Rare earth metals provide superior conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to copper in electrical wiring applications. Copper remains widely used due to its excellent electrical conductivity, affordability, and ease of installation.
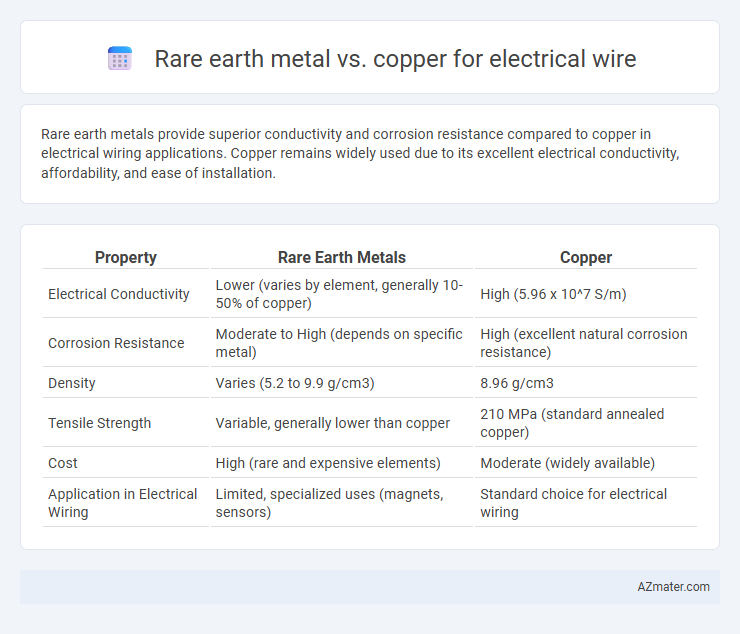
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rare Earth Metals | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | Lower (varies by element, generally 10-50% of copper) | High (5.96 x 10^7 S/m) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate to High (depends on specific metal) | High (excellent natural corrosion resistance) |
| Density | Varies (5.2 to 9.9 g/cm3) | 8.96 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | Variable, generally lower than copper | 210 MPa (standard annealed copper) |
| Cost | High (rare and expensive elements) | Moderate (widely available) |
| Application in Electrical Wiring | Limited, specialized uses (magnets, sensors) | Standard choice for electrical wiring |
Introduction: Rare Earth Metals vs Copper in Electrical Wiring
Rare earth metals exhibit superior magnetic and conductive properties compared to copper, making them ideal for specialized electrical wiring applications requiring enhanced performance. Copper remains the industry standard due to its excellent electrical conductivity, durability, and cost-effectiveness in general wiring installations. Advances in rare earth metal alloys are gradually enabling higher efficiency and miniaturization in high-tech electrical systems, positioning them as promising alternatives to traditional copper wiring.
Material Properties: Conductivity and Efficiency Comparison
Rare earth metals typically exhibit lower electrical conductivity than copper, making copper the preferred choice for electrical wiring due to its superior efficiency in conducting electricity. Copper's conductivity is approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, significantly higher than the range found in rare earth metals, which hinders their use in applications requiring minimal resistive losses. While rare earth metals possess unique magnetic and thermal properties beneficial in specialized components, copper remains dominant for wires due to its optimal balance of conductivity, ductility, and cost-effectiveness.
Availability and Sourcing: Supply Chain Considerations
Rare earth metals are less abundant and geologically concentrated, leading to supply chain vulnerabilities due to geographic and political constraints, primarily dominated by a few countries like China. Copper, in contrast, has a more widespread global distribution and established mining infrastructure, ensuring a relatively stable and diverse supply. The sourcing of rare earth metals often involves complex extraction processes, while copper's supply chain benefits from mature refining and recycling systems, making copper more reliable for electrical wire applications.
Cost Analysis: Rare Earth Metals vs Copper
Rare earth metals, such as neodymium and dysprosium, significantly increase the cost of electrical wire compared to copper due to their scarcity and complex extraction processes, driving up raw material expenses by up to five times. Copper remains the cost-effective choice for electrical wiring, with prices averaging around $9,000 per metric ton, while rare earth metals can exceed $50,000 per metric ton depending on market demand and purity. The economic feasibility of using rare earth metals in wiring is currently limited to specialized applications requiring high magnetic or thermal properties, whereas copper's balance of conductivity and affordability dominates mainstream electrical wiring markets.
Durability and Lifespan in Electrical Applications
Rare earth metals exhibit superior corrosion resistance and maintain conductivity under extreme environmental conditions, significantly enhancing durability compared to copper in electrical wire applications. Copper, widely used due to its excellent conductivity and cost-effectiveness, tends to oxidize over time, which can reduce its lifespan in harsh or high-temperature environments. For long-term electrical systems requiring stability and minimal maintenance, rare earth metal alloys offer extended lifespan advantages despite higher initial material costs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Rare earth metals used in electrical wires often require energy-intensive mining and chemical processing, leading to significant environmental degradation and hazardous waste generation compared to copper, which has a more established and efficient recycling infrastructure. Copper's high recyclability reduces the demand for virgin mining, minimizing habitat disruption and greenhouse gas emissions, whereas rare earth element extraction is often associated with toxic byproducts and water contamination. Sustainable electrical wiring solutions favor copper due to its abundant availability, lower ecological footprint, and proven recyclability, while rare earth metals remain challenging to source responsibly without long-term environmental harm.
Performance Under High Temperatures
Rare earth metals exhibit superior thermal stability and maintain conductivity better than copper when exposed to high temperatures, making them ideal for specialized electrical wire applications in extreme environments. Copper's performance degrades due to oxidation and increased resistivity at elevated temperatures, limiting its efficiency in high-heat conditions. Rare earth-based alloys, such as neodymium-copper composites, offer enhanced durability and consistent electrical performance under thermal stress.
Weight and Flexibility for Wire Design
Rare earth metals, such as neodymium and dysprosium, offer superior magnetic properties but generally exhibit higher density and lower electrical conductivity compared to copper, impacting wire weight and flexibility negatively. Copper remains the preferred choice in electrical wire design due to its optimal balance of low density (8.96 g/cm3), excellent ductility, and high conductivity (5.96 x 10^7 S/m), enabling lighter and more flexible wiring solutions. The higher weight and rigidity of rare earth metals limit their use in wire applications where flexibility and ease of installation are critical factors.
Industry Adoption and Current Innovations
Rare earth metals, such as neodymium and praseodymium, are gaining traction in electrical wire applications due to their superior magnetic properties and increased conductivity compared to copper. While copper remains the industry standard for electrical wiring because of its excellent electrical conductivity, cost-effectiveness, and widespread availability, innovations in rare earth metal composites are driving efforts to enhance wire efficiency and thermal performance. Industry adoption of rare earth metal-infused wires is expanding primarily in high-performance sectors like aerospace and renewable energy, where their ability to reduce energy loss and improve durability justifies higher material costs.
Future Trends and Technological Advancements
Rare earth metals, such as neodymium and dysprosium, are increasingly integrated into electrical wire technology for their superior magnetic and conductive properties compared to traditional copper. Advances in nanotechnology and alloy engineering enhance the efficiency and durability of rare earth metal-infused wires, promoting their use in high-performance and miniaturized electronic devices. Emerging trends highlight a growing demand for rare earth materials driven by the electric vehicle and renewable energy sectors, which may challenge copper's dominance in electrical wiring applications.
Infographic: Rare earth metal vs Copper for Electrical wire
 azmater.com
azmater.com