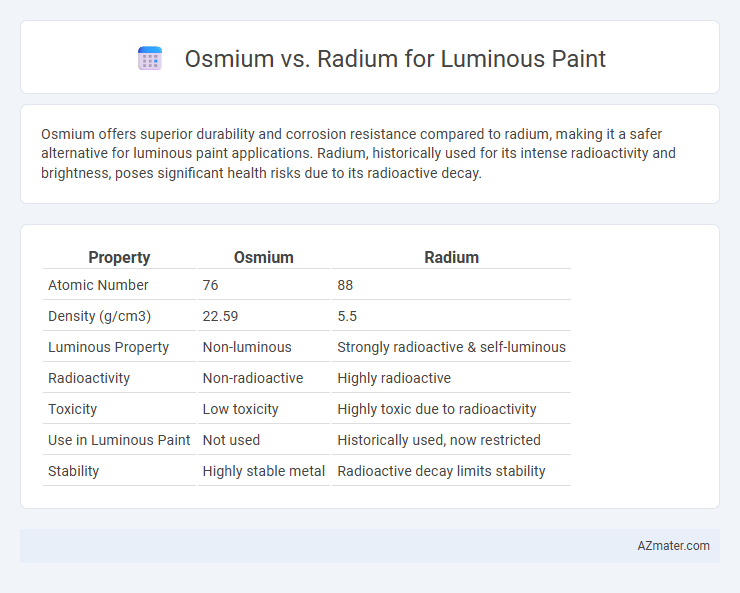
Osmium offers superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to radium, making it a safer alternative for luminous paint applications. Radium, historically used for its intense radioactivity and brightness, poses significant health risks due to its radioactive decay.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Osmium | Radium |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 76 | 88 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 22.59 | 5.5 |
| Luminous Property | Non-luminous | Strongly radioactive & self-luminous |
| Radioactivity | Non-radioactive | Highly radioactive |
| Toxicity | Low toxicity | Highly toxic due to radioactivity |
| Use in Luminous Paint | Not used | Historically used, now restricted |
| Stability | Highly stable metal | Radioactive decay limits stability |
Introduction to Luminous Paints
Luminous paints utilize specific radioactive elements to emit visible light through radioluminescence or phosphorescence. Radium, historically used due to its strong alpha radiation, became popular for luminous watch dials but posed significant health risks from radiation exposure. Osmium, less common in luminous paints, does not possess the same radioactive properties, making radium more notable despite its dangers in this application.
Overview of Osmium in Luminous Applications
Osmium, a dense and rare transition metal, offers exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, making it a valuable candidate for luminous paint applications. Its high melting point and chemical stability ensure long-lasting luminescence when integrated with phosphorescent compounds. Unlike radium, osmium poses significantly lower radiological hazards, enhancing safety in luminous materials used for watches and instruments.
Radium: Historical Use in Luminous Paint
Radium was historically used in luminous paint due to its intense radioactivity, which caused phosphors to glow brightly in the dark. The element's radioactive properties made it a popular choice for watch dials, instrument panels, and military equipment during the early 20th century. However, the health risks associated with radium radiation exposure led to its replacement by safer alternatives in luminous paint applications.
Chemical Properties: Osmium vs Radium
Osmium, a dense transition metal with high corrosion resistance and low reactivity, contrasts sharply with Radium, an alkaline earth metal known for its intense radioactivity and high chemical reactivity. Osmium's stable oxidation states and inertness make it unsuitable for luminous paint, whereas Radium's radioactive decay emits alpha particles that historically activated phosphors for glowing effects. The hazardous nature of Radium's radioactivity led to its replacement by safer materials, highlighting the importance of chemical stability and safety in luminous paint applications.
Brightness and Longevity Comparison
Osmium and radium exhibit distinct differences in brightness and longevity when used in luminous paint. Radium provides intense initial brightness due to its strong radioactivity but poses significant health risks and fades over time as its radioisotopic decay progresses. Osmium, while less radioactive, offers improved longevity and safer handling characteristics, making it a more sustainable option for applications requiring prolonged luminescence.
Safety and Health Considerations
Osmium is rarely used in luminous paint due to its high density and toxicity, whereas radium poses significant health risks because of its strong radioactivity, which can cause severe radiation sickness and cancer. Radium's historical use in luminous paint led to serious health issues among workers, resulting in strict regulations and the development of safer alternatives like tritium and phosphorescent pigments. Modern luminous paint formulations prioritize non-radioactive materials, making osmium and radium largely obsolete for safety and health compliance.
Environmental Impact of Both Elements
Osmium, a dense and rare transition metal, poses minimal environmental risk when used in luminous paint due to its low chemical reactivity and limited bioavailability, reducing contamination concerns during disposal. Radium, on the other hand, is highly radioactive and presents significant environmental hazards through radiation contamination, bioaccumulation, and long-term ecosystem damage, necessitating strict handling and disposal protocols. The environmental impact of radium in luminous paints is substantially greater compared to osmium, making osmium a safer choice for reducing ecological harm.
Regulations and Restrictions
Osmium is seldom used in luminous paint due to its scarcity and high toxicity, with stringent regulations limiting its handling under international hazardous material guidelines. Radium, historically employed for luminous paint, faces extensive regulatory restrictions globally due to its intense radioactivity, leading to bans on its use in consumer products by agencies such as the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) and the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom). Current luminous paint formulations favor safer alternatives like strontium aluminate, compliant with environmental safety standards and devoid of the strict radiological controls applied to radium.
Modern Alternatives to Osmium and Radium
Modern alternatives to osmium and radium for luminous paint primarily include phosphorescent materials like strontium aluminate, which provide safer and longer-lasting luminescence without the radioactivity associated with radium or the scarcity of osmium. Strontium aluminate offers superior brightness and durability, making it the preferred choice in watch dials, emergency signs, and safety markings. Advances in photoluminescent technology continue to enhance glow intensity and lifespan while eliminating health risks tied to traditional luminous elements.
Conclusion: Best Choice for Luminous Paint
Osmium is not commonly used in luminous paint due to its extreme density and rarity, whereas radium, historically used for its strong radioluminescence, has been largely replaced because of its high radioactivity and associated health risks. Modern luminous paints favor safer alternatives like tritium and phosphorescent compounds, as radium poses significant safety hazards despite its brightness. Therefore, radium is not the best choice for luminous paint, and osmium's impracticality excludes it, making engineered phosphorescent materials the optimal solution for safe, long-lasting luminescence.
Infographic: Osmium vs Radium for Luminous Paint
 azmater.com
azmater.com