Bronze gears offer superior wear resistance and corrosion protection, ideal for heavy-load and low-speed applications. Nickel gears provide enhanced hardness and durability, making them suitable for high-speed, precision mechanisms.
Table of Comparison
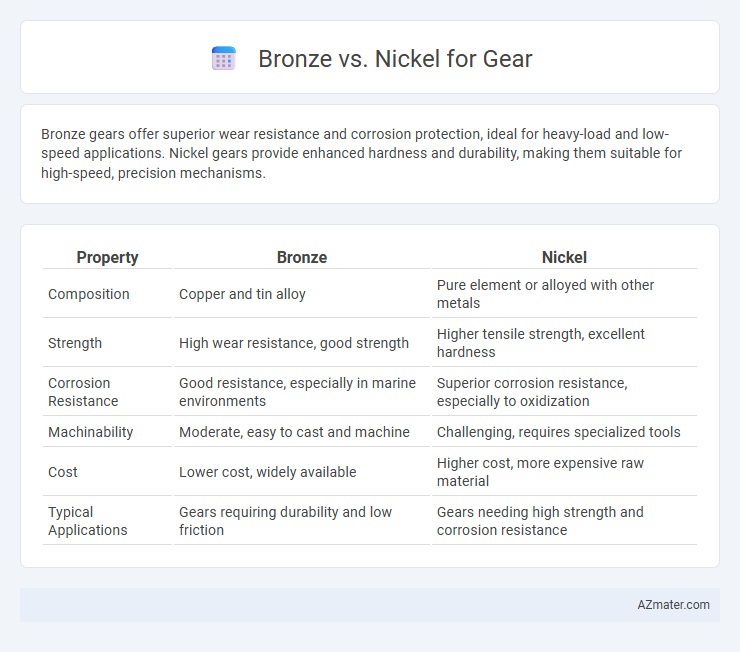
| Property | Bronze | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper and tin alloy | Pure element or alloyed with other metals |
| Strength | High wear resistance, good strength | Higher tensile strength, excellent hardness |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good resistance, especially in marine environments | Superior corrosion resistance, especially to oxidization |
| Machinability | Moderate, easy to cast and machine | Challenging, requires specialized tools |
| Cost | Lower cost, widely available | Higher cost, more expensive raw material |
| Typical Applications | Gears requiring durability and low friction | Gears needing high strength and corrosion resistance |
Introduction to Gear Materials: Bronze vs Nickel
Bronze gears offer superior wear resistance and excellent corrosion protection, making them ideal for heavy-duty and high-load applications. Nickel gears provide enhanced hardness and improved fatigue strength, supporting precision and durability in high-speed mechanisms. Choosing between bronze and nickel depends on operational conditions, load requirements, and environmental factors affecting gear performance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Bronze gears exhibit superior wear resistance and excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for low-speed, high-load applications where durability is critical. Nickel gears provide higher tensile strength and enhanced hardness, offering improved performance in high-speed, high-temperature environments. Both materials balance strength and durability, but bronze is preferred for quieter operation and better friction characteristics, while nickel excels in toughness and impact resistance.
Wear Resistance and Durability
Bronze gears exhibit superior wear resistance due to their self-lubricating properties and ability to conform under load, making them ideal for high-friction applications. Nickel gears offer enhanced durability with excellent corrosion resistance and strength, performing well in harsh environments but may wear faster under continuous abrasion. Selecting between bronze and nickel gears depends on balancing the need for wear resistance in sliding contacts against the demand for long-term structural integrity and environmental resilience.
Corrosion Resistance in Varied Environments
Bronze offers superior corrosion resistance in marine and industrial environments due to its natural resistance to saltwater and oxidizing agents, making it ideal for gears exposed to harsh conditions. Nickel-plated gears provide good corrosion protection by forming a dense, protective oxide layer, but may degrade faster in highly acidic or chloride-rich settings. Selecting bronze or nickel gears depends on the specific environmental challenges, with bronze preferred for long-term durability in corrosive atmospheres.
Lubrication Requirements and Performance
Bronze gears exhibit superior self-lubricating properties due to embedded oil reservoirs within their porous structure, significantly reducing the need for external lubrication and enhancing wear resistance. Nickel-plated gears require consistent lubrication to prevent surface corrosion and minimize friction, as their hard, smooth coating alone does not provide inherent lubrication. In high-load or high-speed applications, bronze gears maintain performance with less maintenance, while nickel-coated gears depend on lubricant quality and application frequency to sustain optimal functionality.
Cost Analysis: Bronze vs Nickel Gears
Bronze gears typically offer a lower initial cost compared to nickel-coated gears due to less expensive raw materials and simpler manufacturing processes. Nickel plating on gears increases durability and corrosion resistance but adds a significant premium, often 20-30% higher in production costs. When evaluating long-term expenses, bronze gears may incur higher maintenance costs, whereas nickel-coated gears provide better cost-efficiency through extended lifespan and reduced wear.
Applications in Industrial Machinery
Bronze gears offer superior wear resistance and excellent load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for heavy-duty industrial machinery such as conveyors and pumps where durability is critical. Nickel gears excel in corrosion resistance and maintain strength under high temperatures, suiting applications in chemical processing equipment and precision instruments exposed to harsh environments. Choosing between bronze and nickel gears depends on specific industrial conditions like mechanical stress, temperature, and exposure to corrosive substances.
Maintenance and Longevity Considerations
Bronze gears exhibit superior corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties, reducing maintenance frequency and extending operational life compared to nickel-plated gears, which require regular lubrication to prevent wear and corrosion. The inherent durability of bronze minimizes the risk of pitting and galling, enhancing longevity in harsh environments. Nickel coatings provide a hard surface layer, improving wear resistance but may degrade over time, necessitating more frequent inspections and maintenance interventions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bronze gears, made primarily from copper and tin, offer better corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, reducing waste and resource consumption compared to nickel gears. Nickel plating involves energy-intensive mining and refining processes, leading to higher carbon emissions and potential soil and water contamination. Choosing bronze gears supports sustainable manufacturing by minimizing environmental pollutants and enhancing recyclability due to its simpler metal composition.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Gear
Bronze offers excellent wear resistance and corrosion protection, making it ideal for gears in harsh environments or where lubrication is limited. Nickel gears provide superior strength and hardness, suitable for high-load applications requiring durability and precision. Selecting between bronze and nickel depends on specific operational demands such as load capacity, environmental conditions, and maintenance requirements.
Infographic: Bronze vs Nickel for Gear
 azmater.com
azmater.com