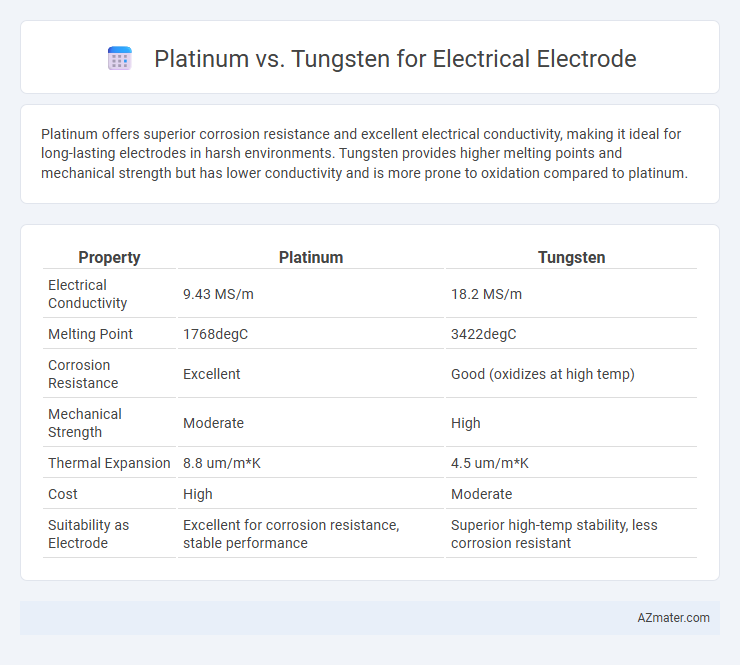
Platinum offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for long-lasting electrodes in harsh environments. Tungsten provides higher melting points and mechanical strength but has lower conductivity and is more prone to oxidation compared to platinum.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Platinum | Tungsten |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 9.43 MS/m | 18.2 MS/m |
| Melting Point | 1768degC | 3422degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good (oxidizes at high temp) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Thermal Expansion | 8.8 um/m*K | 4.5 um/m*K |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Suitability as Electrode | Excellent for corrosion resistance, stable performance | Superior high-temp stability, less corrosion resistant |
Introduction to Platinum and Tungsten Electrodes
Platinum electrodes offer exceptional corrosion resistance and high conductivity, making them ideal for precise electrochemical applications such as sensors and analytical instruments. Tungsten electrodes provide superior hardness and durability at high temperatures, commonly used in welding and electrical discharge machining due to their excellent thermal stability. Both materials serve critical roles in electrical electrodes but are selected based on specific performance requirements like corrosion resistance for platinum and wear resistance for tungsten.
Key Material Properties: Platinum vs Tungsten
Platinum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and high electrical conductivity, making it ideal for stable and long-lasting electrical electrodes. Tungsten features a very high melting point and excellent mechanical strength, which is beneficial for electrodes exposed to extreme heat and wear. While platinum excels in chemical inertness, tungsten provides superior thermal stability and cost-effectiveness for high-temperature electrical applications.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Platinum offers excellent electrical conductivity with a resistivity of approximately 10.6 uO*cm, making it highly efficient for electrical electrodes, especially in high-corrosion environments. Tungsten, while having a higher resistivity around 5.6 uO*cm, provides superior thermal and mechanical stability, which can be advantageous under extreme conditions. When comparing electrical conductivity alone, tungsten generally outperforms platinum, but the choice depends on balancing conductivity with durability and environmental resistance.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Platinum offers superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to tungsten, making it ideal for use in harsh electrical electrode environments. Tungsten, while highly conductive and heat-resistant, tends to oxidize at high temperatures, which can degrade electrode performance over time. The exceptional chemical stability of platinum ensures longer electrode lifespan and reliable conductivity in corrosive or high-temperature applications.
Thermal Stability and Temperature Performance
Platinum electrodes exhibit superior thermal stability and can withstand continuous high-temperature exposure up to approximately 1700degC without significant degradation, making them ideal for precision electrical applications. Tungsten, although possessing a higher melting point around 3422degC, suffers from oxidation and brittleness at elevated temperatures in atmospheric conditions, limiting its effective operating range to below 900degC in open air. Therefore, platinum electrodes outperform tungsten in temperature performance due to their resistance to thermal cycling and oxidation, ensuring longer service life and consistent electrical conductivity in high-temperature environments.
Electrode Durability and Lifespan
Platinum electrodes exhibit superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to tungsten due to their exceptional resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and high-temperature stability in electrical applications. Tungsten, while cost-effective and possessing a high melting point, tends to degrade faster under continuous electrical stress, leading to reduced electrode lifespan and more frequent replacements. Choosing platinum electrodes ensures sustained reliable performance and minimizes maintenance costs in demanding electrical environments.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Platinum electrodes have a significantly higher cost compared to tungsten due to platinum's rarity and superior corrosion resistance, making them ideal for high-precision and long-lifespan applications despite the expense. Tungsten electrodes, widely available and more affordable, offer excellent conductivity and high melting points, making them the primary choice for most industrial electrical applications where cost-efficiency is critical. Market availability favors tungsten, as it is abundantly produced and globally distributed, whereas platinum electrodes face supply constraints tied to mining and market demand fluctuations.
Applications in Electrical and Electronic Devices
Platinum electrodes excel in high-corrosion and high-temperature environments, making them ideal for sensors, fuel cells, and electrochemical analyzers due to their excellent conductivity and chemical inertness. Tungsten electrodes offer superior durability and high melting points, which suit their use in lighting elements, electron emitters, and high-power electrical switches where mechanical strength and thermal stability are critical. Both materials serve distinct roles in electrical and electronic devices, with platinum favored for precision and chemical resistance, while tungsten is preferred for robustness and high-temperature performance.
Environmental and Safety Aspects
Platinum electrodes offer superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, reducing environmental contamination and ensuring safer handling in sensitive applications. Tungsten electrodes, while cost-effective and highly durable under high temperatures, pose environmental concerns due to potential tungsten dust exposure, which can cause respiratory issues if not properly managed. Implementing stringent safety protocols and appropriate disposal methods is crucial for minimizing health risks and environmental impact for both electrode materials.
Choosing the Right Electrode: Platinum or Tungsten
Platinum offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term stability and biocompatibility in electrical electrodes. Tungsten provides higher melting points and mechanical strength, suitable for high-temperature environments where durability and wear resistance are critical. Choosing between platinum and tungsten electrodes depends on the specific application demands, balancing electrical performance with environmental resistance and operational longevity.
Infographic: Platinum vs Tungsten for Electrical Electrode
 azmater.com
azmater.com