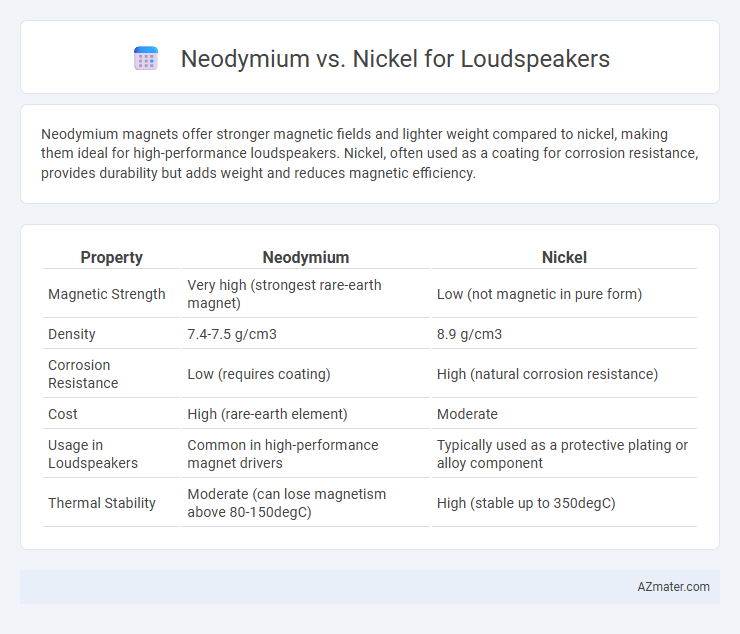
Neodymium magnets offer stronger magnetic fields and lighter weight compared to nickel, making them ideal for high-performance loudspeakers. Nickel, often used as a coating for corrosion resistance, provides durability but adds weight and reduces magnetic efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Neodymium | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Strength | Very high (strongest rare-earth magnet) | Low (not magnetic in pure form) |
| Density | 7.4-7.5 g/cm3 | 8.9 g/cm3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low (requires coating) | High (natural corrosion resistance) |
| Cost | High (rare-earth element) | Moderate |
| Usage in Loudspeakers | Common in high-performance magnet drivers | Typically used as a protective plating or alloy component |
| Thermal Stability | Moderate (can lose magnetism above 80-150degC) | High (stable up to 350degC) |
Introduction to Loudspeaker Magnets
Neodymium magnets, made from an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron, are favored in loudspeaker design for their exceptional magnetic strength and lightweight properties compared to traditional nickel-based magnets. Nickel, often used as a plating material rather than the core magnet, provides corrosion resistance but lacks the magnetic power density of neodymium magnets. The introduction of neodymium magnets revolutionized loudspeaker performance by enabling smaller, more efficient drivers with higher sound fidelity and improved power handling.
Overview of Neodymium and Nickel Magnets
Neodymium magnets, composed primarily of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB), offer exceptional magnetic strength and lightweight properties, making them ideal for compact, high-performance loudspeaker designs. Nickel, often used as a plating material for neodymium magnets, provides corrosion resistance and durability but has weaker magnetic properties compared to pure nickel magnets. Pure nickel magnets are rare and generally less powerful, so neodymium magnets with nickel plating remain the industry standard for loudspeaker applications due to their superior magnetic flux density and stability.
Magnetic Properties Comparison
Neodymium magnets exhibit significantly higher magnetic strength and energy density compared to nickel magnets, making them ideal for loudspeaker applications requiring compact size and powerful magnetic fields. Neodymium's rare-earth composition provides a higher coercivity and temperature stability, enhancing speaker efficiency and sound clarity. In contrast, nickel, often used as a coating material rather than a magnet, offers lower magnetic performance and is typically employed for corrosion resistance rather than magnetic force in loudspeakers.
Influence on Sound Quality
Neodymium magnets provide stronger magnetic fields than nickel, enabling more precise control of the speaker diaphragm and resulting in clearer, more dynamic sound reproduction. Nickel, often used as a plating material rather than a magnet, primarily contributes to corrosion resistance without significantly affecting acoustic performance. Loudspeakers with neodymium magnets typically exhibit improved sensitivity and frequency response, directly enhancing sound quality compared to those with nickel-based components.
Weight and Size Considerations
Neodymium magnets offer significant advantages over nickel magnets in loudspeaker applications due to their higher magnetic strength, allowing for smaller and lighter designs without sacrificing performance. This weight reduction is critical for portable and in-ear loudspeakers where minimizing bulk enhances user comfort and device efficiency. Despite this, nickel-based magnets remain heavier and larger, often limiting their use to applications where cost is a primary concern rather than compactness.
Durability and Longevity
Neodymium magnets exhibit superior durability in loudspeakers due to their high resistance to corrosion and demagnetization compared to nickel-based magnets. Nickel, often used as a plating material rather than a core magnet, provides moderate protection but lacks the long-term magnetic stability essential for consistent audio performance. Neodymium's enhanced longevity ensures sustained magnetic strength, making it the preferred choice for high-end, durable loudspeaker components.
Cost and Availability
Neodymium magnets, known for their high magnetic strength and lightweight properties, typically cost more than nickel magnets, influencing loudspeaker manufacturing budgets. While neodymium is less abundant and extracted through complex processes, nickel is widely available and cheaper, making it a cost-effective choice for mass production. Despite the higher price, neodymium's superior performance often justifies its cost in premium loudspeaker models.
Applications in Loudspeaker Design
Neodymium magnets offer significantly higher magnetic flux density than nickel, making them ideal for compact, high-performance loudspeaker designs where weight reduction is critical. Nickel, often used as a plating material on magnets, provides corrosion resistance but lacks the strong magnetic properties required for efficient loudspeaker voice coils. In modern loudspeaker applications, neodymium magnets enable greater sensitivity and power handling, contributing to improved sound clarity and compact form factors preferred in professional audio and portable devices.
Environmental and Safety Factors
Neodymium magnets, widely used in loudspeakers, offer stronger magnetic fields with less material, reducing environmental impact by lowering raw mineral extraction and weight during transportation. Nickel coatings protect neodymium magnets from corrosion but pose environmental concerns as nickel mining and processing produce toxic waste and potential allergenic effects. Compared to nickel magnets, neodymium magnets require careful disposal due to their rare earth material toxicity, emphasizing the importance of recycling programs to minimize ecological harm.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Magnet
Neodymium magnets offer superior magnetic strength and lighter weight, making them ideal for high-performance and compact loudspeakers where efficiency and sound clarity are crucial. Nickel, often used as a protective coating on magnets, provides durability and corrosion resistance but lacks the magnetic power needed for advanced audio applications. Selecting between neodymium and nickel-coated magnets ultimately depends on balancing the need for magnetic strength, weight constraints, and environmental durability in loudspeaker design.
Infographic: Neodymium vs Nickel for Loudspeaker
 azmater.com
azmater.com