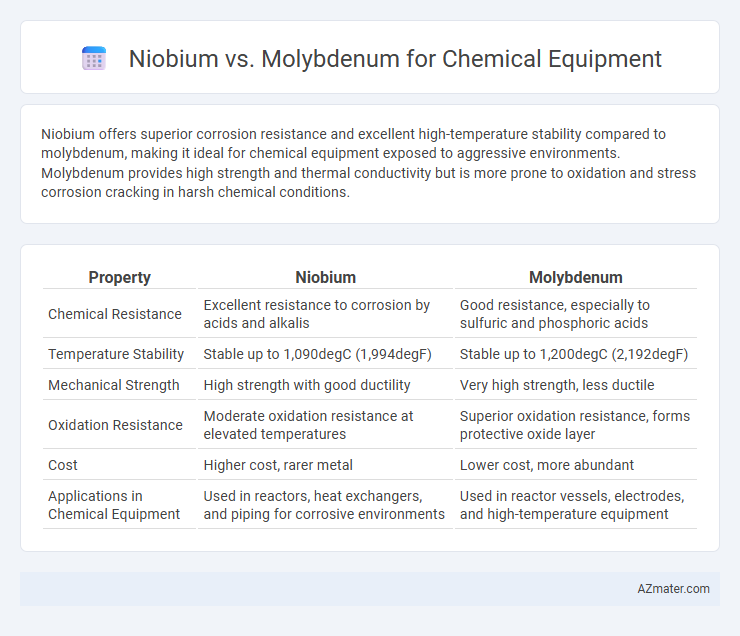
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent high-temperature stability compared to molybdenum, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive environments. Molybdenum provides high strength and thermal conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and stress corrosion cracking in harsh chemical conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium | Molybdenum |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to corrosion by acids and alkalis | Good resistance, especially to sulfuric and phosphoric acids |
| Temperature Stability | Stable up to 1,090degC (1,994degF) | Stable up to 1,200degC (2,192degF) |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength with good ductility | Very high strength, less ductile |
| Oxidation Resistance | Moderate oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures | Superior oxidation resistance, forms protective oxide layer |
| Cost | Higher cost, rarer metal | Lower cost, more abundant |
| Applications in Chemical Equipment | Used in reactors, heat exchangers, and piping for corrosive environments | Used in reactor vessels, electrodes, and high-temperature equipment |
Overview of Niobium and Molybdenum
Niobium offers excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive environments. Molybdenum features outstanding thermal stability and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, commonly used in chemical processing industries. Both metals enhance durability and safety in chemical reactors, heat exchangers, and piping systems due to their distinct anti-corrosive properties.
Material Properties Comparison
Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance and excellent ductility, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive acidic environments, especially sulfuric and hydrofluoric acids. Molybdenum offers high melting points and good thermal stability, alongside strong resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-rich solutions, which is critical for high-temperature chemical processing. Both materials provide robust chemical stability, but niobium excels in weldability and formability, while molybdenum outperforms in hardness and strength under elevated temperatures.
Corrosion Resistance in Chemical Environments
Niobium exhibits superior corrosion resistance in highly acidic environments such as hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive media. Molybdenum enhances corrosion resistance in alkaline and oxidizing conditions but is less effective than niobium in reducing acids. The unique passivation behavior of niobium provides excellent protection against pitting and crevice corrosion, extending equipment lifespan in harsh chemical processes.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Niobium offers superior mechanical strength compared to molybdenum, making it highly resistant to deformation under stress in chemical equipment applications. Its excellent durability stems from enhanced corrosion resistance and toughness, especially in aggressive chemical environments. Molybdenum, while strong, is more brittle and less resistant to certain corrosive agents, limiting its long-term durability in harsh chemical processing conditions.
Thermal Performance and Stability
Niobium exhibits superior thermal performance and stability in chemical equipment due to its high melting point of 2,468degC and exceptional resistance to thermal fatigue and oxidation. Molybdenum, with a melting point of 2,623degC, offers excellent thermal conductivity but is more susceptible to rapid oxidation at elevated temperatures, limiting its stability in harsh chemical environments. Niobium's enhanced corrosion resistance and ability to maintain structural integrity under cyclic thermal stress make it a preferred choice for high-temperature chemical processing applications.
Fabrication and Machinability
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent weldability, making it highly suitable for chemical equipment fabrication where resistance to aggressive chemicals is critical. Molybdenum provides enhanced high-temperature strength and good machinability, although it can be more challenging to weld due to its brittleness when exposed to rapid cooling. Fabrication processes involving niobium benefit from its ductility and ease of forming, while molybdenum requires specialized techniques such as controlled atmosphere machining to avoid oxidation and maintain structural integrity.
Cost and Availability
Niobium and molybdenum are critical materials in chemical equipment due to their corrosion resistance and high-temperature strength. Niobium generally has a higher cost and limited availability compared to molybdenum, which is more abundant and relatively affordable. The decision between the two depends on budget constraints and supply chain stability, with molybdenum often preferred for cost-sensitive applications.
Applications in Chemical Equipment
Niobium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength, making it ideal for chemical reactors, heat exchangers, and pipelines exposed to aggressive acids and high temperatures. Molybdenum is preferred for equipment requiring superior hardness and wear resistance, commonly used in valve components, furnace parts, and catalysts in chemical processing. Both materials enhance durability and performance in chemical equipment but are selected based on specific operational demands such as corrosion environment and mechanical stress.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Niobium offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to molybdenum, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to harsh environments and aggressive chemicals. Molybdenum, while cost-effective, tends to require more frequent maintenance due to its susceptibility to oxidation and wear under prolonged exposure to corrosive substances. Choosing niobium can significantly extend equipment lifespan and reduce downtime, lowering overall maintenance costs in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Niobium offers exceptional resistance to corrosion and high-temperature stability, making it ideal for chemical equipment exposed to aggressive acids and thermal stress. Molybdenum provides superior strength and resistance to wear and oxidation, suitable for applications involving harsh mechanical conditions and high temperatures. Selecting between niobium and molybdenum depends on specific operational requirements such as chemical exposure, temperature ranges, and mechanical stress to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the equipment.
Infographic: Niobium vs Molybdenum for Chemical Equipment
 azmater.com
azmater.com