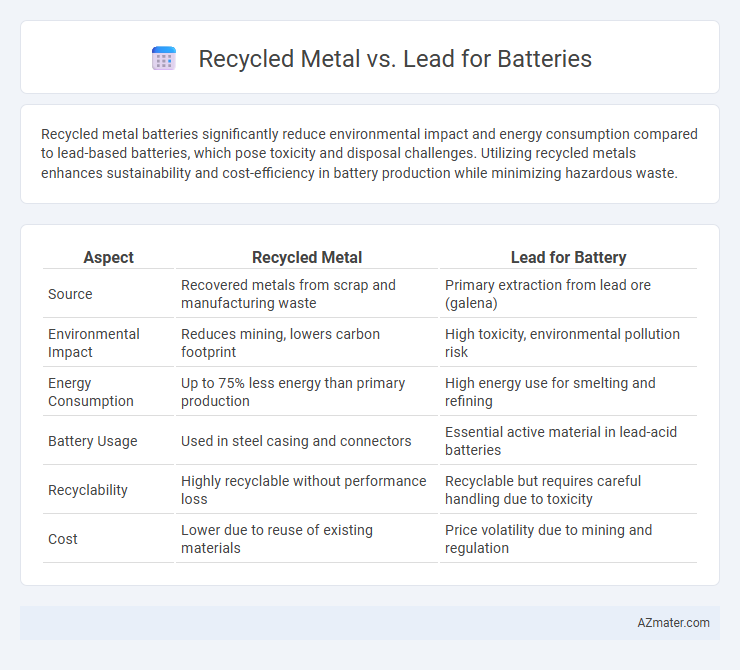
Recycled metal batteries significantly reduce environmental impact and energy consumption compared to lead-based batteries, which pose toxicity and disposal challenges. Utilizing recycled metals enhances sustainability and cost-efficiency in battery production while minimizing hazardous waste.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Recycled Metal | Lead for Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Recovered metals from scrap and manufacturing waste | Primary extraction from lead ore (galena) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces mining, lowers carbon footprint | High toxicity, environmental pollution risk |
| Energy Consumption | Up to 75% less energy than primary production | High energy use for smelting and refining |
| Battery Usage | Used in steel casing and connectors | Essential active material in lead-acid batteries |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable without performance loss | Recyclable but requires careful handling due to toxicity |
| Cost | Lower due to reuse of existing materials | Price volatility due to mining and regulation |
Introduction: The Growing Importance of Battery Material Choices
Recycled metal offers a sustainable alternative to lead in battery production, reducing environmental impact and resource depletion. Lead, traditionally used in batteries, poses significant health and ecological risks due to its toxicity and challenges in recycling processes. Advances in battery technology increasingly favor recycled metals for enhanced efficiency, safety, and environmental compliance.
Environmental Impact: Recycled Metal vs. Lead
Recycled metal used in batteries significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing mining waste and lowering greenhouse gas emissions compared to lead extraction. Lead batteries pose serious risks due to toxic lead contamination, which can harm ecosystems and human health if not properly managed. Utilizing recycled metals in battery production supports sustainability by conserving natural resources and reducing hazardous waste generation.
Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Recycled metal batteries typically offer enhanced sustainability and comparable performance to lead-based batteries, with improved energy density and longer cycle life. Lead batteries, while cost-effective and reliable, often exhibit lower efficiency and shorter lifespan due to heavier weight and slower charge-discharge rates. Advances in recycled metals contribute to higher conductivity and faster energy transfer, making them a more efficient choice for modern battery applications.
Cost Analysis: Recycled Metal Batteries vs. Lead Batteries
Recycled metal batteries typically offer lower raw material costs compared to lead batteries due to the reduced need for mining and processing virgin metals, leading to significant cost savings in production. Lead batteries, while initially cheaper to manufacture, incur higher environmental remediation and disposal costs, which impact their overall lifecycle expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership, recycled metal batteries demonstrate improved economic efficiency and sustainability by minimizing material costs and reducing regulatory compliance expenditures.
Safety and Health Implications
Recycled metal in batteries offers significant safety advantages over lead, as it reduces exposure to toxic lead fumes and dust, which are hazardous to respiratory health and can cause neurological damage. The use of recycled metals also minimizes environmental contamination from heavy metals, lowering risks of soil and water pollution that directly impact human health. Innovations in battery manufacturing with recycled metals promote safer handling and disposal processes, further protecting workers and communities from lead poisoning and associated chronic illnesses.
Lifespan and Durability Factors
Recycled metal batteries generally offer enhanced lifespan and durability compared to traditional lead-acid batteries due to improved material purity and advanced manufacturing processes. Lead batteries tend to suffer from sulfation and corrosion over time, which significantly reduces their cycle life and structural integrity. The use of recycled metals in battery production also promotes consistent performance and resistance to degradation, extending overall battery reliability.
Availability and Supply Chain Considerations
Recycled metal offers enhanced availability by utilizing existing scrap materials, reducing dependence on finite lead ore deposits and stabilizing supply chains against geopolitical disruptions. Lead, traditionally used in batteries, faces constrained availability due to environmental regulations and declining mining activities, impacting long-term supply stability. Incorporation of recycled metals supports circular economy principles, enabling more consistent supply and lowering the carbon footprint associated with raw material extraction for battery manufacturing.
Applications in Modern Energy Storage
Recycled metal in battery production reduces environmental impact while maintaining high conductivity and durability essential for modern energy storage systems. Lead remains a prevalent choice in lead-acid batteries due to its reliable performance and cost-effectiveness for applications like automotive starters and backup power. Emerging technologies increasingly explore recycled metals for lithium-ion and flow batteries, enhancing sustainability and efficiency in renewable energy storage and grid stabilization.
Policy and Regulatory Influences
Policies on recycled metal for batteries emphasize environmental sustainability, promoting the reduction of lead usage due to its toxic impact under regulations such as the EU Battery Directive and the U.S. Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. Regulatory frameworks increasingly incentivize the adoption of recycled metals in battery production to meet stricter limits on lead emissions and hazardous waste disposal. Compliance with these policies drives innovation in recycling technologies and the development of safer, lead-free battery alternatives.
The Future of Sustainable Battery Materials
Recycled metals offer a promising pathway for sustainable battery production by significantly reducing the environmental impact associated with mining and refining raw materials. Lead, once dominant in battery technology due to its high recyclability and cost-effectiveness, faces challenges from toxicity concerns and regulatory restrictions that drive innovation toward safer alternatives. Advances in recycled metal technologies and alternative materials aim to improve energy density, lifecycle, and ecological footprint, shaping the future of sustainable battery materials.
Infographic: Recycled metal vs Lead for Battery
 azmater.com
azmater.com