rust |
| Weight | Heavy | Moderate |
| Malleability | Highly malleable, easy to shape | Less malleable, tougher to form complex shapes |
| Cost | High initial cost | Lower cost, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Non-recyclable, toxic concerns | Recyclable, eco-friendly options available |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35 W/m*K | 50 W/m*K |
Introduction to Lead and Steel Roofing
Lead roofing offers exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it a traditional choice in historic and high-end construction with an average lifespan of over 100 years. Steel roofing provides a modern, lightweight alternative with high tensile strength, excellent weather resistance, and efficient energy reflectivity, commonly coated with zinc or aluminum for enhanced protection. Both materials require specific installation techniques and maintenance to maximize longevity and performance in various climate conditions.
Historical Use of Lead vs Steel in Roofing
Lead has been used in roofing since Roman times due to its malleability, corrosion resistance, and longevity, making it ideal for complex roofing shapes and detailed architectural elements. Steel roofing became prominent during the Industrial Revolution, offering superior strength, affordability, and ease of mass production compared to traditional materials like lead. Although steel provides modern durability and structural support, lead's historical use remains significant, especially in heritage buildings and restoration projects.
Material Properties: Lead vs Steel
Lead roofing offers exceptional malleability and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for complex roof shapes and long-term durability in harsh weather. Steel roofing provides superior tensile strength and impact resistance, ensuring structural integrity under heavy loads and extreme conditions. Both materials feature distinct thermal expansion rates, with lead expanding more significantly than steel, affecting installation methods and long-term performance.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Lead roofing offers exceptional durability with a lifespan of up to 100 years due to its natural resistance to corrosion and weathering. Steel roofs, typically coated with protective layers like galvanized or stainless steel, provide strong resistance against impact and rust, lasting around 40 to 70 years depending on maintenance and environmental conditions. Choosing between lead and steel roofing hinges on balancing longer lifespan and self-healing properties of lead against the affordability and structural strength of steel.
Weather Resistance: Lead vs Steel
Lead offers exceptional weather resistance due to its natural corrosion resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperature fluctuations without deteriorating. Steel, while strong and durable, requires protective coatings to prevent rust and may suffer corrosion over time when exposed to moisture and harsh weather conditions. The inherent malleability and longevity of lead make it a preferred choice for roofing in environments with frequent rain or snow.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead roofing offers excellent durability and recyclability, with a high reclamation rate that reduces landfill waste and supports circular economy principles. Steel roofs provide significant environmental benefits through energy-efficient manufacturing processes, lightweight transport, and 100% recyclability, contributing to lower carbon footprints over their lifecycle. Both materials promote sustainability, but steel's lower toxicity and widespread recycling infrastructure make it preferable for eco-conscious construction projects.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Maintenance
Lead roofing typically incurs higher installation costs due to its weight and specialized handling requirements, while steel roofing offers lower upfront expenses with easier and faster installation. Maintenance expenses for lead roofs are generally minimal because of lead's natural durability and resistance to corrosion, whereas steel roofs may require periodic treatments or coatings to prevent rust and extend lifespan. Overall, steel roofing often proves more cost-effective for budget-conscious projects, while lead may offer long-term savings in maintenance despite higher initial investment.
Weight and Structural Requirements
Lead roofing is significantly heavier than steel, with lead weighing approximately 110 lb per square foot compared to steel's 40 lb per square foot, necessitating stronger structural support for lead installations. Steel's lighter weight reduces the load on the building's framework, often allowing for more flexible and cost-effective structural design. Choosing steel over lead can minimize reinforcement needs, especially in renovation projects or structures with weight limitations.
Aesthetics and Architectural Flexibility
Lead roofing offers a traditional, matte gray finish that naturally patinas over time, providing timeless elegance suited for heritage and classical architecture. Steel roofing is available in a wide range of colors, finishes, and profiles, allowing for greater architectural flexibility and modern design integration. Steel's adaptability to various shapes and styles makes it ideal for contemporary structures seeking both durability and aesthetic customization.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Roofing Material
Lead offers superior durability and malleability, making it ideal for complex roof designs and long-lasting protection against corrosion. Steel provides a cost-effective and lightweight alternative with strong structural support and resistance to weather damage. Selecting the right roofing material depends on budget constraints, architectural requirements, and desired longevity.
Infographic: Lead vs Steel for Roof
 azmater.com
azmater.com