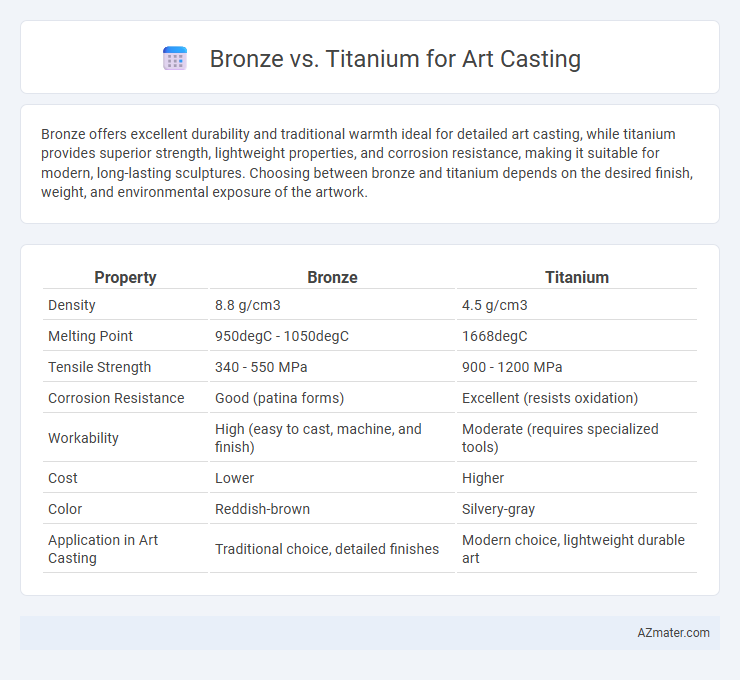
Bronze offers excellent durability and traditional warmth ideal for detailed art casting, while titanium provides superior strength, lightweight properties, and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for modern, long-lasting sculptures. Choosing between bronze and titanium depends on the desired finish, weight, and environmental exposure of the artwork.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bronze | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.8 g/cm3 | 4.5 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 950degC - 1050degC | 1668degC |
| Tensile Strength | 340 - 550 MPa | 900 - 1200 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (patina forms) | Excellent (resists oxidation) |
| Workability | High (easy to cast, machine, and finish) | Moderate (requires specialized tools) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Color | Reddish-brown | Silvery-gray |
| Application in Art Casting | Traditional choice, detailed finishes | Modern choice, lightweight durable art |
Introduction to Art Casting Metals
Bronze and titanium are prominent metals used in art casting, each offering distinct properties that influence artistic outcomes. Bronze, an alloy primarily of copper and tin, is celebrated for its excellent castability, fine detail reproduction, and warm patina, making it a traditional choice for sculptures. Titanium, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and modern aesthetic, provides artists with innovative possibilities despite its higher cost and complex casting process.
Overview of Bronze in Art Casting
Bronze is a traditional and highly valued metal in art casting due to its excellent durability, workability, and warm, rich patina that develops over time, making it ideal for detailed sculptures and statues. It consists primarily of copper and tin, which provide superior strength and resistance to corrosion compared to other metals. Artists and foundries favor bronze for its ability to capture fine artistic details and its long-lasting finish, ensuring artworks maintain aesthetic and structural integrity for centuries.
The Rise of Titanium in Sculpture
Titanium's emergence in art casting stems from its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and ability to capture fine details, making it increasingly favored over traditional bronze. Sculptors appreciate titanium's lightweight properties, which enable the creation of larger, more dynamic forms without compromising structural integrity. Advances in casting technology and finishing techniques have further propelled titanium's popularity in modern sculpture, challenging bronze's historical dominance.
Physical Properties: Bronze vs Titanium
Bronze exhibits a density of approximately 8.9 g/cm3, offering excellent hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for detailed artistic casting. Titanium, with a lower density around 4.5 g/cm3, provides superior strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments. The higher melting point of titanium (around 1,668degC) compared to bronze (around 950degC) requires advanced casting techniques but results in lightweight, durable art sculptures.
Casting Techniques: Differences and Challenges
Bronze casting involves traditional lost-wax techniques that benefit from bronze's excellent fluidity and lower melting point around 950degC, enabling fine detail replication and easier mold filling. Titanium casting, with a much higher melting point near 1668degC, demands advanced vacuum or inert gas environments to prevent oxidation and requires specialized equipment such as plasma arc or electron beam melting, making the process more complex and costly. Challenges in titanium casting also include controlling shrinkage rates and ensuring proper mold materials to withstand extreme temperatures, impacting the precision and finish of art sculptures.
Aesthetic Qualities and Visual Appeal
Bronze exhibits a warm, rich patina that deepens over time, offering classic earth tones ideal for traditional and historical art casting. Titanium provides a modern, sleek appearance with a naturally bright silver-gray finish that resists corrosion and maintains its luster without tarnishing. The choice between bronze and titanium significantly impacts the artwork's visual feel, with bronze evoking timeless elegance and titanium delivering contemporary, lightweight sophistication.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Titanium exhibits superior durability compared to bronze, offering exceptional resistance to corrosion, wear, and fatigue, making it ideal for art casting exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Bronze, while historically favored for its aesthetic warmth and ease of casting, is more susceptible to oxidation and surface patina over time, which can affect long-term integrity. The longevity of titanium sculptures significantly surpasses that of bronze, maintaining structural stability and appearance for centuries with minimal maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Bronze vs Titanium
Bronze offers a cost-effective solution for art casting with material prices averaging $3 to $5 per pound, making it more accessible for large-scale or intricate sculptures. Titanium, while providing superior strength and corrosion resistance, commands a significantly higher price range of $15 to $30 per pound, increasing overall casting expenses. The difference in melting points--bronze around 950degC versus titanium at approximately 1,668degC--also influences energy costs during the casting process, further affecting the economic feasibility for artists.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Bronze, composed primarily of copper and tin, emits moderate levels of toxic fumes during casting, requiring effective ventilation and protective equipment to ensure worker safety. Titanium casting produces fewer harmful emissions and is non-toxic, but its high melting point demands specialized, energy-intensive equipment, increasing environmental impact. Choosing between bronze and titanium involves balancing the lower toxicity and greater durability of titanium against the lower energy consumption and established safety protocols of bronze casting.
Choosing the Right Metal for Your Art
Bronze offers timeless appeal, excellent corrosion resistance, and a fine surface finish ideal for detailed art casting, while titanium provides superior strength, lightweight properties, and exceptional durability for modern sculptures. Artists should consider bronze for traditional aesthetics and warm patinas, whereas titanium suits contemporary designs requiring longevity and minimal maintenance. Evaluating factors like cost, weight, and environmental exposure ensures selecting the right metal aligns with artistic vision and functional needs.
Infographic: Bronze vs Titanium for Art Casting
 azmater.com
azmater.com