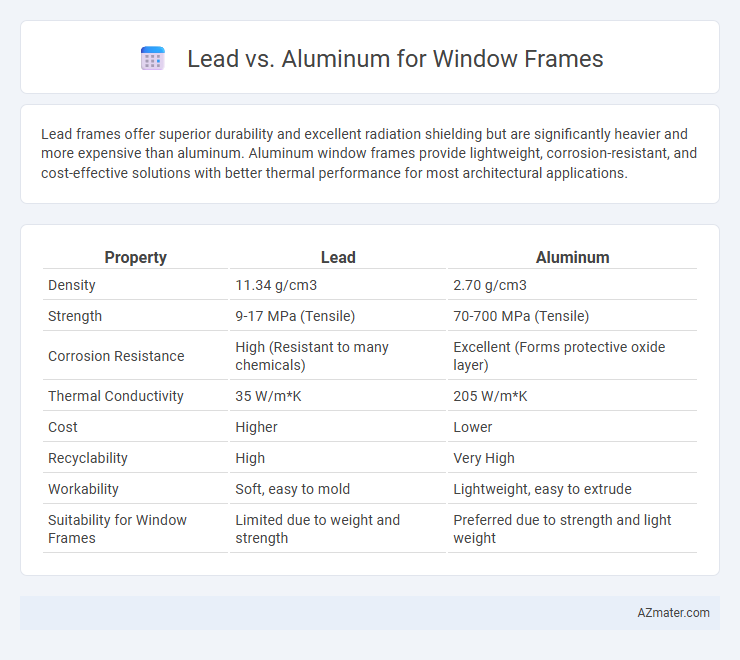
Lead frames offer superior durability and excellent radiation shielding but are significantly heavier and more expensive than aluminum. Aluminum window frames provide lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and cost-effective solutions with better thermal performance for most architectural applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Lead | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 11.34 g/cm3 | 2.70 g/cm3 |
| Strength | 9-17 MPa (Tensile) | 70-700 MPa (Tensile) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High (Resistant to many chemicals) | Excellent (Forms protective oxide layer) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 35 W/m*K | 205 W/m*K |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Recyclability | High | Very High |
| Workability | Soft, easy to mold | Lightweight, easy to extrude |
| Suitability for Window Frames | Limited due to weight and strength | Preferred due to strength and light weight |
Introduction to Window Frame Materials
Window frame materials like lead and aluminum offer distinct properties that impact durability and design. Lead is a heavy, malleable metal known for its excellent corrosion resistance and soundproofing qualities, but it is less common due to weight and health concerns. Aluminum frames provide lightweight strength, excellent weather resistance, and low maintenance, making them popular in modern window manufacturing.
Key Differences: Lead vs Aluminum
Lead window frames offer superior malleability and natural corrosion resistance compared to aluminum, making them ideal for historic restorations. Aluminum frames provide greater strength-to-weight ratio, enhanced durability, and require less maintenance due to anodized or powder-coated finishes. Thermal performance also differs, with aluminum typically needing thermal breaks to improve insulation, whereas lead provides moderate thermal mass but less energy efficiency overall.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Lead window frames offer exceptional corrosion resistance but lack the structural strength required for large or load-bearing applications. Aluminum frames provide superior strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for modern window designs that demand durability and longevity. Despite lead's durability in harsh environments, aluminum's resistance to warping, cracking, and weathering ensures longer-lasting performance with minimal maintenance.
Insulation Properties: Lead vs Aluminum
Lead window frames offer superior thermal insulation due to their higher density and lower thermal conductivity compared to aluminum, minimizing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. Aluminum frames, while lightweight and durable, conduct heat rapidly, often requiring thermal breaks or additional insulation to enhance performance in cold or hot climates. Choosing lead for window frames significantly reduces heat loss and gain, making it a preferred material in applications where insulation is critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Weathering
Aluminum window frames exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their natural oxide layer, which protects against weathering and prolongs durability in various climates. Lead frames, while historically common, are prone to oxidation and can develop surface deterioration when exposed to moisture and pollutants. Aluminum's lightweight nature combined with its resistance to rust and corrosion makes it a preferred choice for long-lasting window applications in harsh weather conditions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead window frames pose significant environmental risks due to their toxicity and challenges in recycling, contributing to soil and water contamination during disposal. Aluminum frames offer greater sustainability through high recyclability rates, reduced carbon footprint over their lifecycle, and resistance to corrosion, minimizing maintenance and replacement frequency. Choosing aluminum supports environmental goals by enabling energy-efficient manufacturing and promoting circular economy principles in building materials.
Safety and Health Considerations
Lead window frames pose significant health risks due to lead's toxicity, which can cause neurological damage and poisoning, especially in children. Aluminum frames are safer as they are non-toxic and resistant to corrosion, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into the environment. Choosing aluminum enhances indoor air quality and reduces exposure to hazardous materials, promoting a healthier living space.
Cost Analysis: Lead vs Aluminum
Aluminum window frames generally cost more upfront than lead due to higher raw material and manufacturing expenses but offer better long-term value through durability and lower maintenance costs. Lead frames have a lower initial price but tend to require more frequent repairs and may incur higher labor costs over time because of their susceptibility to corrosion and structural weakness. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses reveals aluminum as the more cost-effective option for window frames despite its higher initial investment.
Aesthetic Options and Design Flexibility
Lead window frames offer a classic, elegant aesthetic with a distinct patina that enhances traditional and historic architectural designs. Aluminum frames provide superior design flexibility due to their lightweight strength, allowing for sleek, slim profiles and expansive glass panels that suit modern, minimalist styles. Aluminum can be anodized or powder-coated in a wide range of colors, enabling more customized and contemporary visual options compared to the limited natural color variations of lead.
Making the Right Choice for Your Window Frames
Choosing between lead and aluminum for window frames involves weighing durability, maintenance, and aesthetic preferences. Aluminum frames offer lightweight strength, corrosion resistance, and low upkeep, ideal for modern designs and energy efficiency. Lead frames, though heavier and less common, provide superior malleability and a traditional look but require regular maintenance to prevent oxidation and structural wear.
Infographic: Lead vs Aluminum for Window Frame
 azmater.com
azmater.com